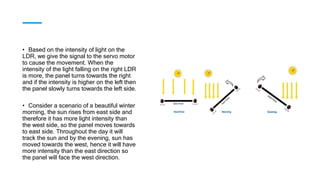
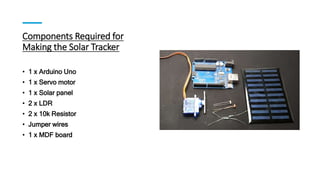
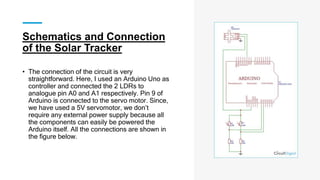
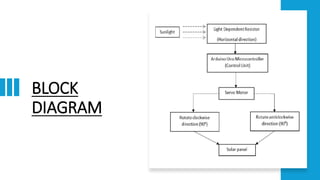
The document discusses the importance of renewable energy, particularly solar energy, in combating climate change. It details a microcontroller-based solar panel tracking system that maximizes energy capture by adjusting the panel's orientation to follow the sun's movement. The paper describes the system's components, assembly instructions, and a sample code for operation.
![LITERATURE SURVEY
• This paper [1] describes the complete design and
construction of a microcontroller based automatic
solar panel tracking system. The solar panel is fixed
and no automatic tracking of sun light based on its
intensity.
• This paper [2] explain about the effects of global
warming and how can we take advantage from this
effect like how the Solar energy is used for electrical
energy generation. Solar tracking System is based on
AVR microcontroller, which is a 68 brain of a
complete system
• This paper [3] includes a solar array, solar frame and
two actuators, and also it is a dual-axis solar tracker
capable in extreme weather conditions.it has
mechanically linked solar trackers in a large
configuration of solar array, so that they can operate
in unison way
• This paper [4] describe that the targets to reduce
carbon emission and to secure energy supply. It
measures a change in the energy supply system
leading to smart grids for the required innovation. the
key feature in the smart grid application is the
demand side service offered to designated parties by
smart-automation system](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation612-240714151518-cedd2060/85/Sun-detecting-solar-panel-using-arduino-uno-2-320.jpg)