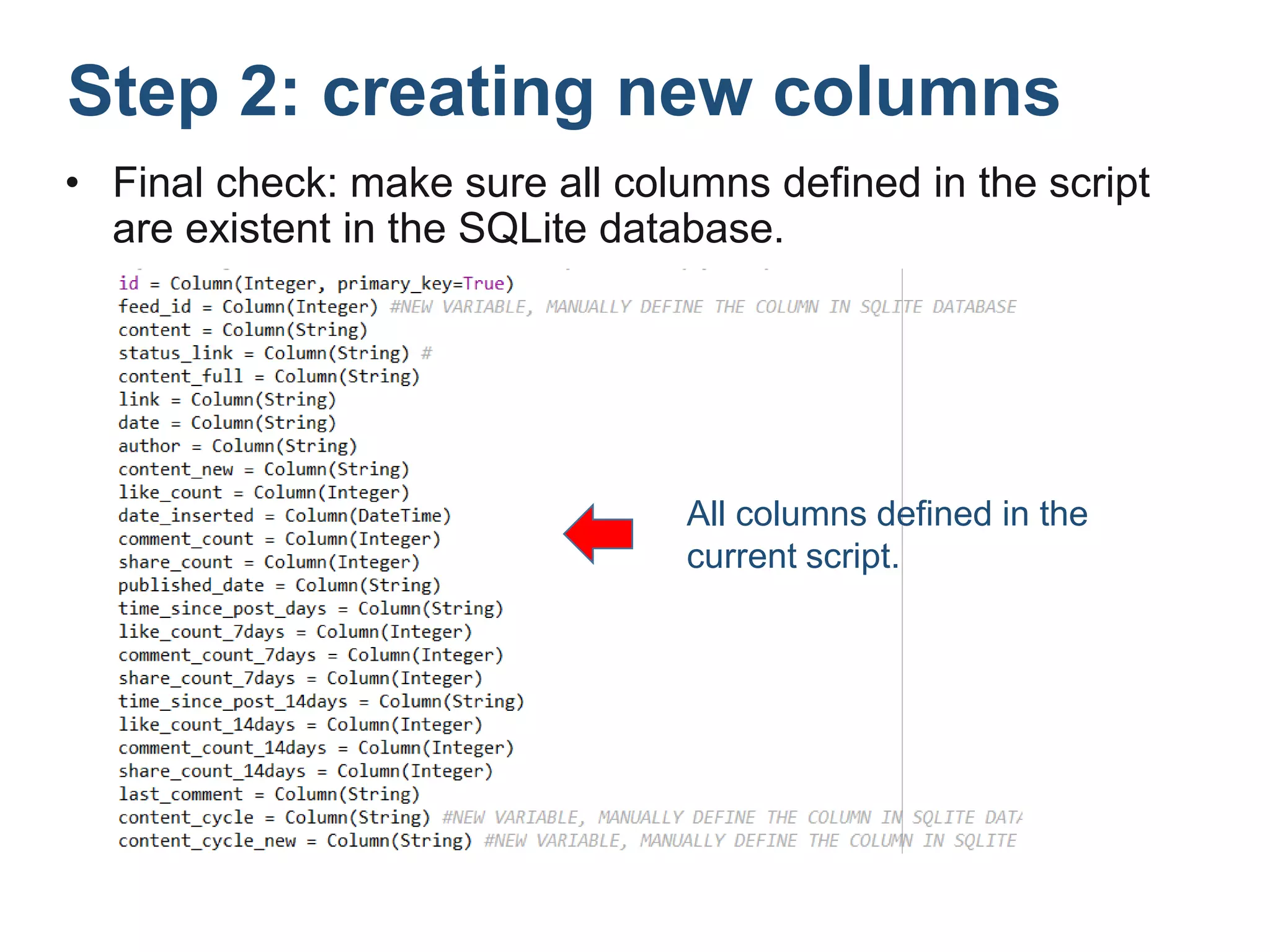
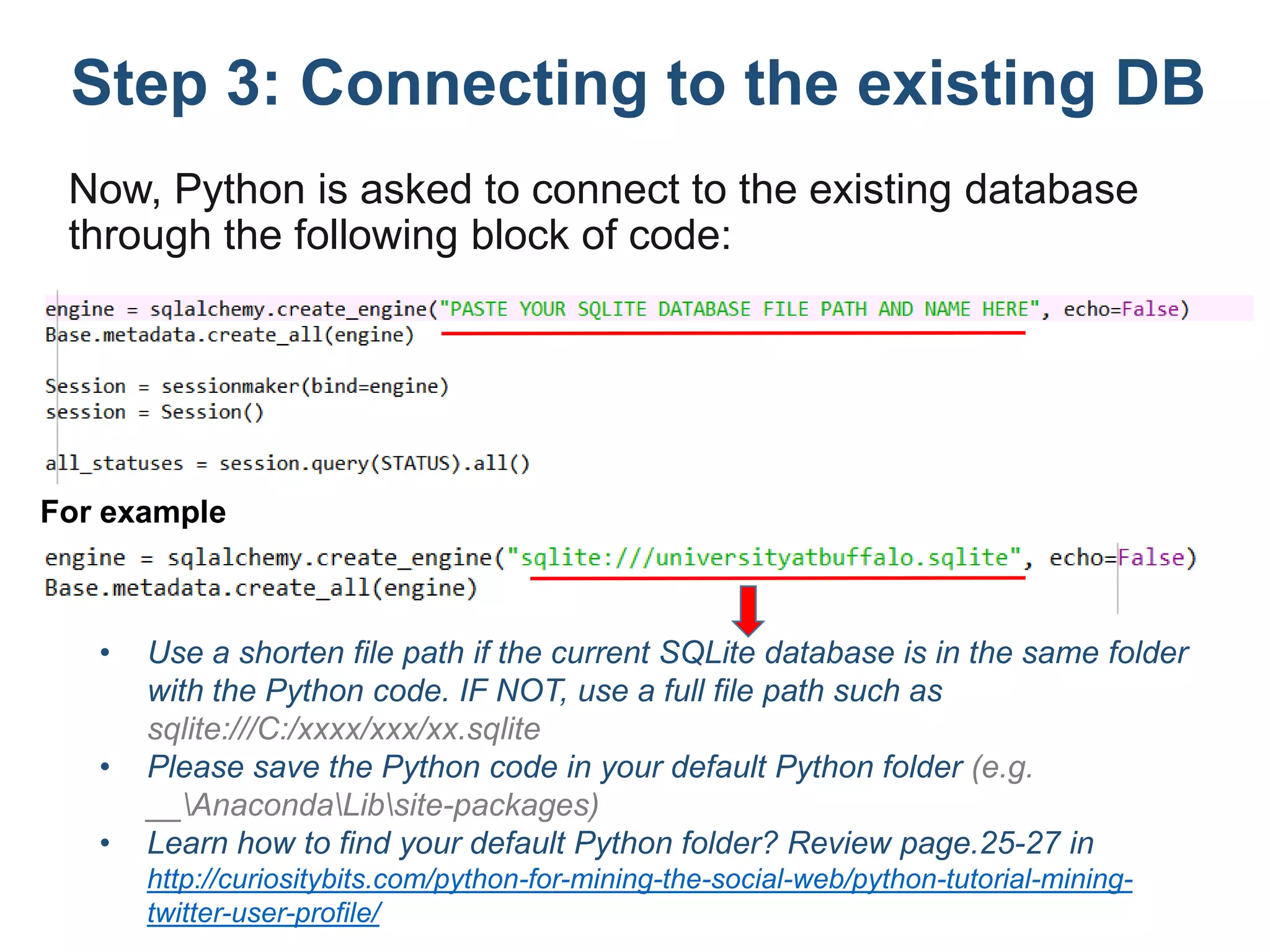
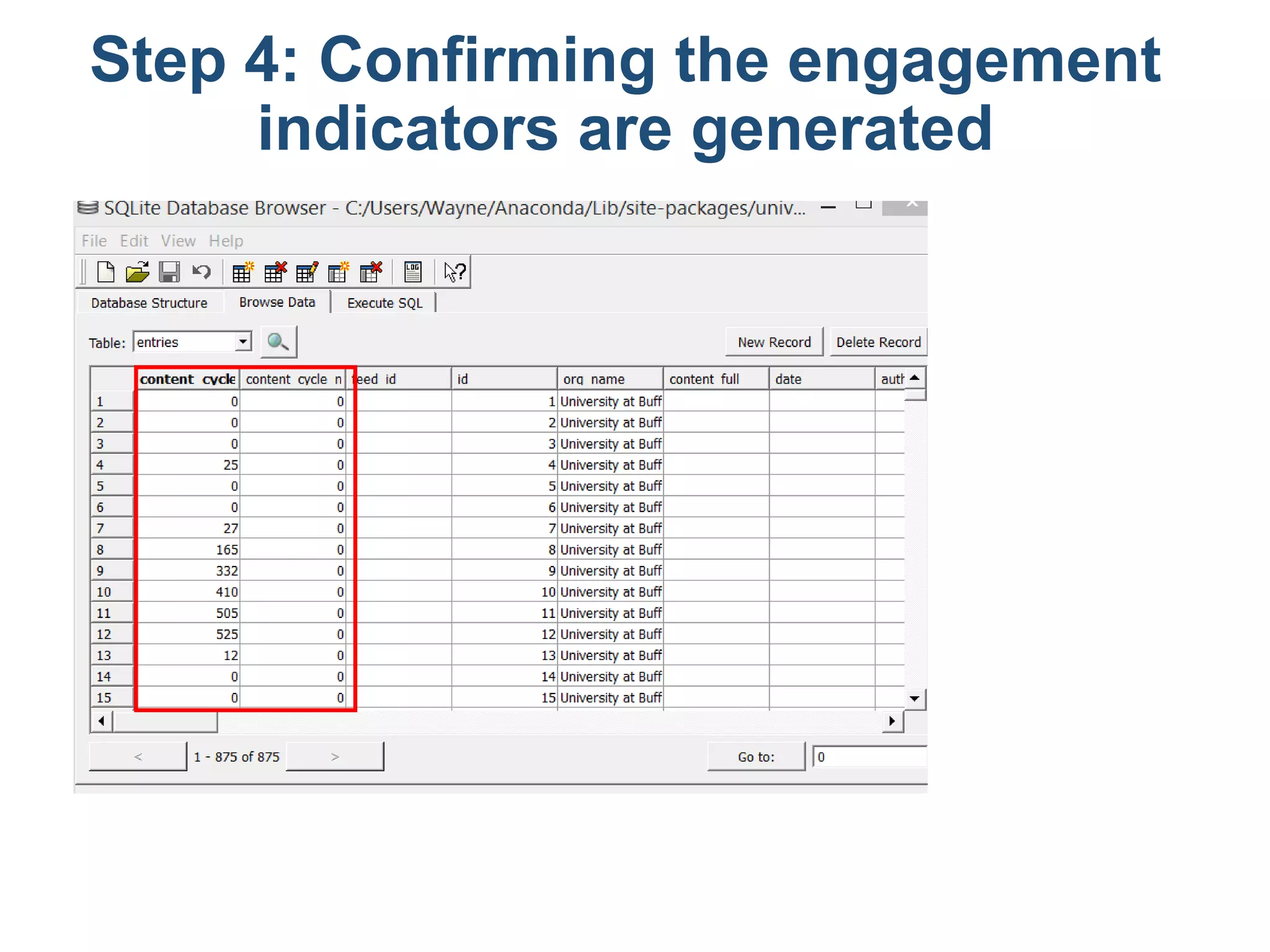
