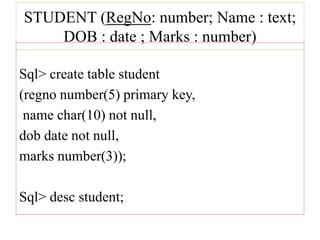
1) The document discusses database management systems and describes a student details database with attributes like registration number, name, date of birth, and phone number.
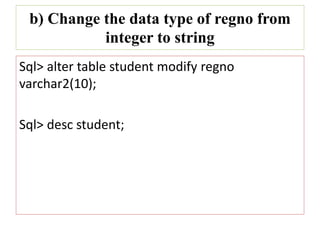
2) It provides SQL commands to perform various operations on the student details table like removing an attribute, changing a data type, adding a new attribute, inserting tuples, and selecting rows based on conditions.
3) The key SQL commands covered are CREATE TABLE, ALTER TABLE, INSERT, and SELECT. Operations like modifying table structure, entering data, and retrieving data based on conditions are demonstrated.


![CREATE TABLE
• This command is used to create a relation by
giving its attributes and initial constraints.
• The relations declared through CREATE TABLE
are called base tables. Syntax: CREATE
TABLE(,……,TABCONSTRAINT
1,…….TABCONSTRAINT N); The syntax for
column definition is [default ][]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/studentdetailsdatabase-221202104923-a3b1f346/85/STUDENT-DETAILS-DATABASE-pptx-4-320.jpg)
![• The syntax for the table constraint is, [constraint ]
[not]NULL|check() Unique|primary
key|references[][on delete cascade] The five
possible column constraints are, not null: used if
null values are not permitted. Check constraint:
used to impose restrictions on column values.
Unique and primary key: to specify if a column is
the primary key. Reference clause: used when the
column is a foreign key and it refers to a unique
or primary key. delete cascade: used to delete all
dependent rows when a referenced row
containing a unique or primary key is deleted.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/studentdetailsdatabase-221202104923-a3b1f346/85/STUDENT-DETAILS-DATABASE-pptx-5-320.jpg)
![Table constraints:
• These constraints apply to the whole table.
The three table constraints are, Primary key,
foreign key, candidate key. Syntax for table
constraints, [constraint] Unique({,}) Primary
key({,}) Foreign key ({,}) References({,}) [on
delete cascade]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/studentdetailsdatabase-221202104923-a3b1f346/85/STUDENT-DETAILS-DATABASE-pptx-6-320.jpg)



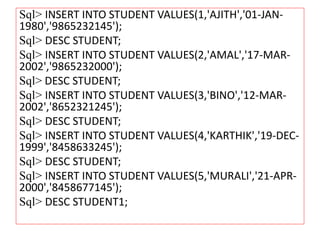
![INSERTING ROWS:
To insert tuple values insert command is used.
Syntax: INSERT INTO [,…..]values(expr
1,expr2……);
Example:
insert into student values(‘s01’’raju’,’2000-feb-
23’);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/studentdetailsdatabase-221202104923-a3b1f346/85/STUDENT-DETAILS-DATABASE-pptx-12-320.jpg)