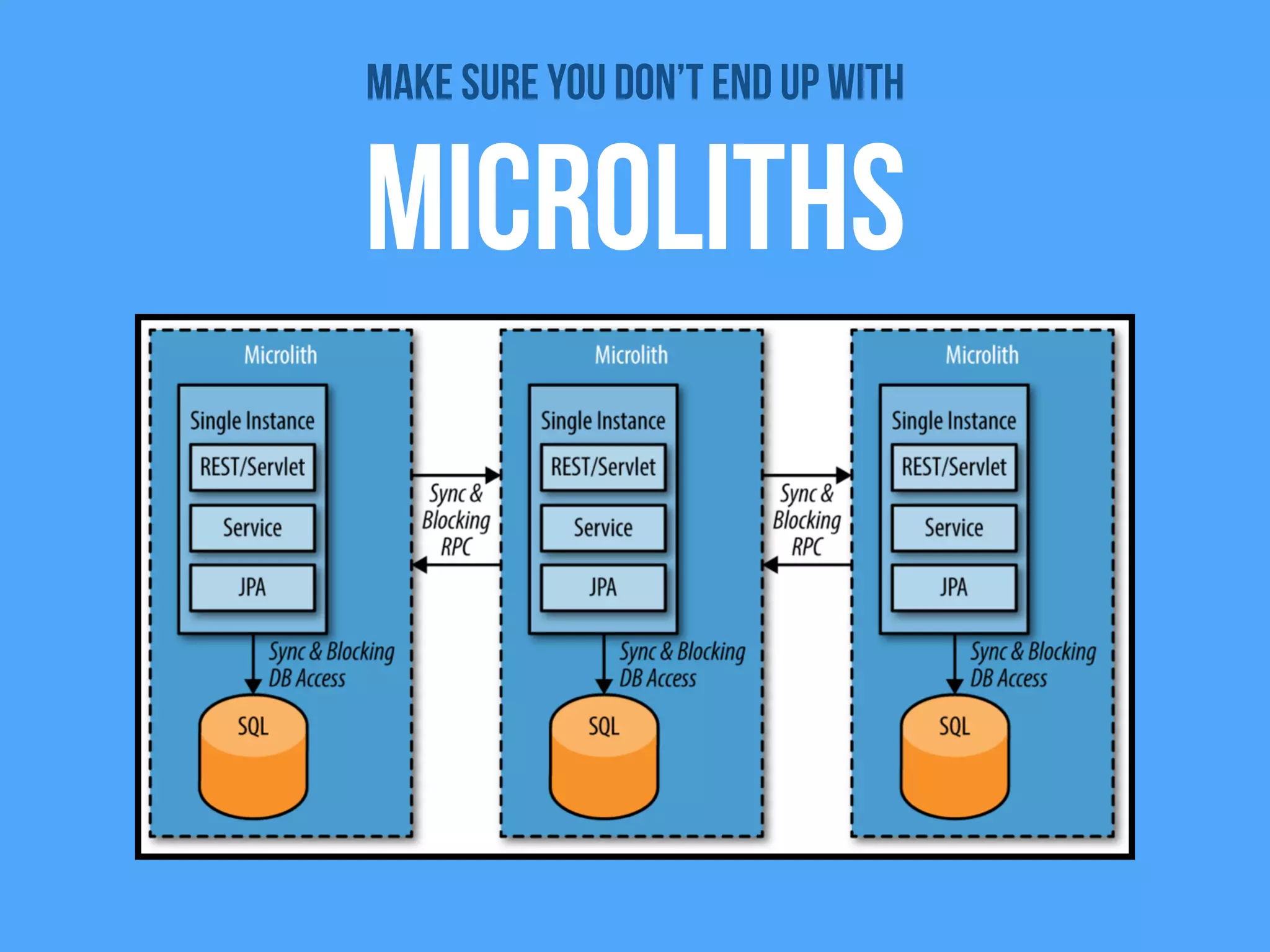