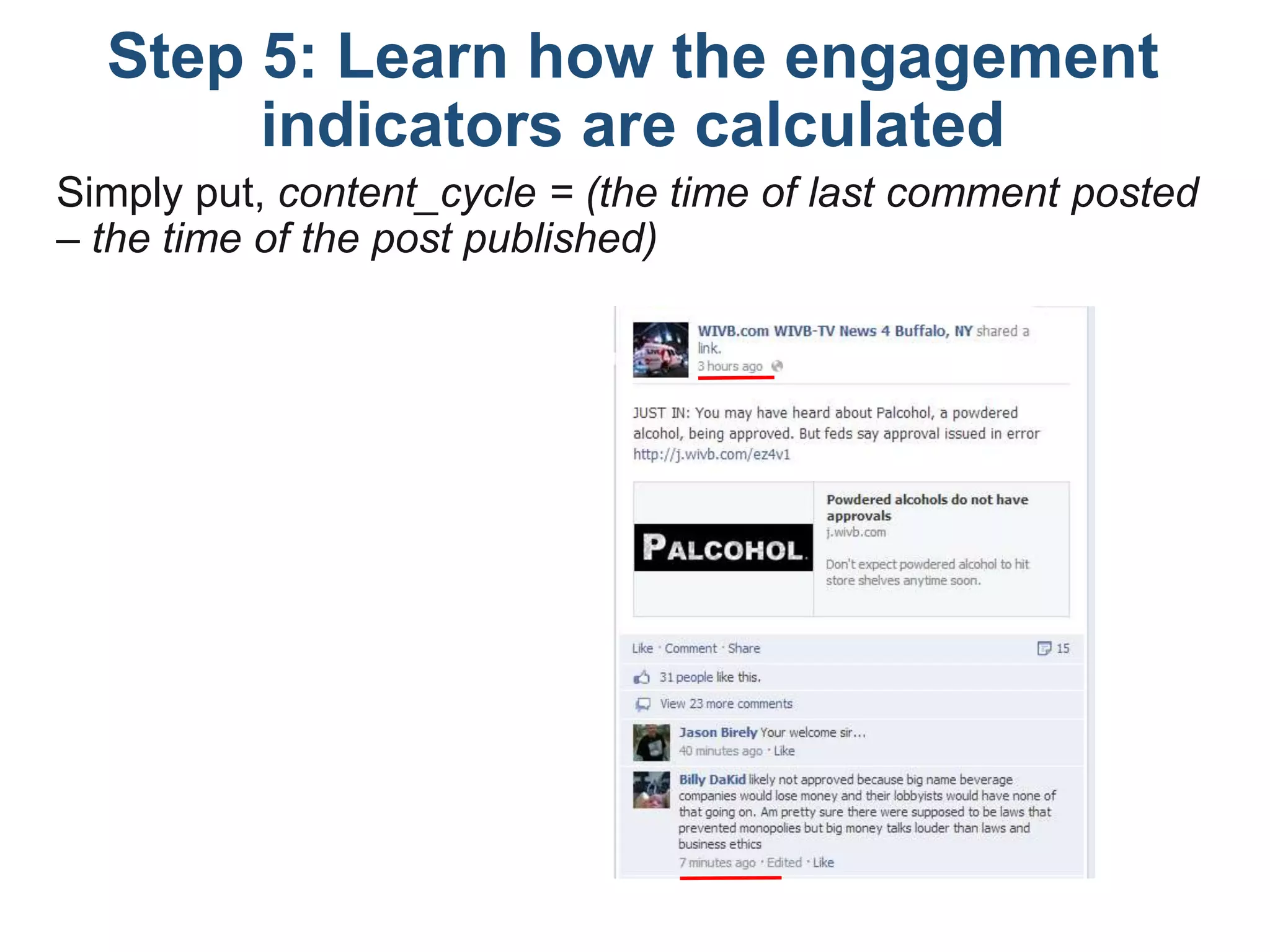
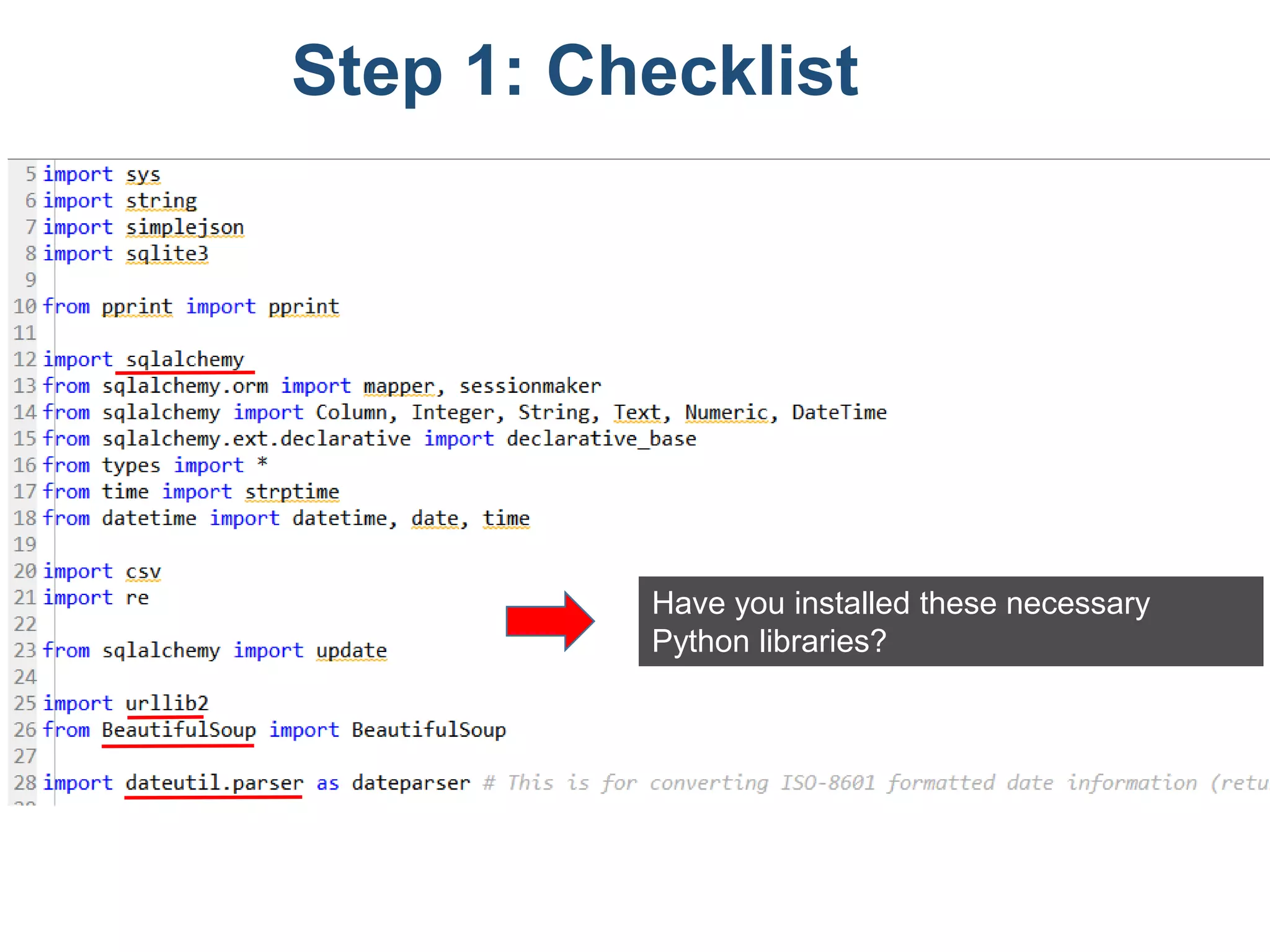
The document outlines a tutorial on how to obtain Facebook engagement indicators such as likes, shares, and comments for posts on a Facebook page. It provides a step-by-step guide, including creating a SQLite database, adding necessary columns, and connecting to the database using Python code. Additionally, it explains how to calculate the content lifecycle and engagement indicators based on user interactions and content performance over time.

