1. Plants have various structural defence mechanisms to prevent pathogen infection, including waxes, cuticles, thickened cell walls, and natural openings that limit pathogen entry.
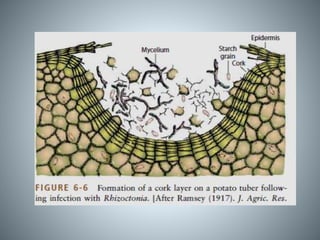
2. After infection occurs, plants form additional defensive structures like cork layers, tyloses, gum deposits, and abscission layers that isolate the pathogen from healthy tissue.
3. Structures like tyloses and sheath formations around hyphae can physically block pathogen spread within the plant. Together, pre-existing and infection-induced structures help plants resist pathogens.