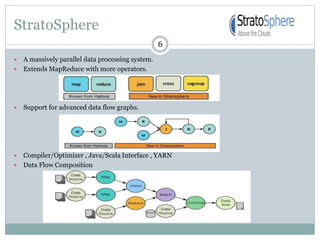
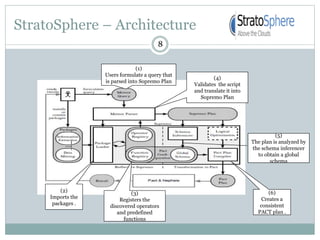
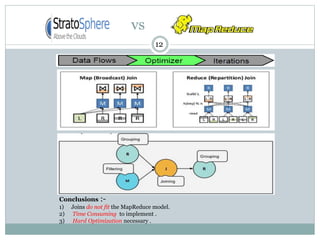
1) Stratosphere is a distributed data processing system that extends the MapReduce model by supporting more operators and advanced data flow graphs composed of operators.
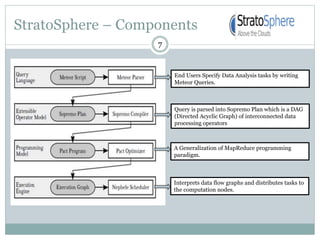
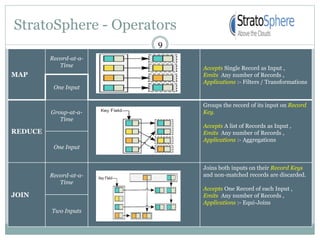
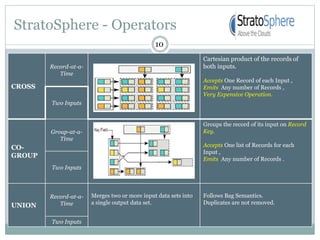
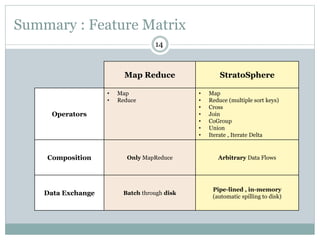
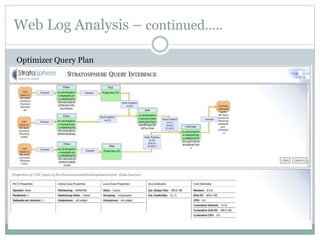
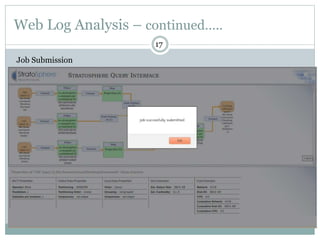
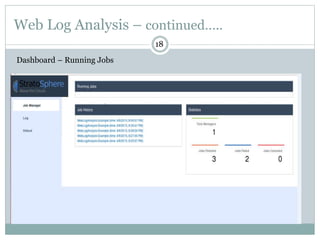
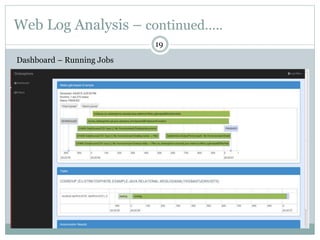
2) It has components like a query parser, compiler, and optimizer that translate queries into execution plans composed of operators like Map, Reduce, Join, Cross, CoGroup, and Union.
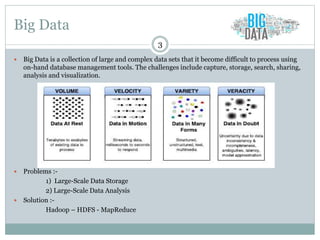
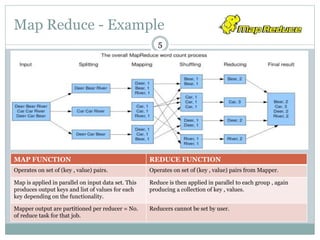
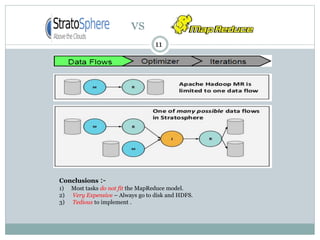
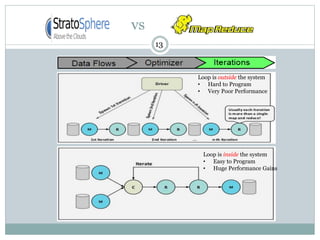
3) Stratosphere supports arbitrary data flows while MapReduce only supports MapReduce, and Stratosphere has better performance through in-memory processing and pipelining compared to MapReduce which always writes to disk.