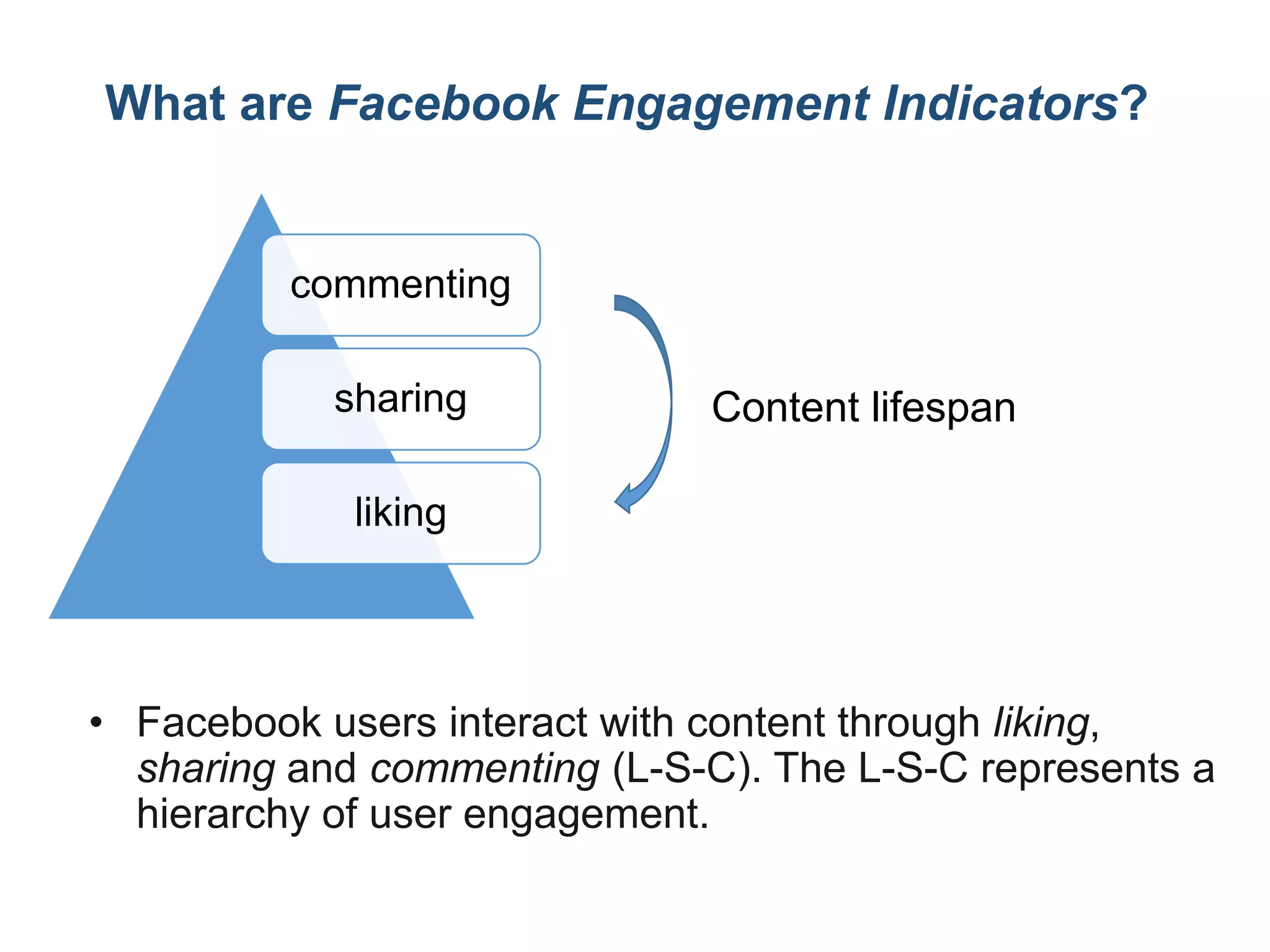



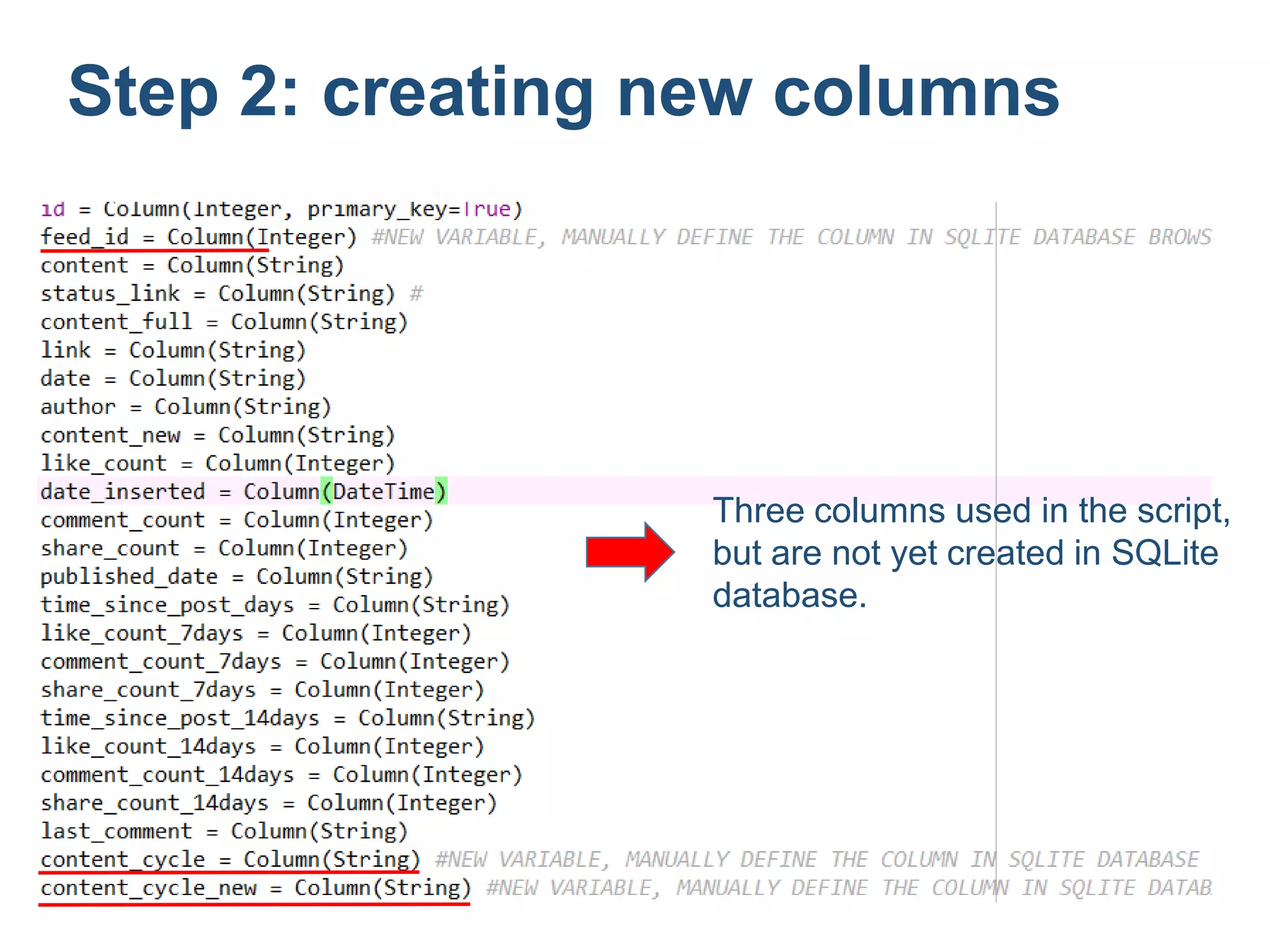
![Now let’s create the three columns:
• In SQLite Database Browser, choose [Edit] – [Modify
Table] – [Edit] – [Add Field]
name type
Feed_id Integer
content_cycle String
content_cycle_new String
Step 2: creating new columns](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stepstogetfacebookengagementindicatornew-140421212244-phpapp01/75/Five-Steps-to-Get-Facebook-Engagement-Indicators-9-2048.jpg)