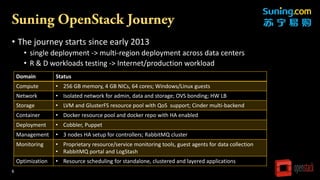
The document outlines Suning's evolution as a leading commercial enterprise in China, highlighting its diverse business operations, including retail and cloud services. It details Suning's cloud journey, challenges faced in deployment and orchestration, and the technical infrastructure supporting its cloud services. The document emphasizes the need for integrated tools for runtime orchestration and management while addressing complexity in resource allocation and application scalability.