This document discusses different ways to define constants and functions for unformatted input/output in C programming language. It describes:
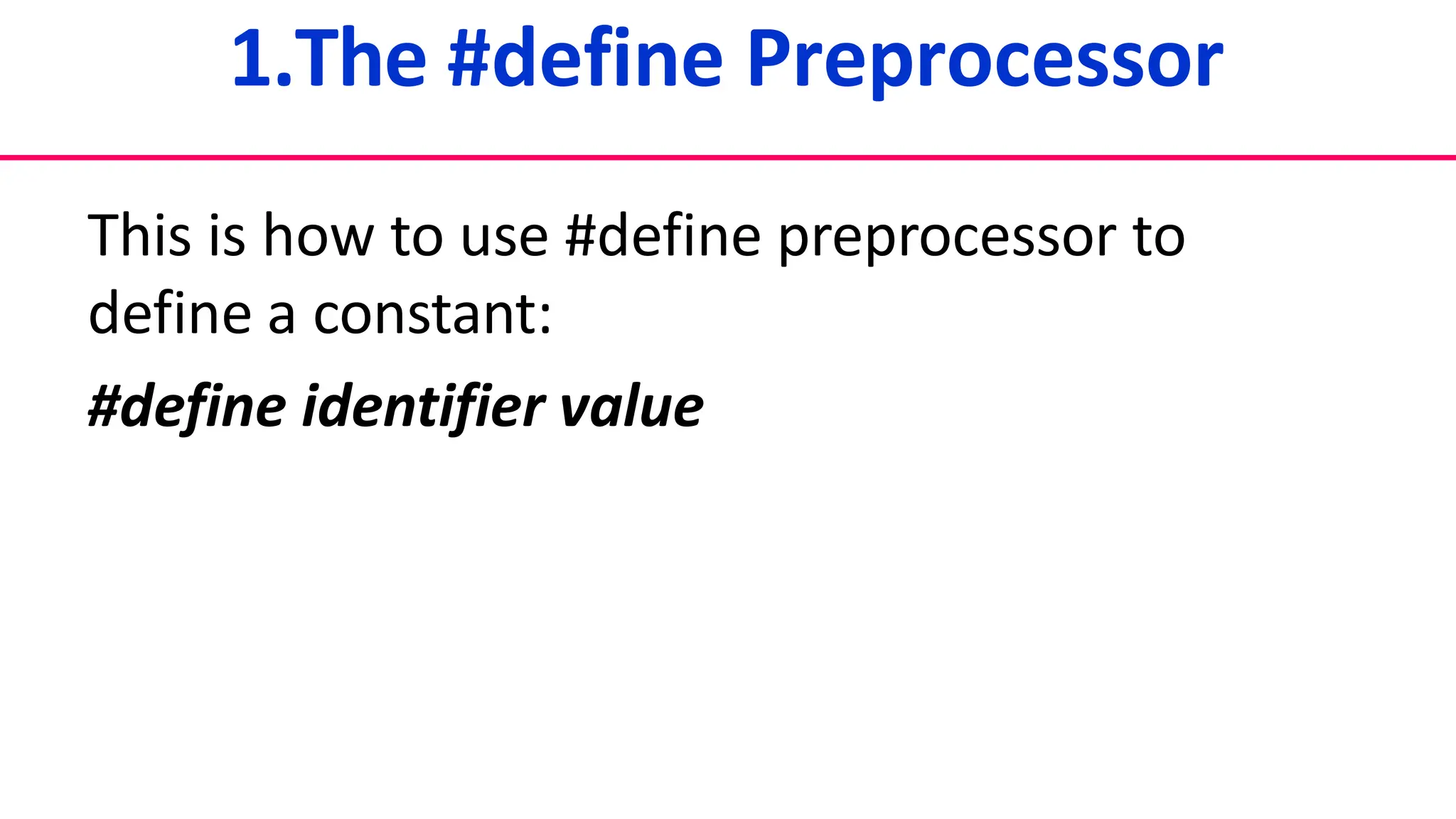
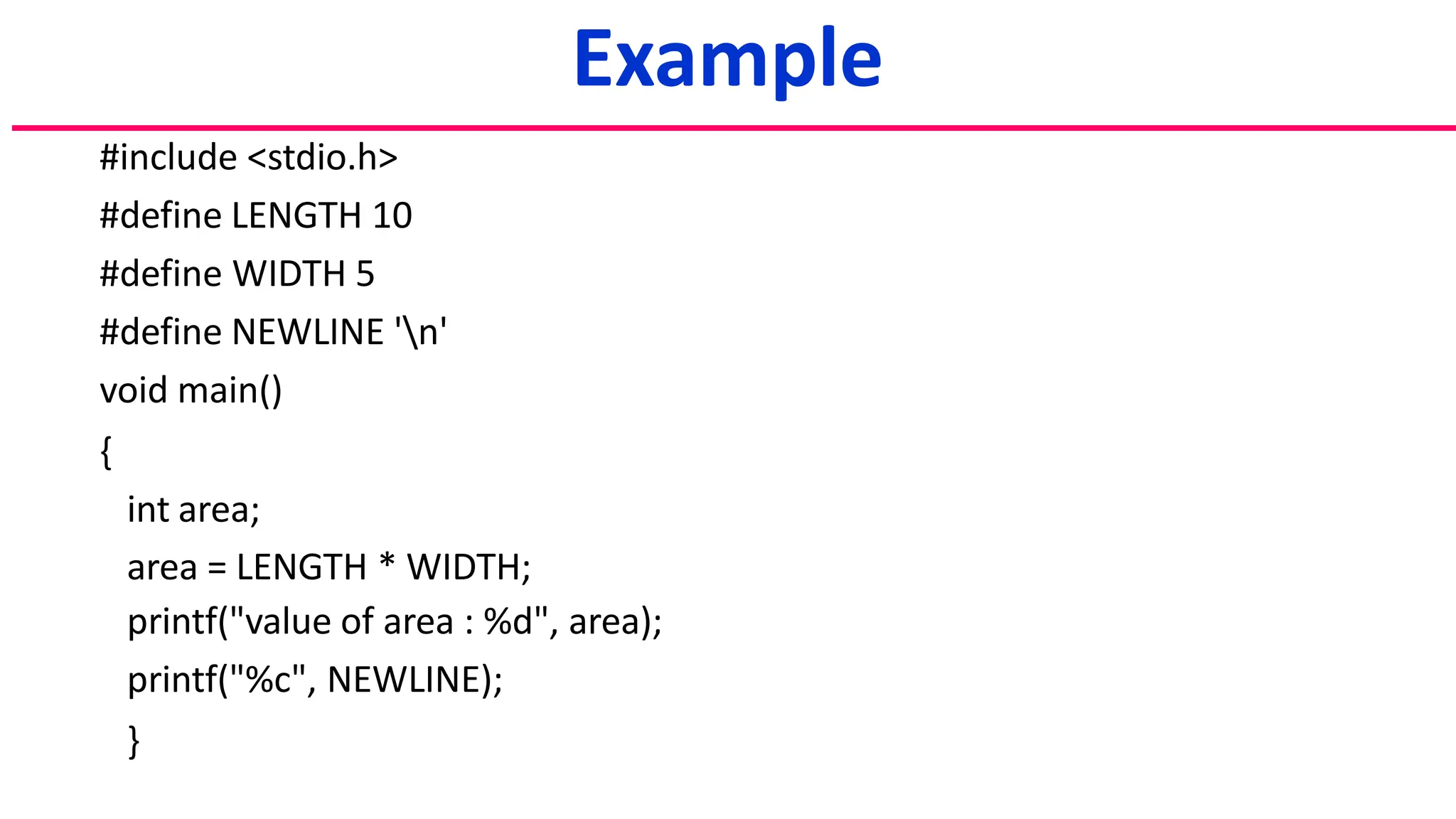
1. Two ways to define constants using #define preprocessor and const keyword.
