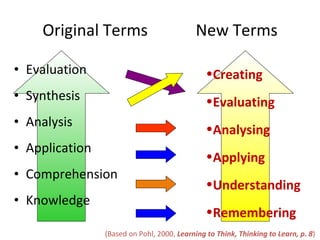
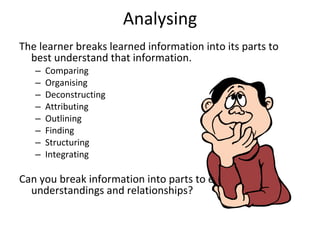
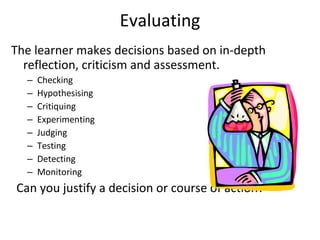
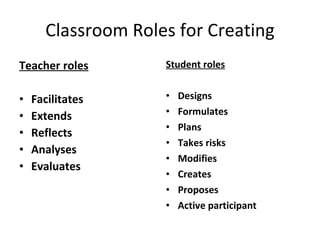
The document discusses student-made video resumes as a creative project for students. Video resumes allow students to combine essay writing skills with visual elements to showcase their skills and experience. Creating a video resume challenges students to think creatively and gives them experience with real-world job skills. Applying Bloom's taxonomy of cognitive objectives, developing a video resume requires students to remember, understand, apply, analyze, evaluate, and create - moving through higher-order thinking skills. Overall, creating a video resume is a pedagogically valuable project that develops students' presentation skills and helps them practice skills needed for future employment.






















![Daniela Munca [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/studentvideoresumes-100313044240-phpapp02/85/Student-Video-Resume-APLE-27-320.jpg)