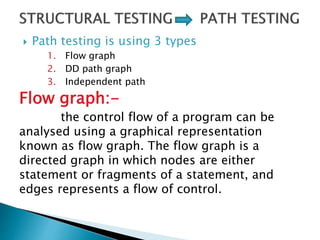
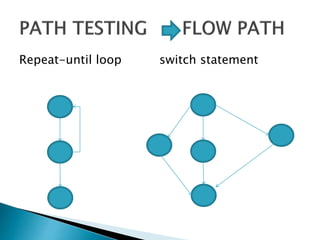
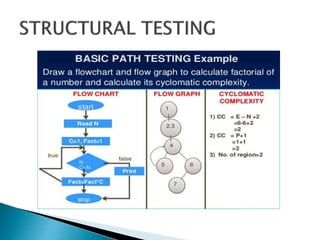
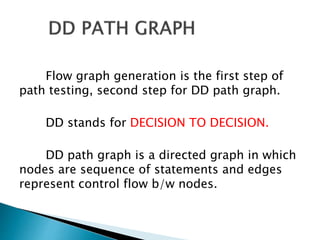
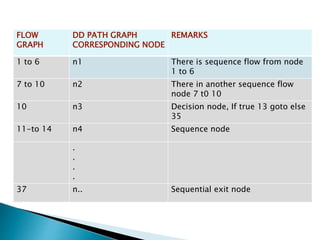
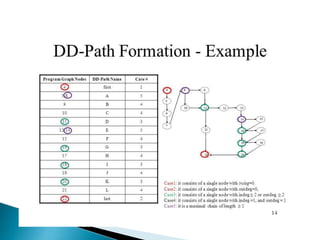
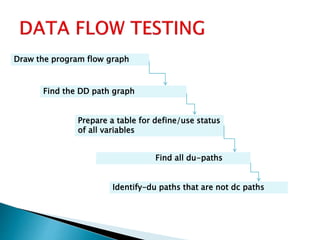
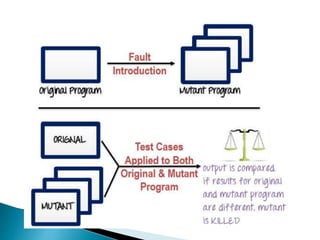
Structural testing examines a program's internal structure like code, design, and implementation. It uses white box testing to analyze program flow and ensure all statements, branches, and paths are executed. Various structural testing techniques exist like path coverage testing, cyclomatic complexity, data flow testing, and mutational testing. Path coverage testing aims to execute every path in a program at least once by generating test cases for all branches and sequences. Cyclomatic complexity measures a program's structural complexity based on control flow. Data flow testing checks for definition-use and clear relationships between variables. Mutational testing systematically alters programs to create mutants, then tests are developed to kill as many mutants as possible.