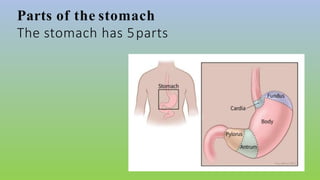
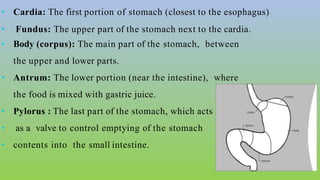
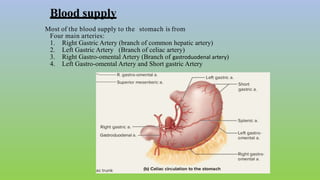
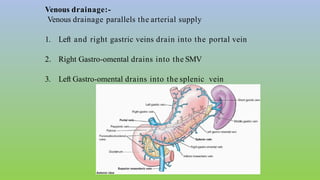
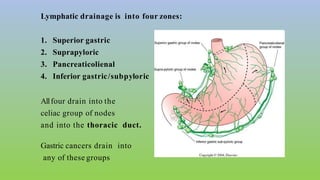
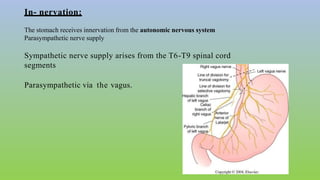
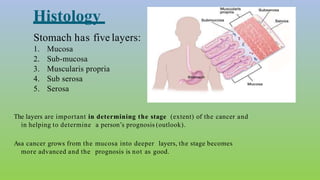
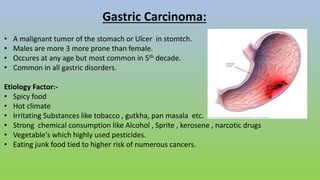
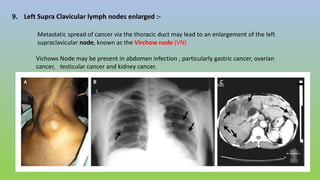
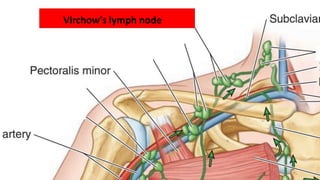
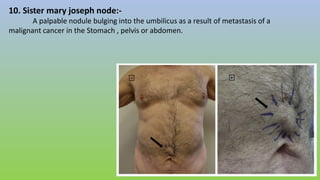
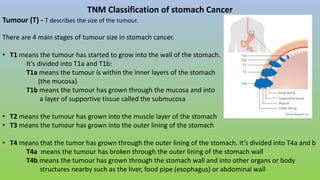
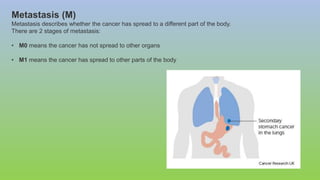
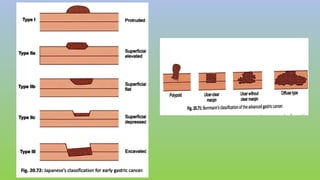
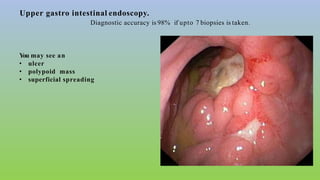
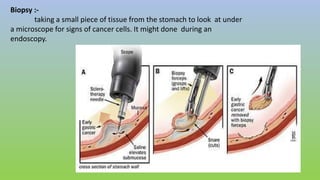
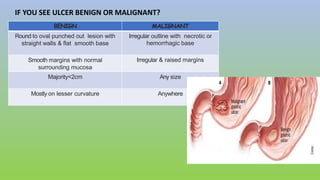
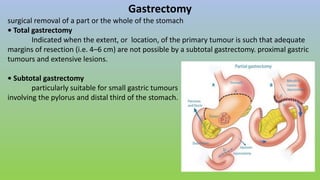
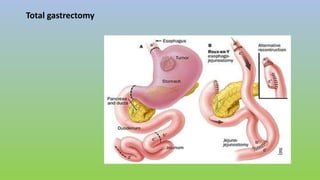
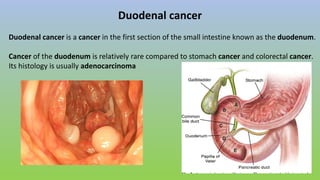
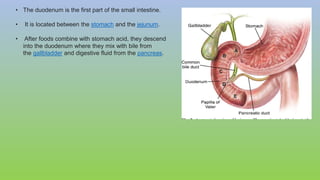
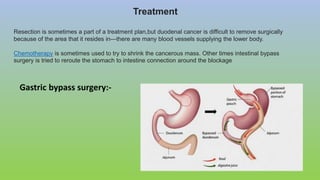
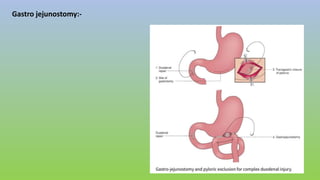
This document provides information on carcinoma of the stomach. It discusses the anatomy of the stomach, including its five parts. It outlines the etiology, risk factors, clinical features, investigations, staging, and management of gastric carcinoma. Key points include that gastric carcinoma commonly presents with nonspecific symptoms in advanced stages. Diagnosis involves endoscopy with biopsy. Treatment options include surgery such as total or subtotal gastrectomy, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy. Post-operative complications can include leakage or hemorrhage. Long-term nutritional deficiencies are also a risk.