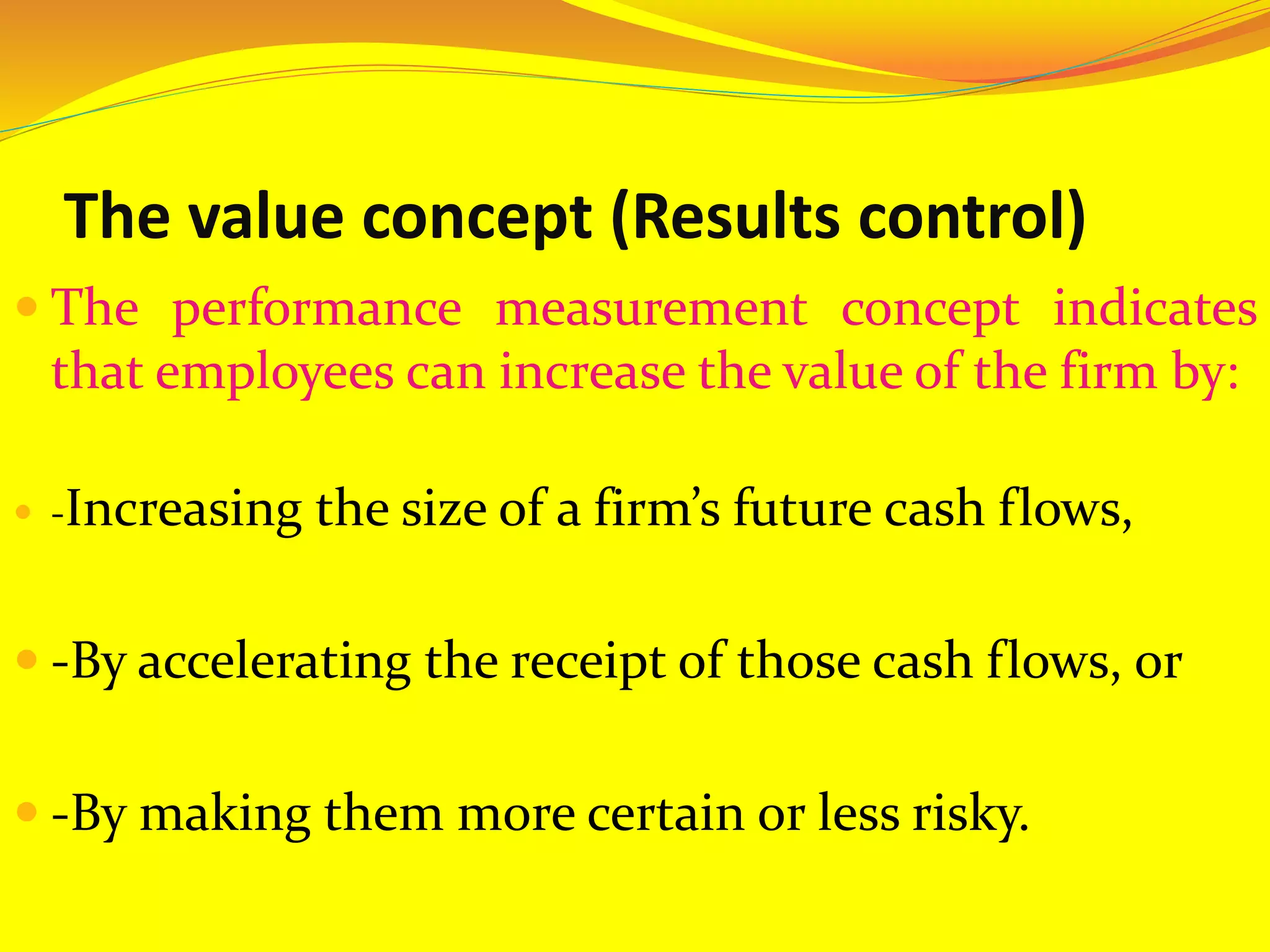
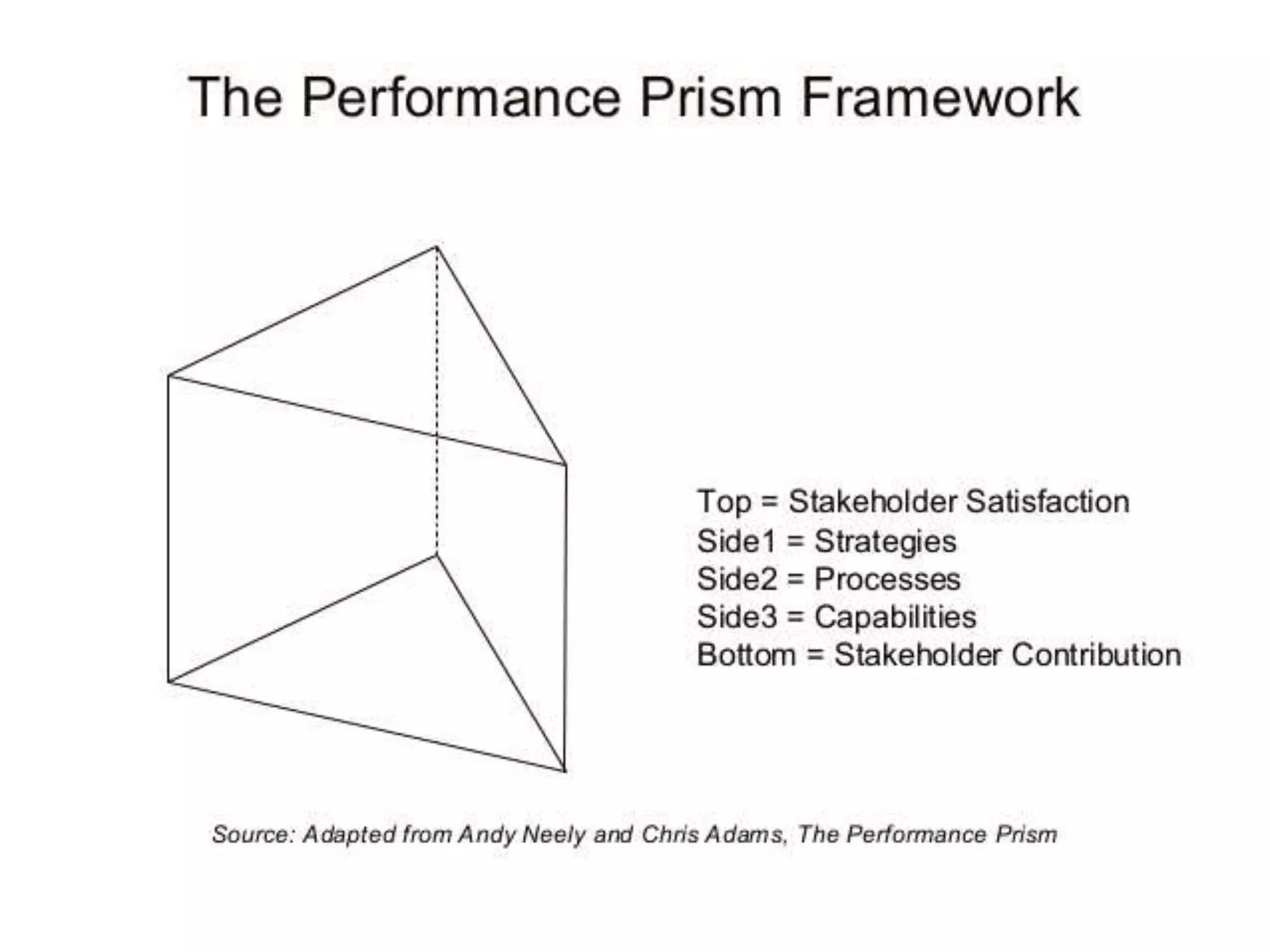
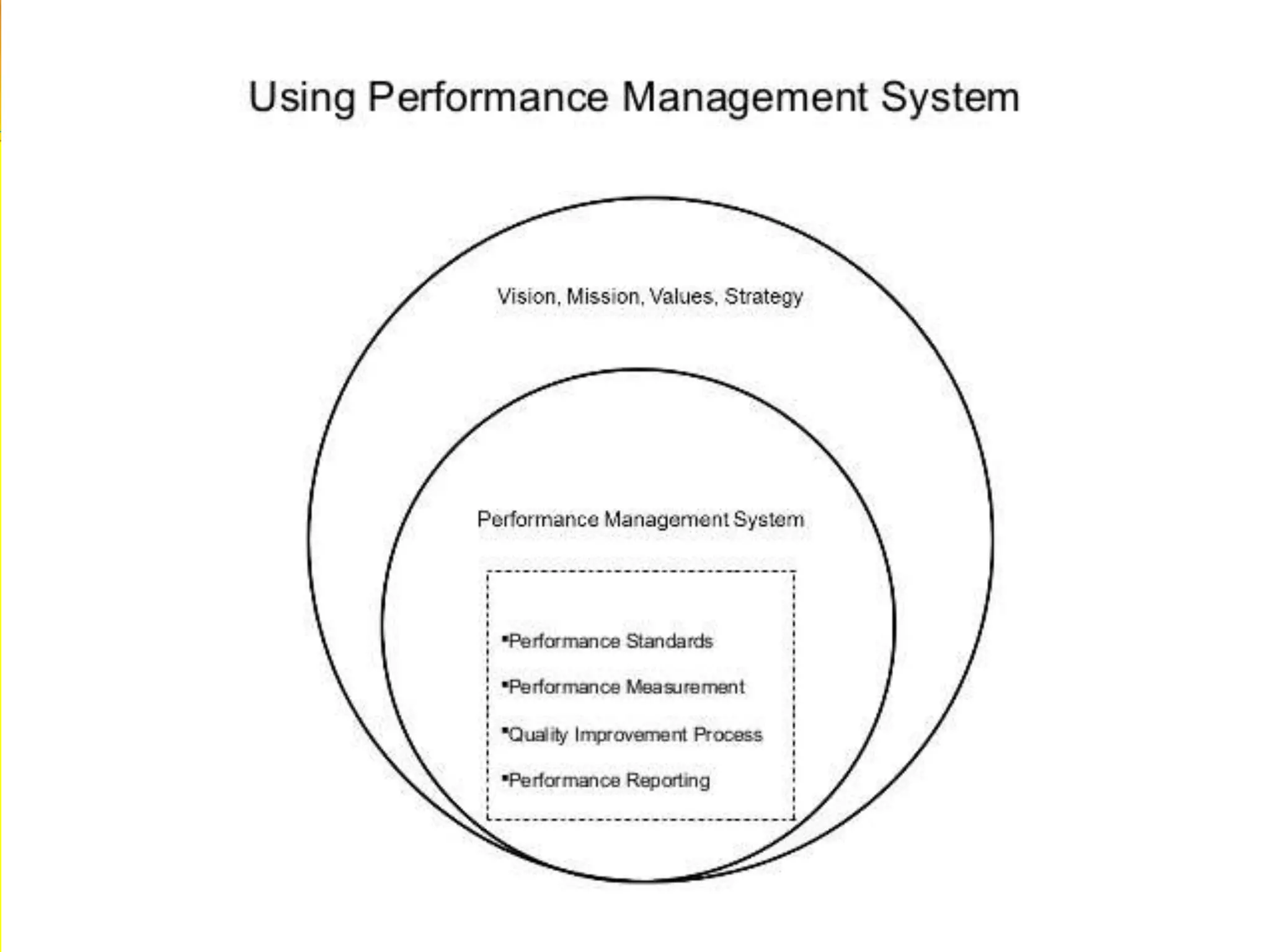
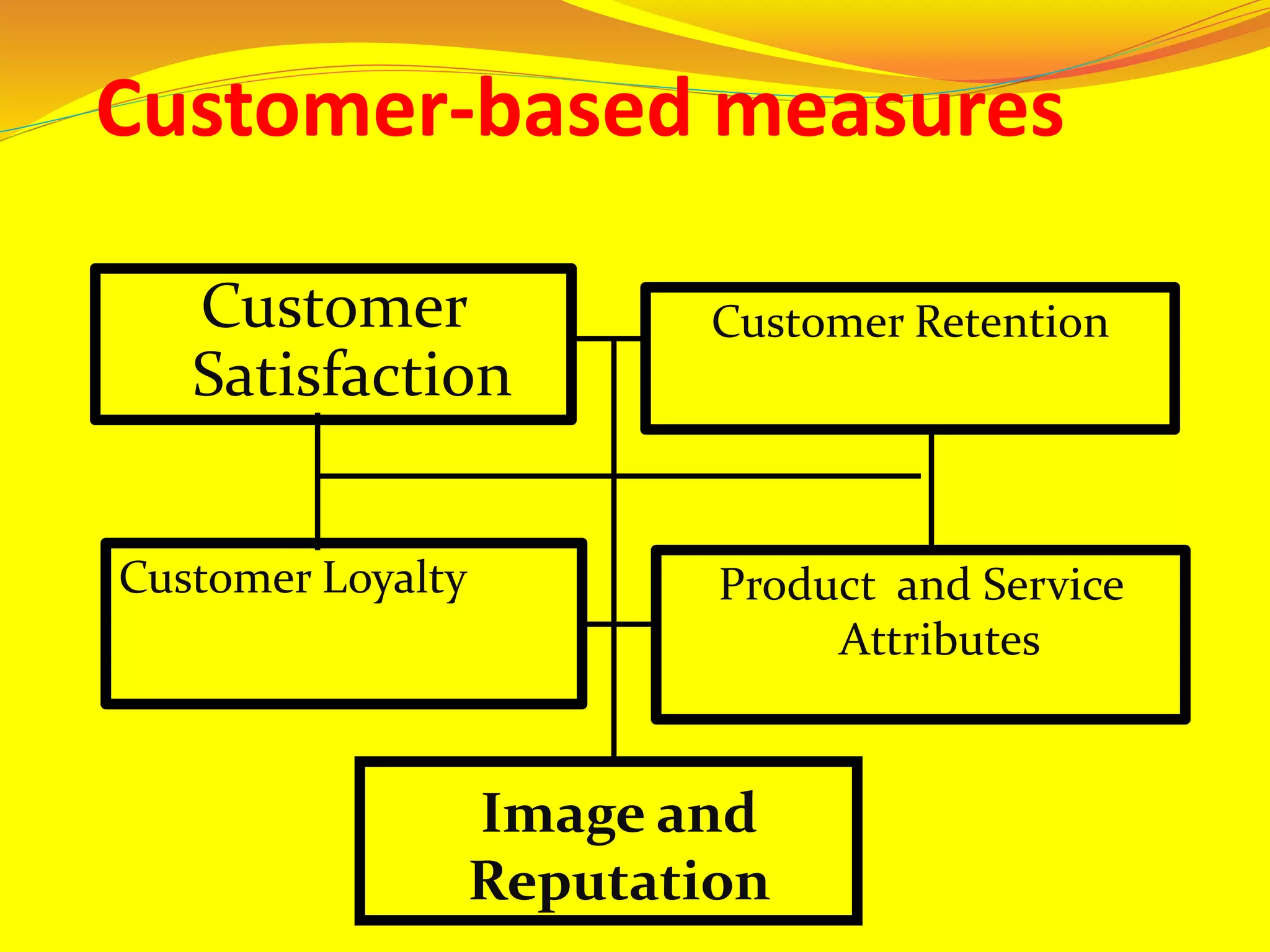
The document discusses performance evaluation and control. It outlines the basic performance pyramid with mission, vision, goals/objectives, strategies, and success drivers at the top feeding into performance measures at the bottom. It emphasizes that performance measures should aim for the long-term and be forward-thinking. Both financial and non-financial measures are needed, with an emphasis on lead indicators over lag indicators. A comprehensive performance measurement system addresses financial performance, customer satisfaction, internal business processes, and organizational learning and growth.