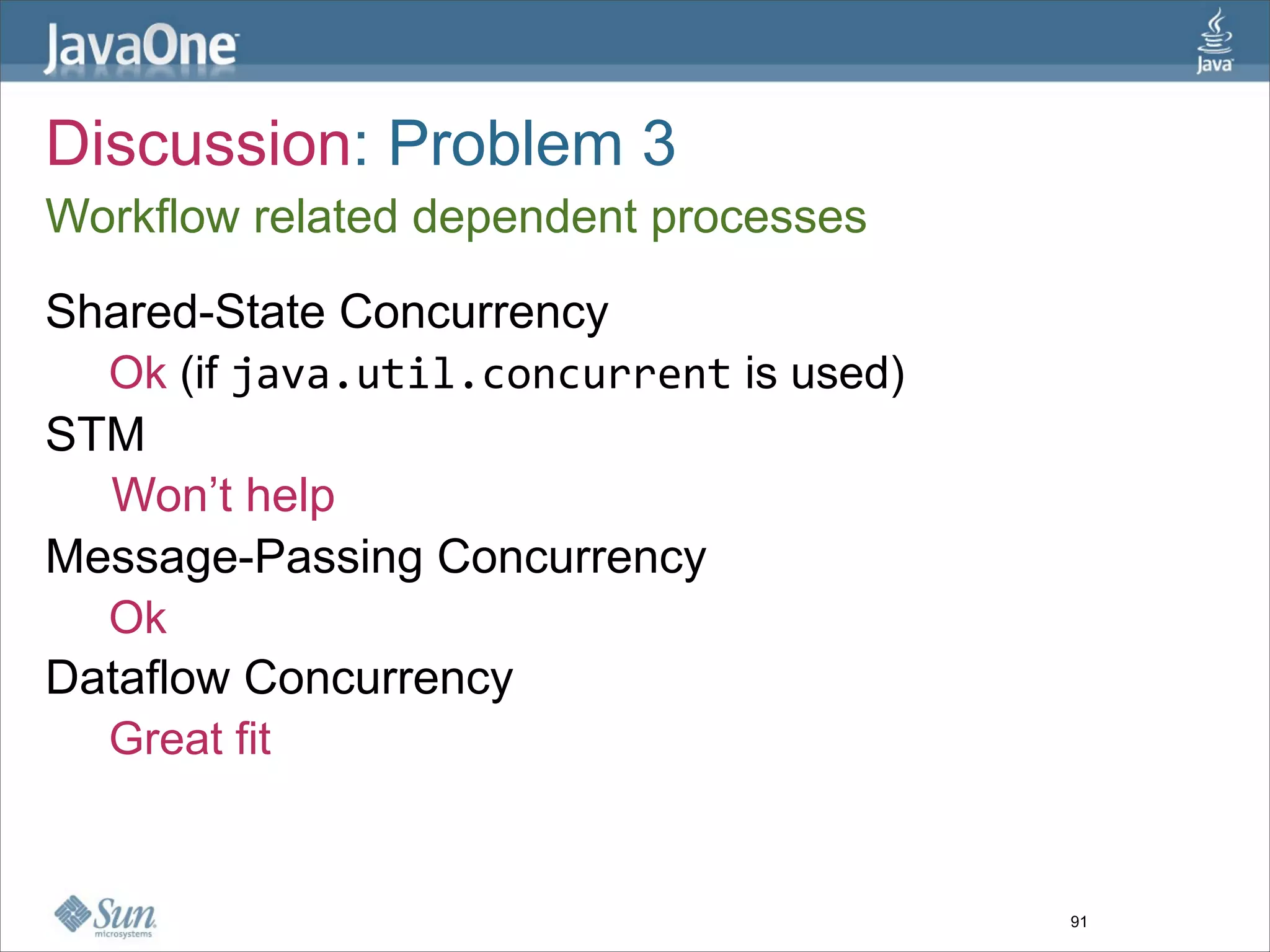
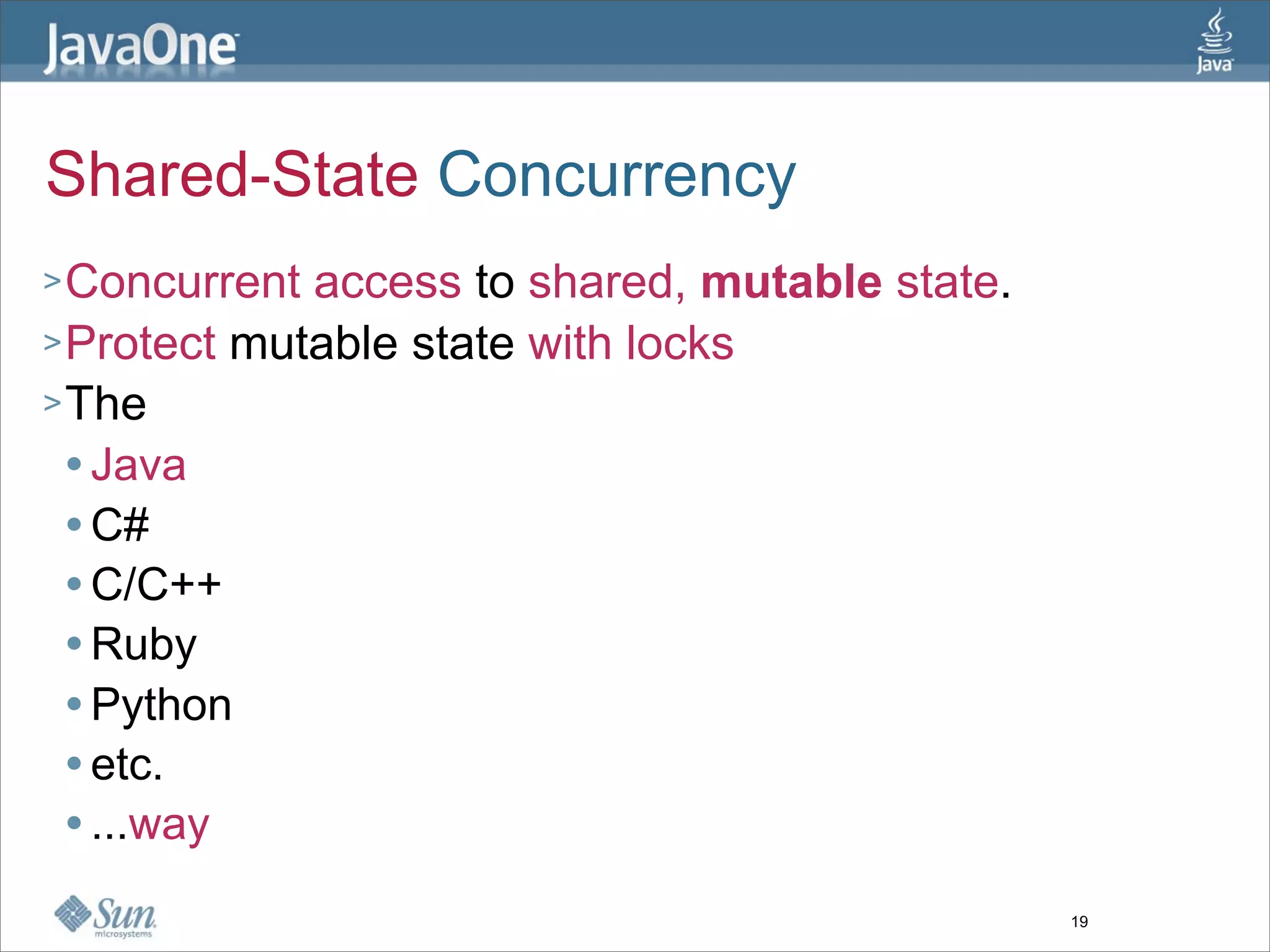
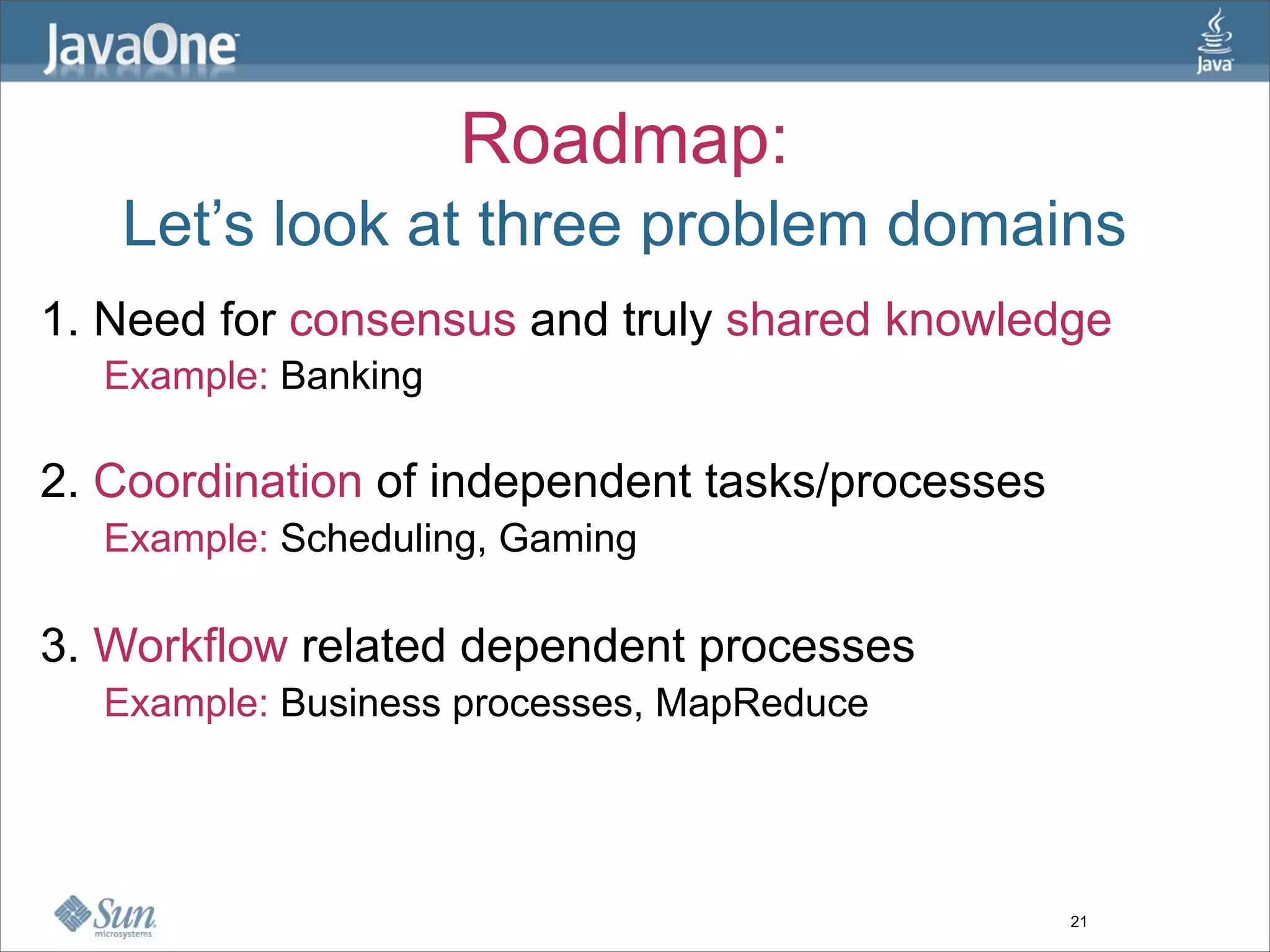
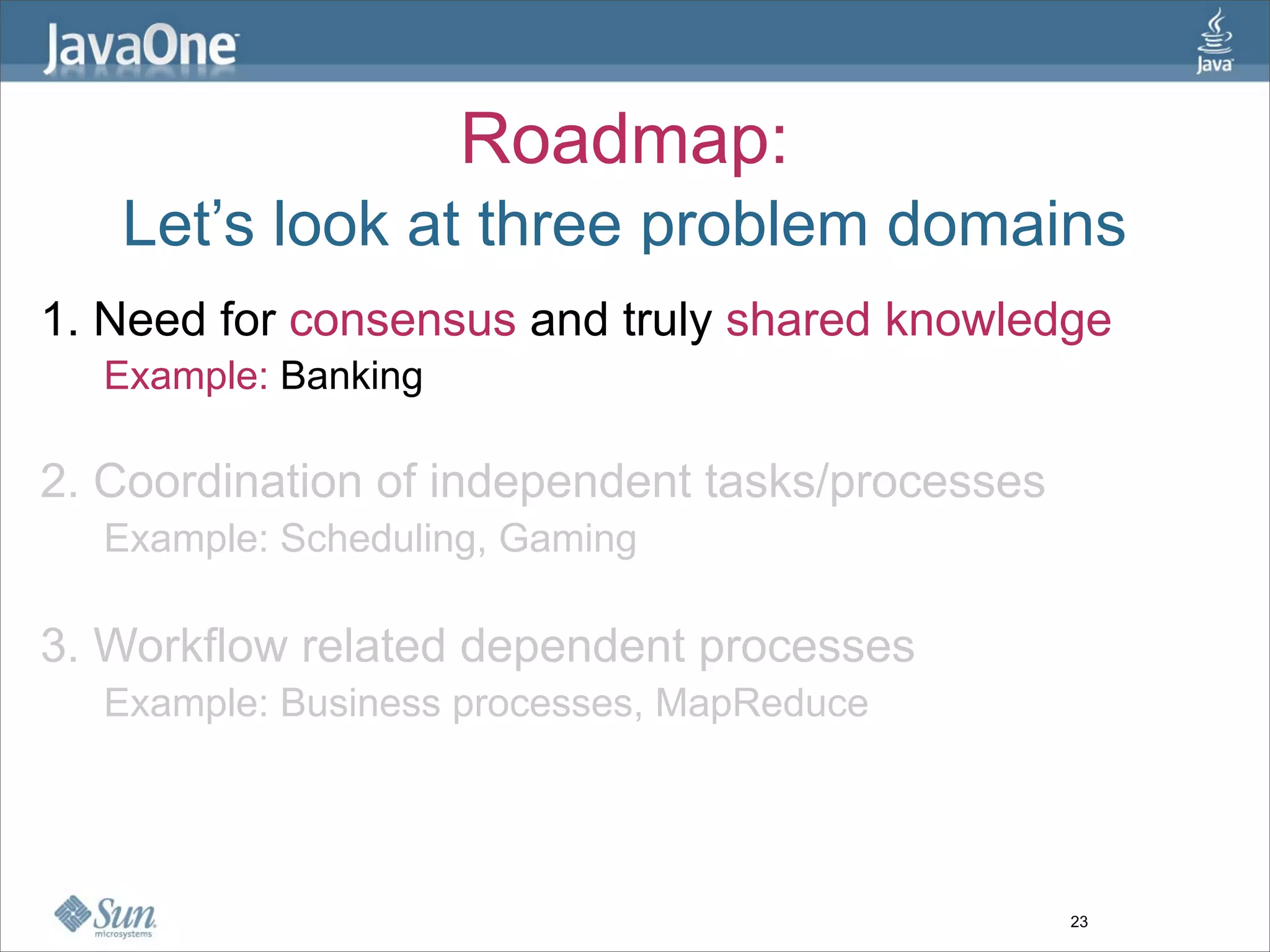
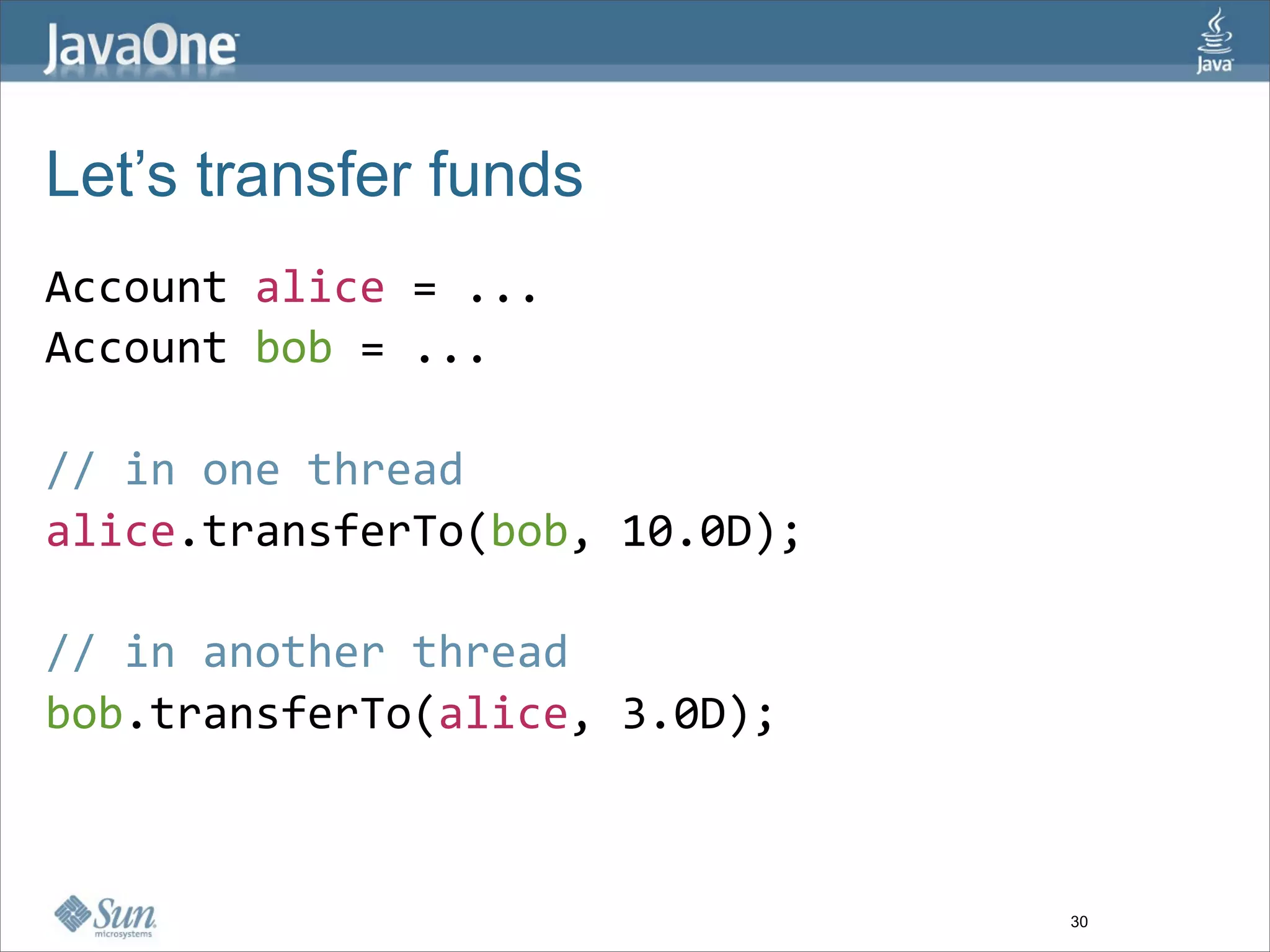
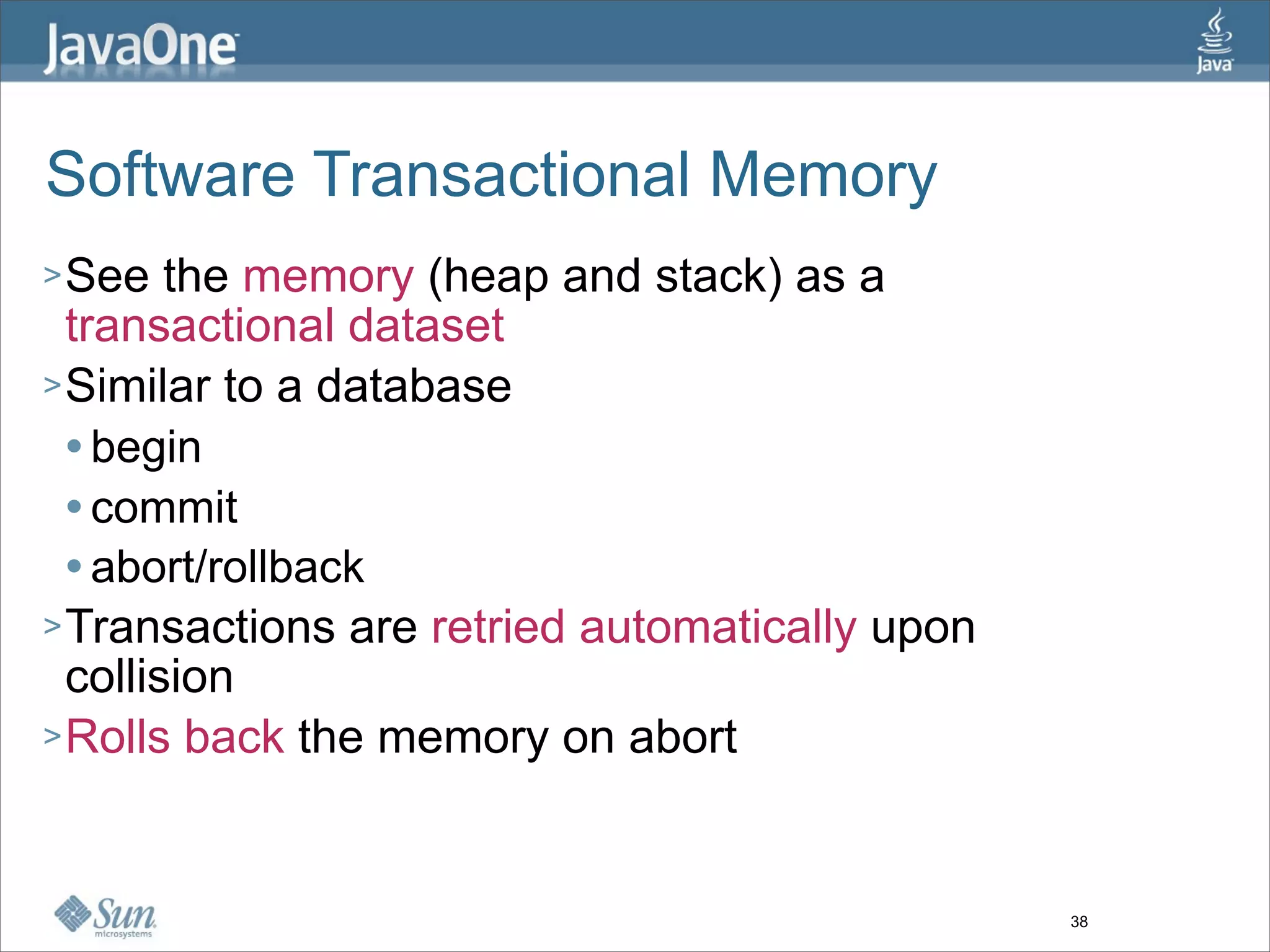
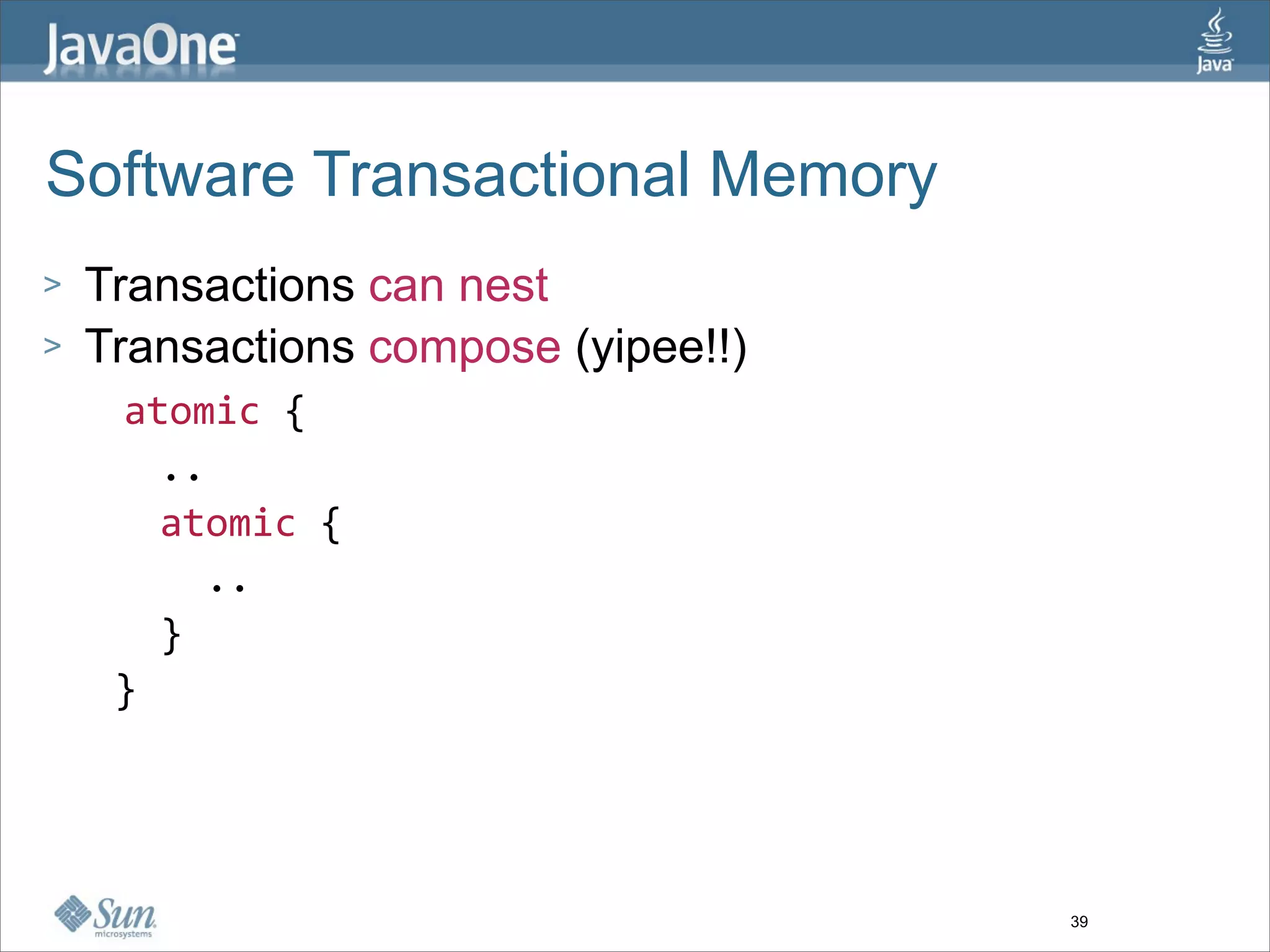
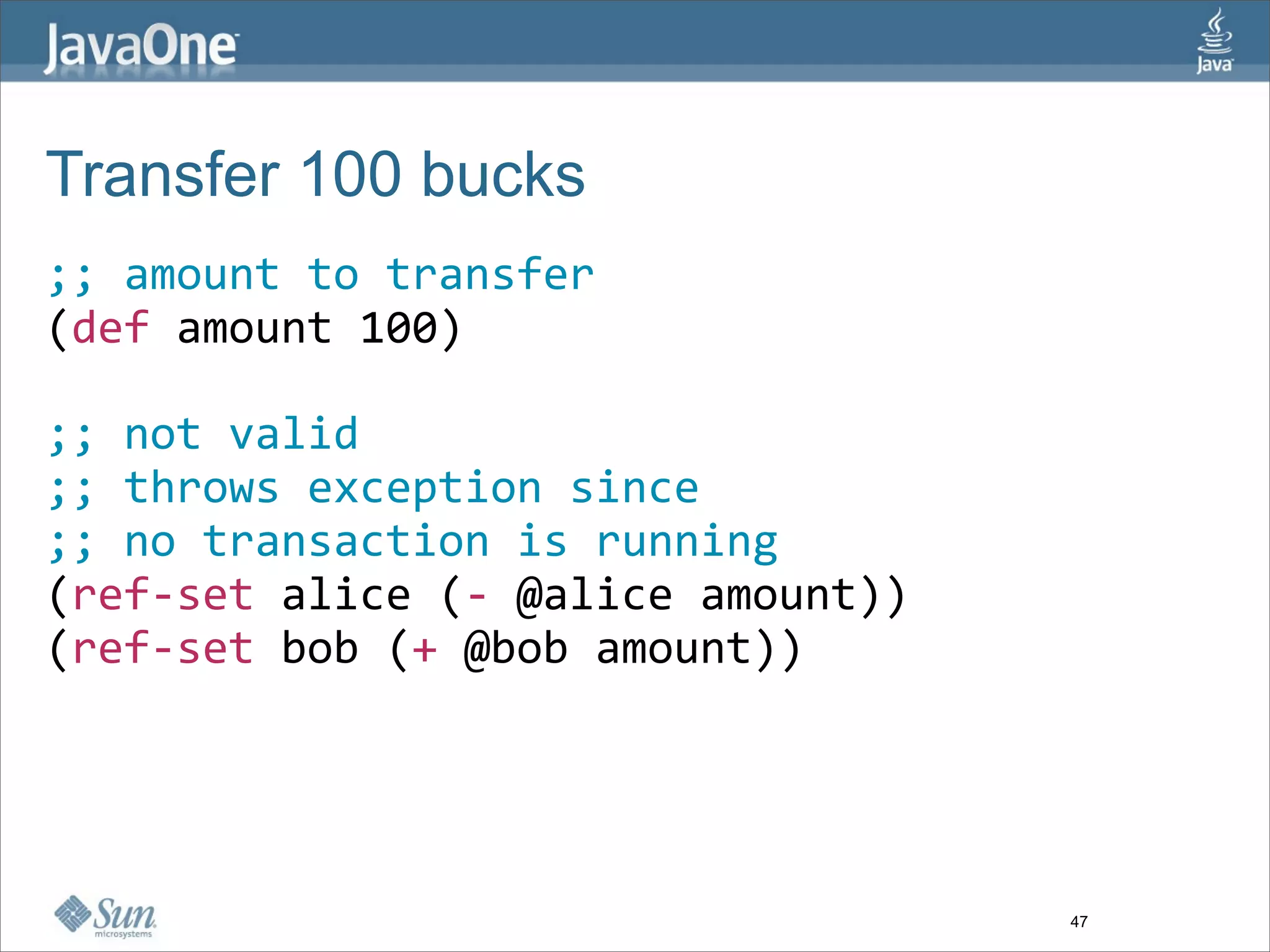