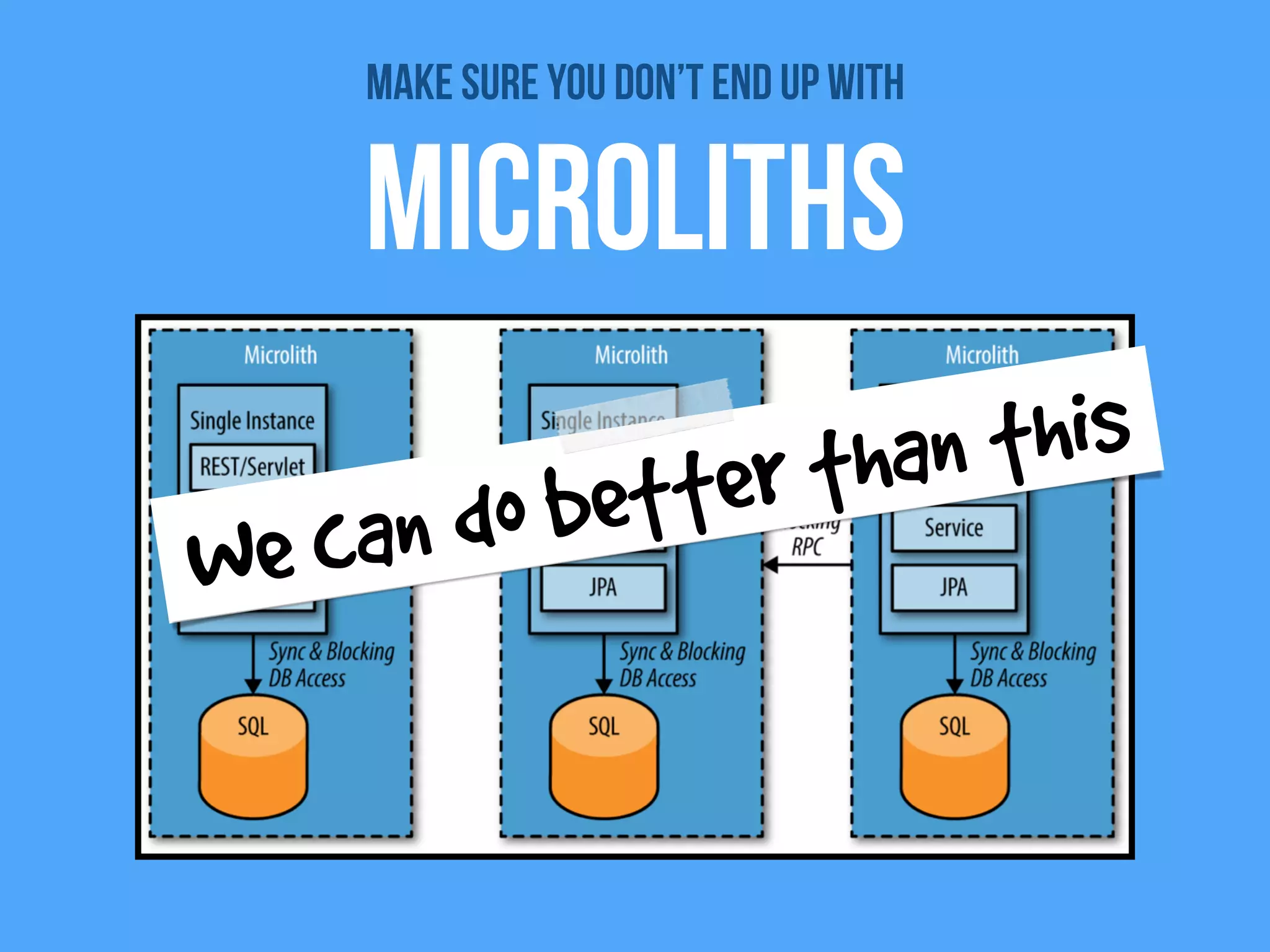
