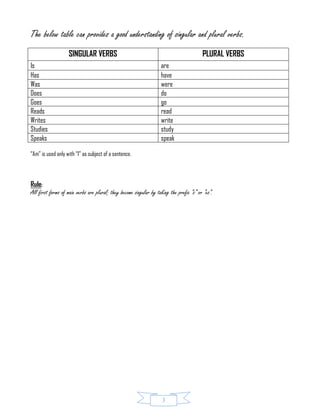
The document serves as a comprehensive guide on subject-verb agreement in English, detailing the rules for matching subjects and verbs in number and form. It covers various scenarios, including singular and plural subjects, collective nouns, and specific constructions that dictate verb forms. Specific examples and rules are provided to aid understanding and correct usage in sentence construction.