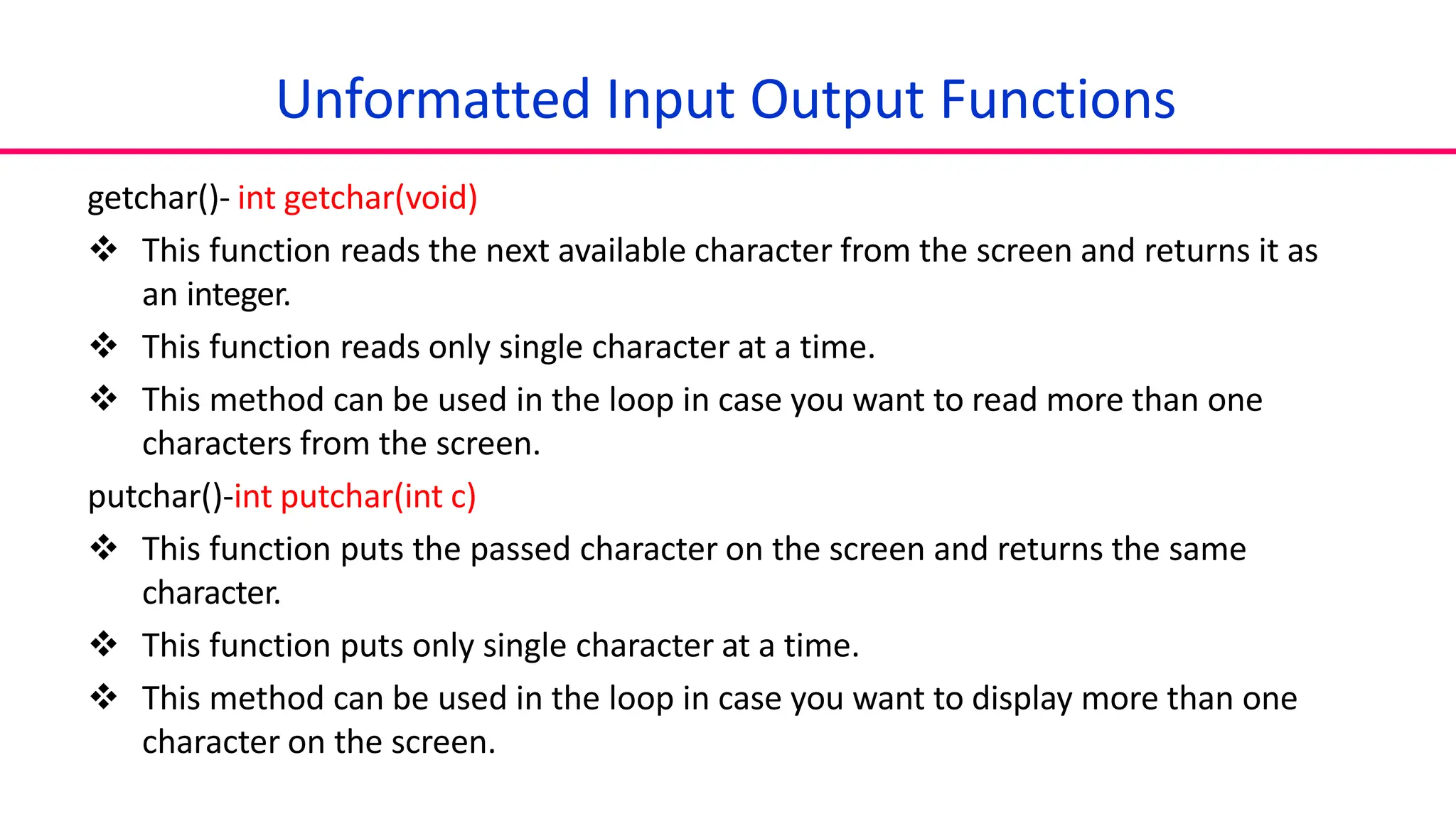
2. Functions like getchar(), putchar(), gets(), puts() to get single character and string input from user and display output.