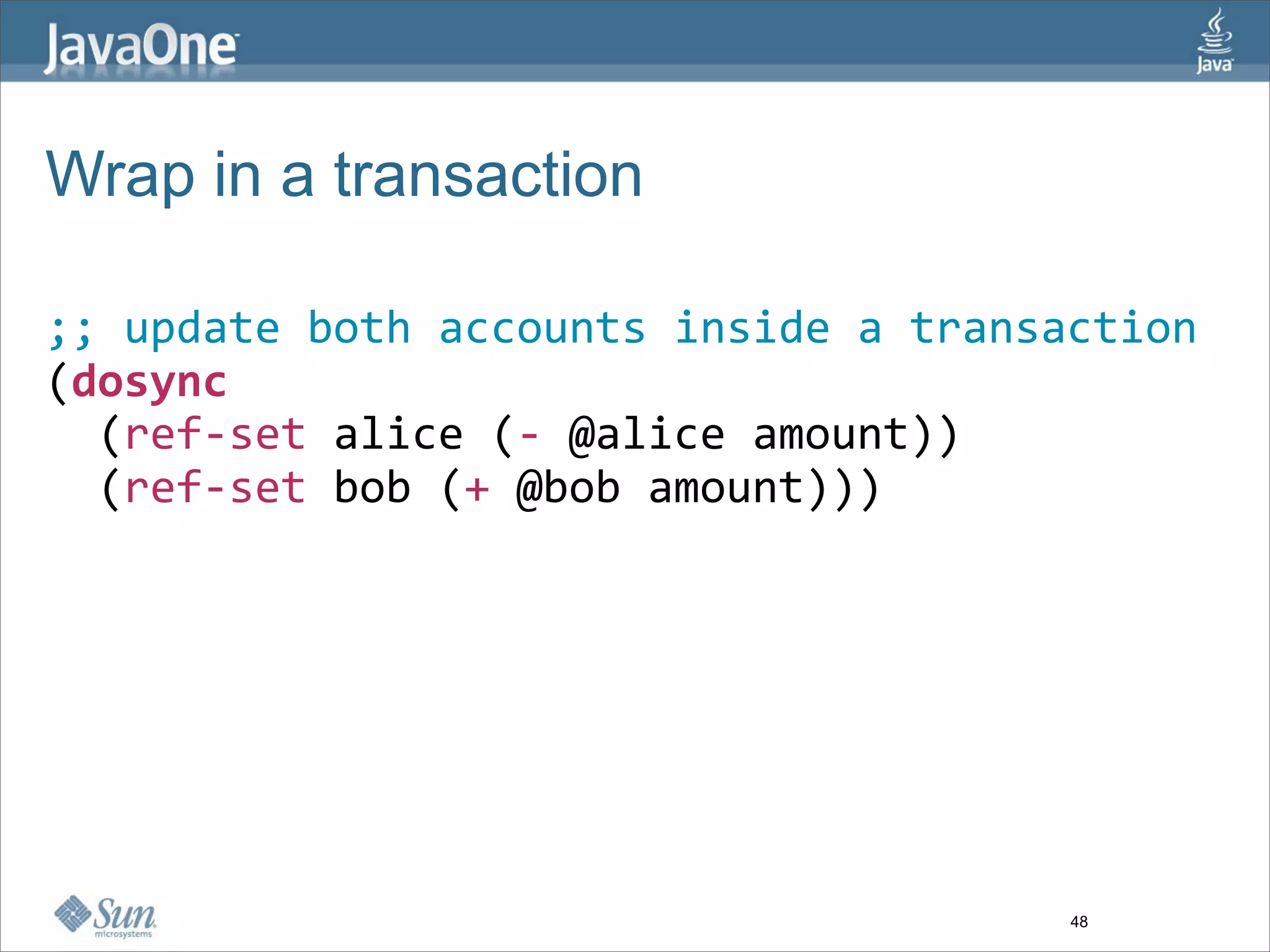
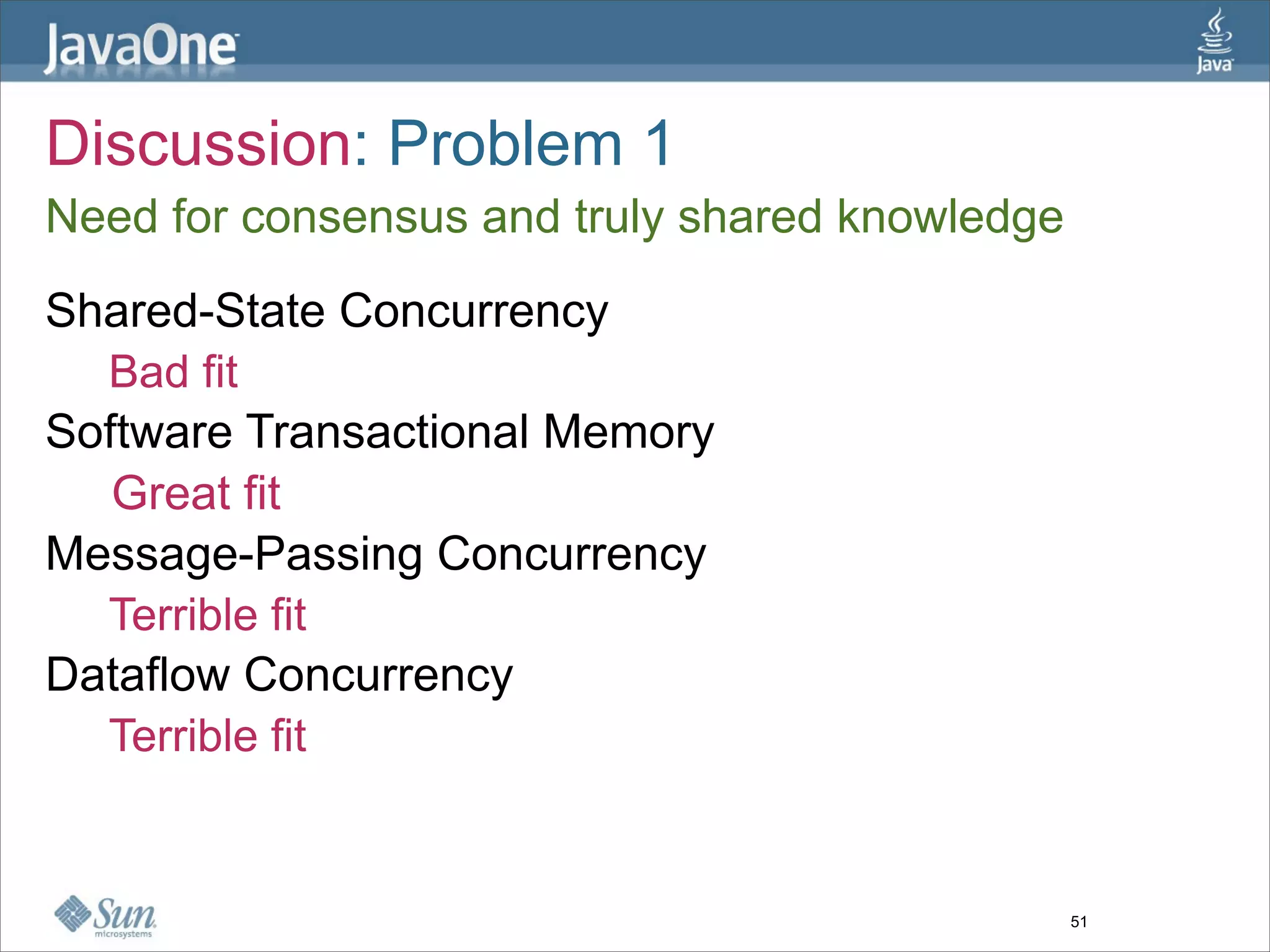
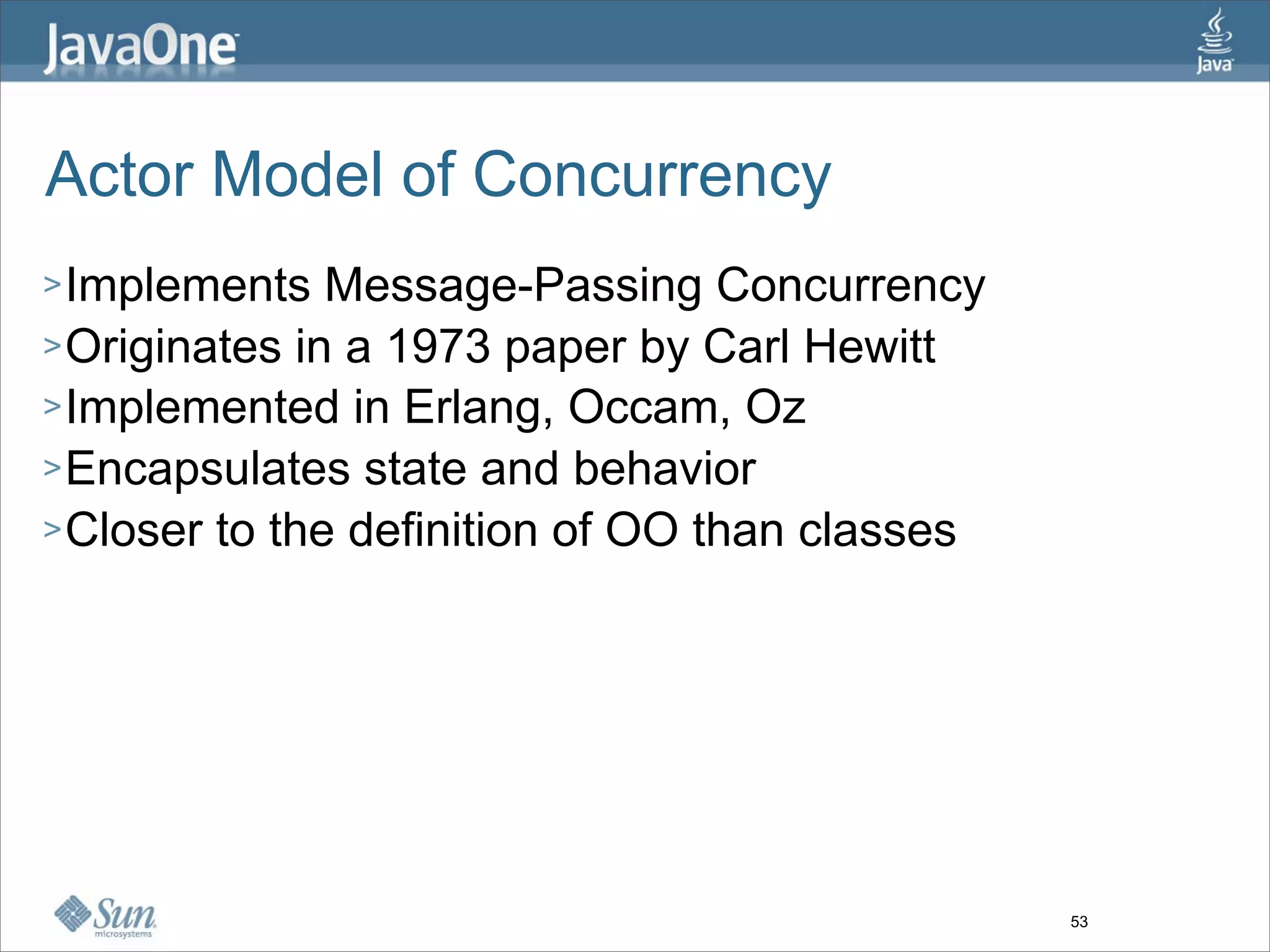
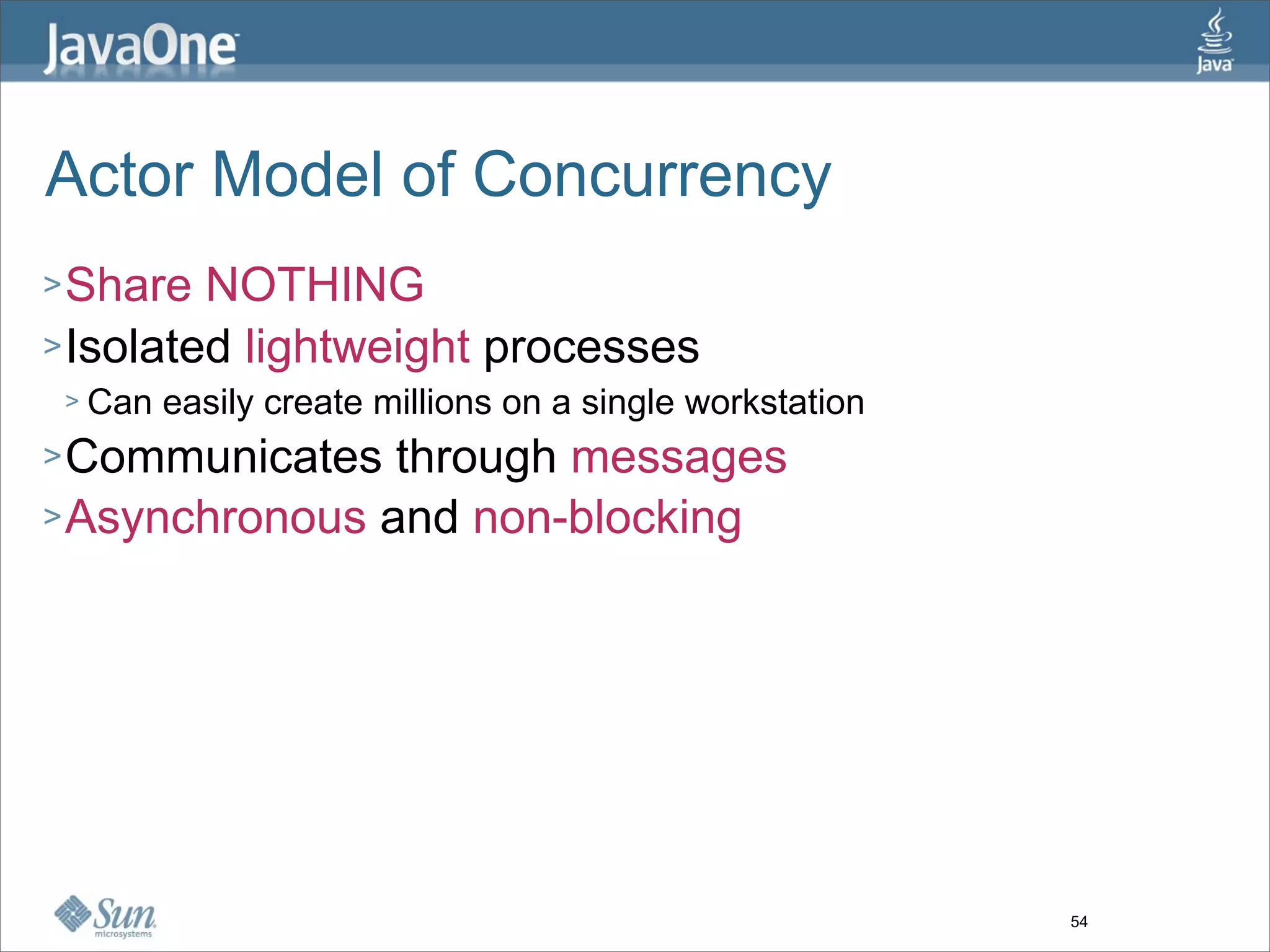
The document discusses alternative concurrency paradigms for the JVM, emphasizing the shortcomings of traditional shared-state concurrency and the rise of multi-processor