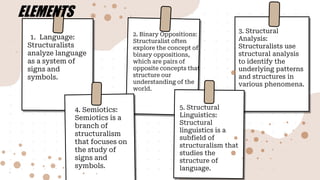
Structuralist theory originated in anthropology and later expanded to other fields like linguistics and psychology. It focuses on analyzing phenomena by examining the underlying structures and systems that organize them. The founders of structuralist theory were Wilhelm Wundt, who established structuralism as the first school of thought in psychology, and Edward B. Titchener, who was mainly associated with it. Structuralism analyzes language as a system of signs and symbols, explores concepts like binary oppositions, uses structural analysis to identify patterns, and studies signs and symbols through semiotics and the structure of language through structural linguistics. The perspective of structuralism is that underlying structures and systems shape individual and societal perceptions of the world.