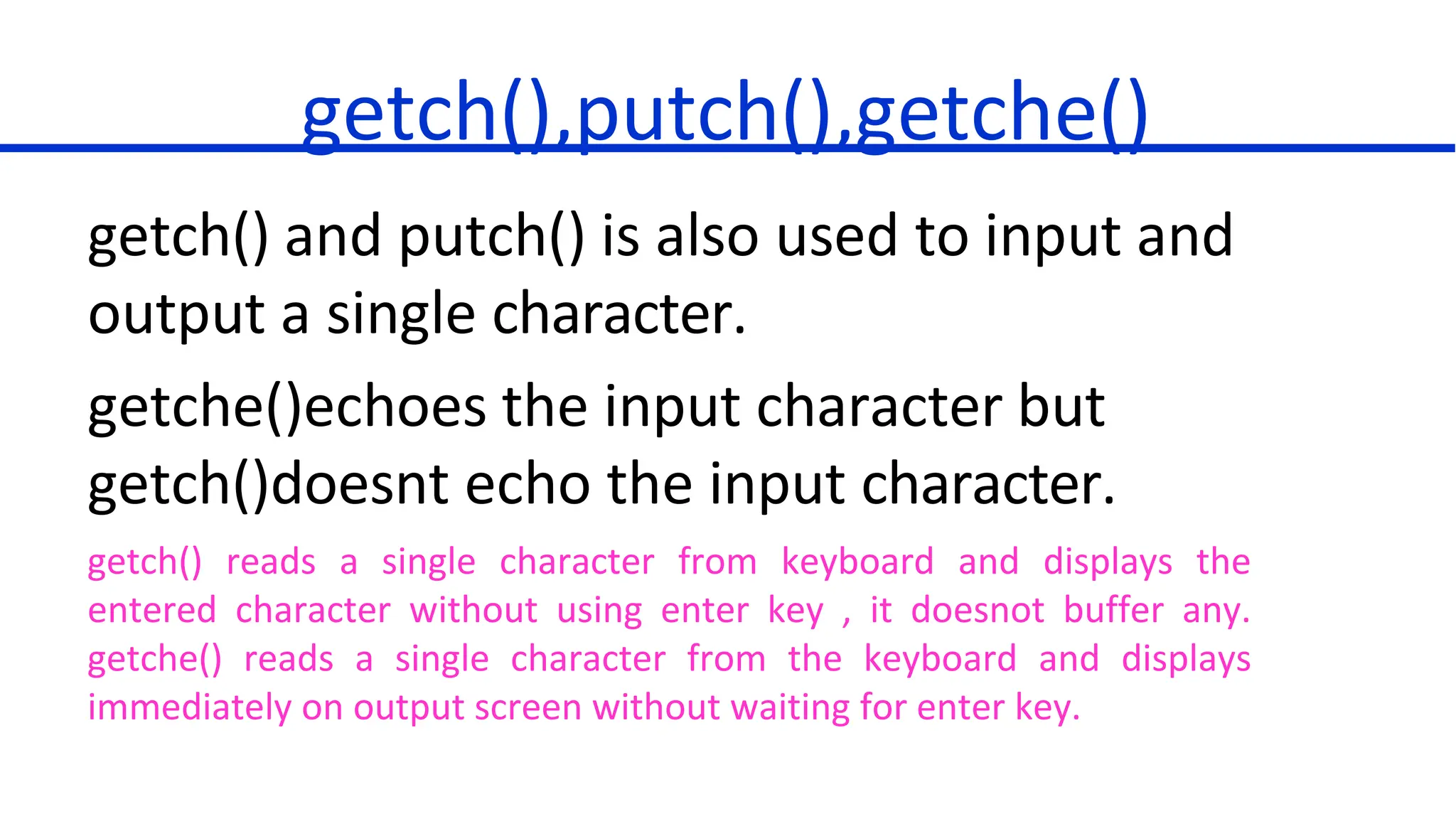
3. Differences between getch(), getche() functions for character input without buffering or echoing.








![#include <stdio.h>
void main( )
{
char str[100];
printf( "Enter a value :");
gets( str );
printf( "nYou entered: ");
puts( str );
}
gets(), puts() -Example](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/constantsandunformattedinputoutputfunctions-231128081802-c95722a3/75/Constants-and-Unformatted-Input-Output-Functions-pptx-13-2048.jpg)