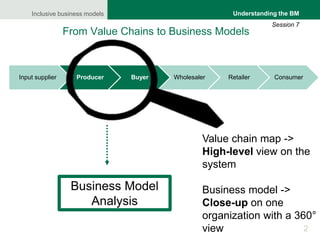
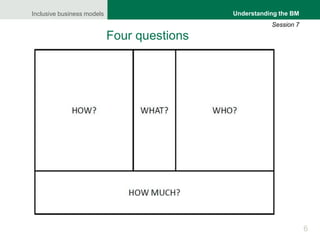
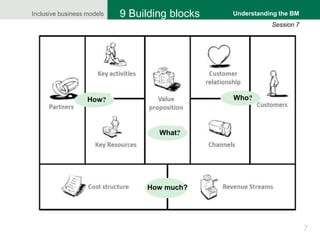
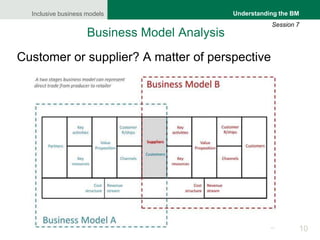
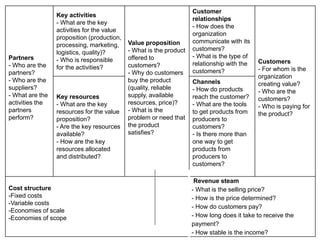
The document focuses on understanding inclusive business models, particularly in the context of agricultural value chains. It provides a framework for analyzing business models through a comprehensive tool, the business model canvas, which highlights essential components such as customer relationships, value propositions, and key activities. Various methodologies for gathering insights from producers, buyers, and stakeholders are also discussed to enhance understanding of how these models operate effectively.