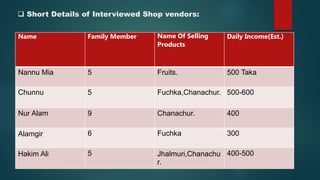
This document summarizes a presentation about street food vendors in Dhaka, Bangladesh. It lists popular street foods sold, such as chicken fry, beef kebab, fuchka, and fruits. It discusses the benefits of street food including employment, low costs, and nutrition. However, it also notes problems like contamination, poor hygiene, and lack of licensing. Interviews with five vendors find they support families of 5-10 and earn $3-6 daily. Issues faced include illegality, capital access, and risks from weather and limited sales. Overall, street vending provides important livelihoods despite challenges.