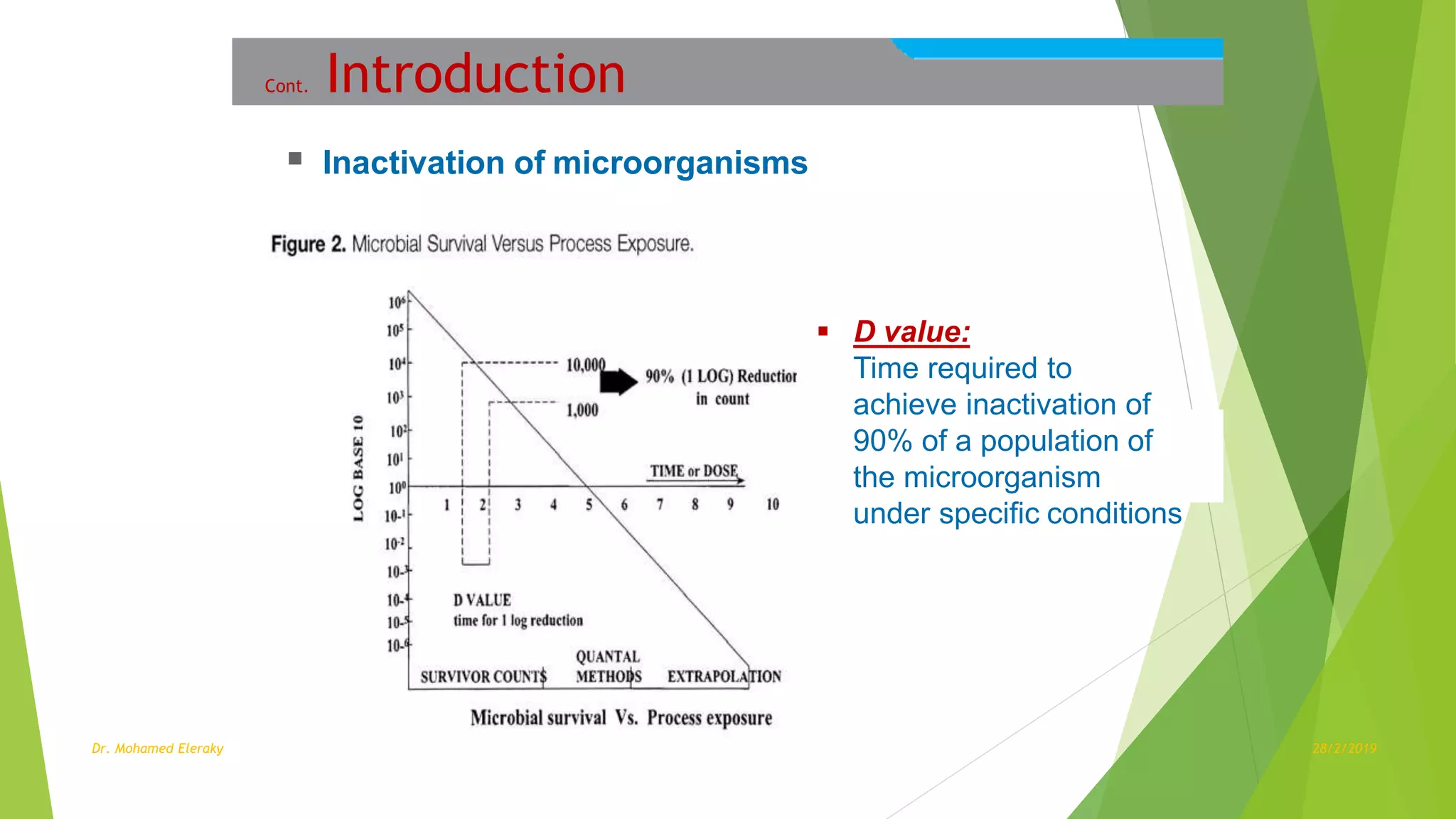
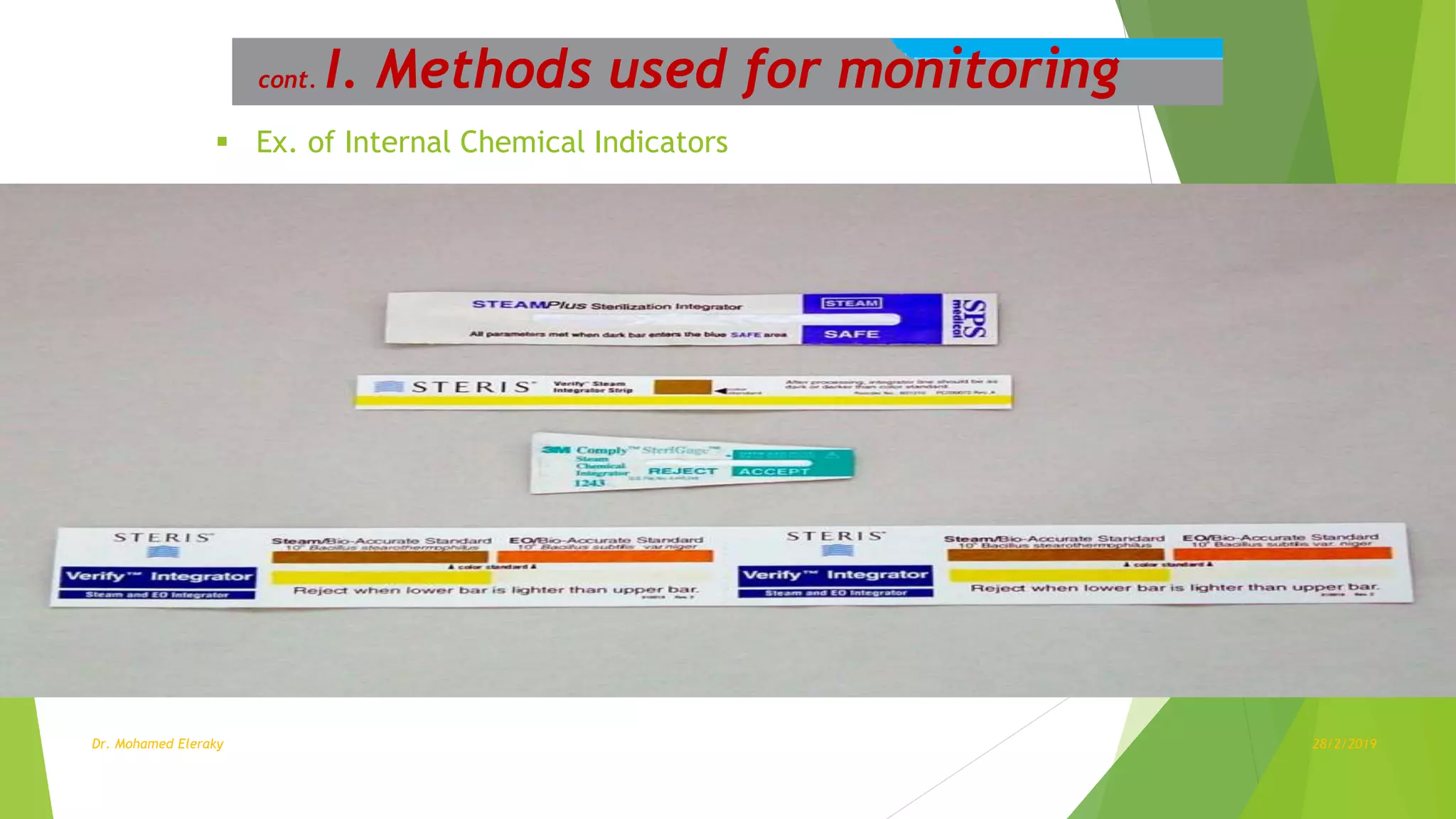
Steam sterilization monitoring involves ensuring sterilized items are free from microorganisms. The document discusses several key aspects of steam sterilization monitoring including: (1) sterility assurance levels and D-values which define sterilization effectiveness, (2) common sterilization methods like steam, gamma radiation and hydrogen peroxide, (3) methods for monitoring sterilization like mechanical, chemical and biological indicators, and (4) levels of assurance including equipment, exposure, pack and load control through proper use of indicators and record keeping. Managing a positive biological indicator requires recalling implantable items, retesting the sterilizer, and putting it back in service only after three consecutive negative retests.