systems. It introduces software transactional memory (STM), message-passing concurrency (actors), and dataflow concurrency as viable alternatives, each suited for different problem domains. The author concludes that a simpler and more effective approach to writing concurrent programs is needed due to the complexities of Java-style concurrency.




























































![API: Dataflow Variable
//
Create
dataflow
variable
val
x,
y,
z
=
new
DataFlowVariable[Int]
//
Access
dataflow
variable
(Wait
to
be
bound)
z()
//
Bind
dataflow
variable
x
<<
40
//
Lightweight
thread
thread
{
y
<<
2
}
81](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stateyouredoingitwrongjavaone2009-090617031310-phpapp02/75/State-You-re-Doing-It-Wrong-Alternative-Concurrency-Paradigms-For-The-JVM-81-2048.jpg)
![API: Dataflow Stream
Deterministic streams (not IO streams)
//
Create
dataflow
stream
val
producer
=
new
DataFlowStream[Int]
//
Append
to
stream
producer
<<<
s
//
Read
from
stream
producer()
82](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stateyouredoingitwrongjavaone2009-090617031310-phpapp02/75/State-You-re-Doing-It-Wrong-Alternative-Concurrency-Paradigms-For-The-JVM-82-2048.jpg)




![Example: Dataflow Variables
//
sequential
version
val
x,
y,
z
=
new
DataFlowVariable[Int]
x
<<
40
y
<<
2
z
<<
x()
+
y()
println("z
=
"
+
z())
88](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stateyouredoingitwrongjavaone2009-090617031310-phpapp02/75/State-You-re-Doing-It-Wrong-Alternative-Concurrency-Paradigms-For-The-JVM-88-2048.jpg)
![Example: Dataflow Variables
//
concurrent
version:
no
difference
val
x,
y,
z
=
new
DataFlowVariable[Int]
thread
{
x
<<
40
}
thread
{
y
<<
2
}
thread
{
z
<<
x()
+
y()
println("z
=
"
+
z())
}
89](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stateyouredoingitwrongjavaone2009-090617031310-phpapp02/75/State-You-re-Doing-It-Wrong-Alternative-Concurrency-Paradigms-For-The-JVM-89-2048.jpg)