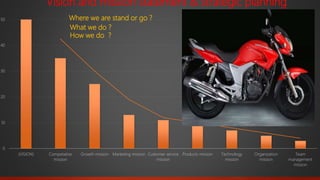
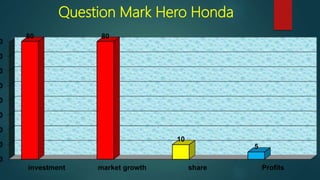
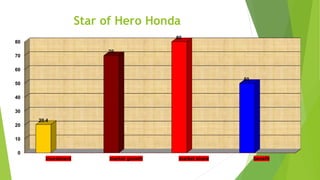
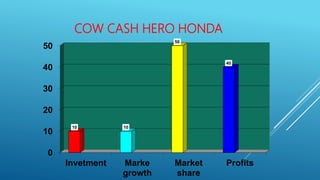
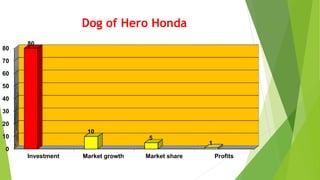
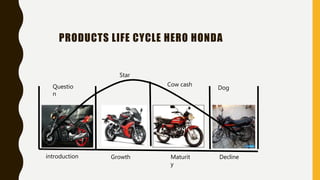
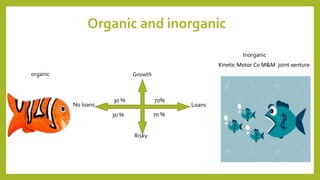
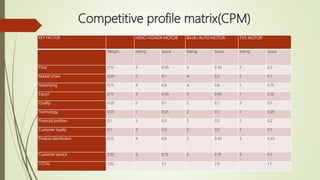
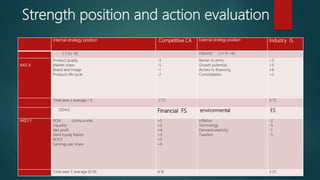
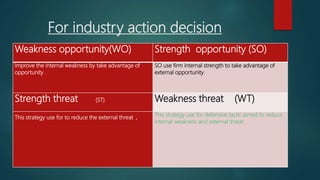
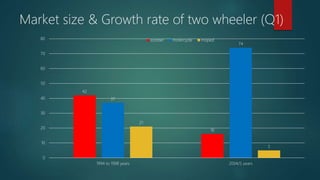
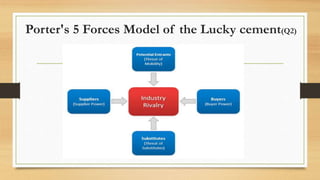
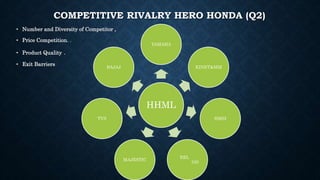
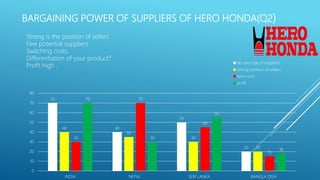
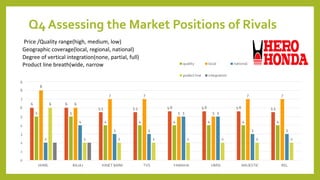
This document provides information about a student named Rehman Khan who is enrolled in the 2nd semester of the MBA program at Benazir Bhutto Shaheed University. Khan is working on a project about the strategic management of Hero Honda for his class instructed by Mr. Khuram Shakir. The document includes details about Hero Honda's vision, mission, products, growth strategy, competitors, and external environment. It analyzes Hero Honda using various frameworks including Porter's five forces, SWOT analysis, strategic group mapping, and more. Key rivals identified include Bajaj, TVS Motors, and a joint venture between Kinetic Motor Co. and Mahindra & Mahindra. The document