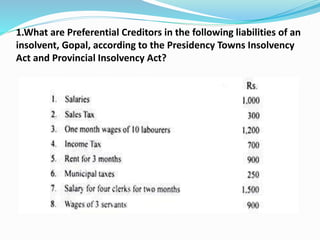
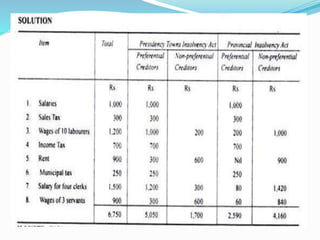
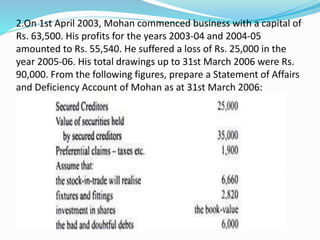
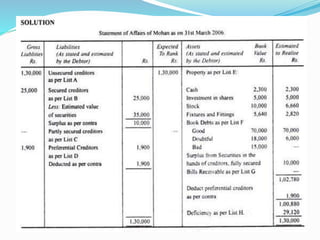
The document discusses insolvency procedures in India. It defines insolvency as when a person is unable to pay their debts in full. There are two main acts that deal with insolvency - the Presidency Towns Insolvency Act and the Provincial Insolvency Act. The key aspects of insolvency procedure include a debtor filing a petition for adjudication, the court appointing a receiver to take possession of the debtor's assets, the receiver selling the assets and distributing the proceeds to creditors, and the court granting the debtor a discharge to release them from debts. The document also explains the various lists involved in a statement of affairs, such as separating creditors into secured, unsecured and preferential categories and