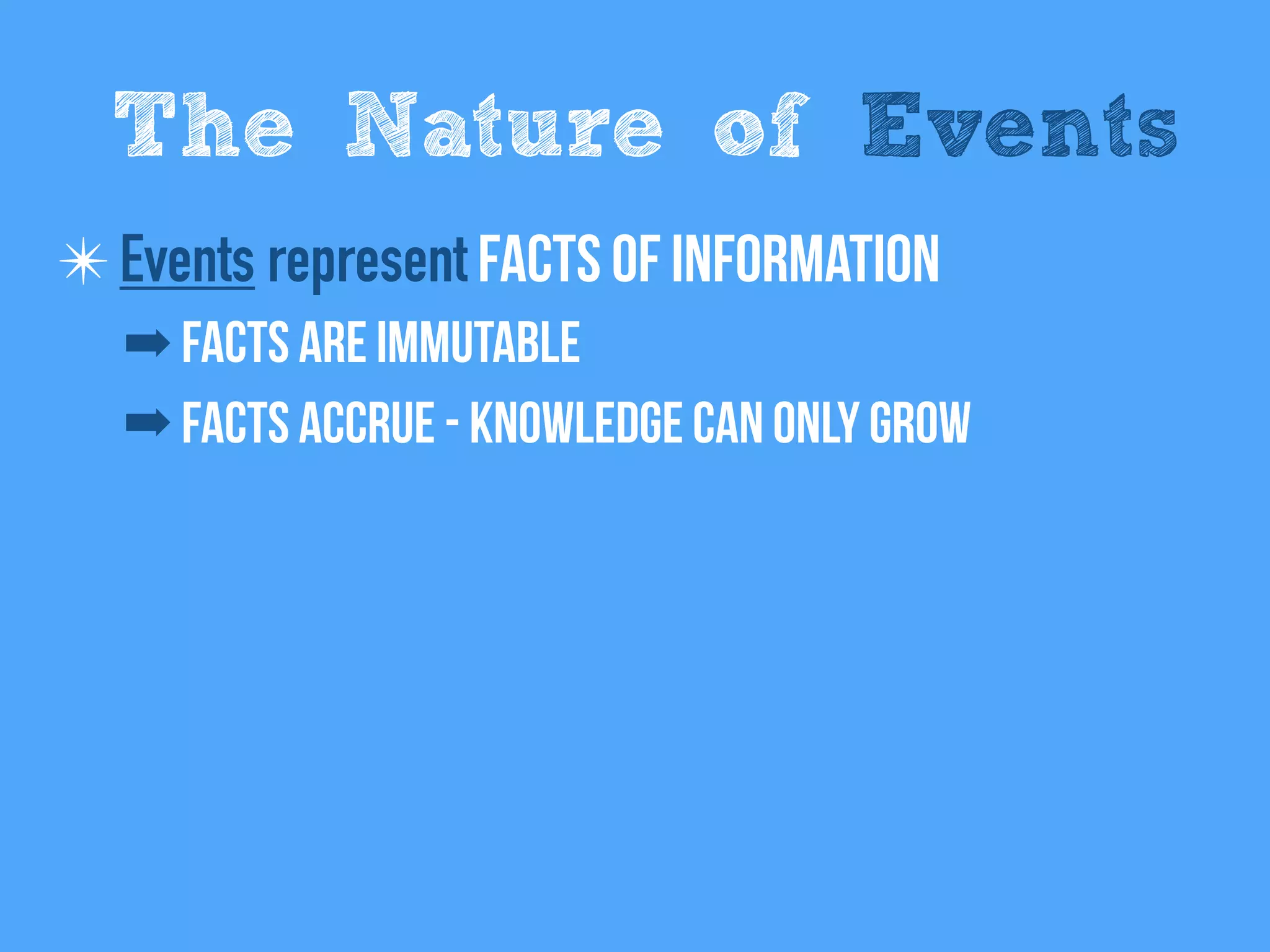
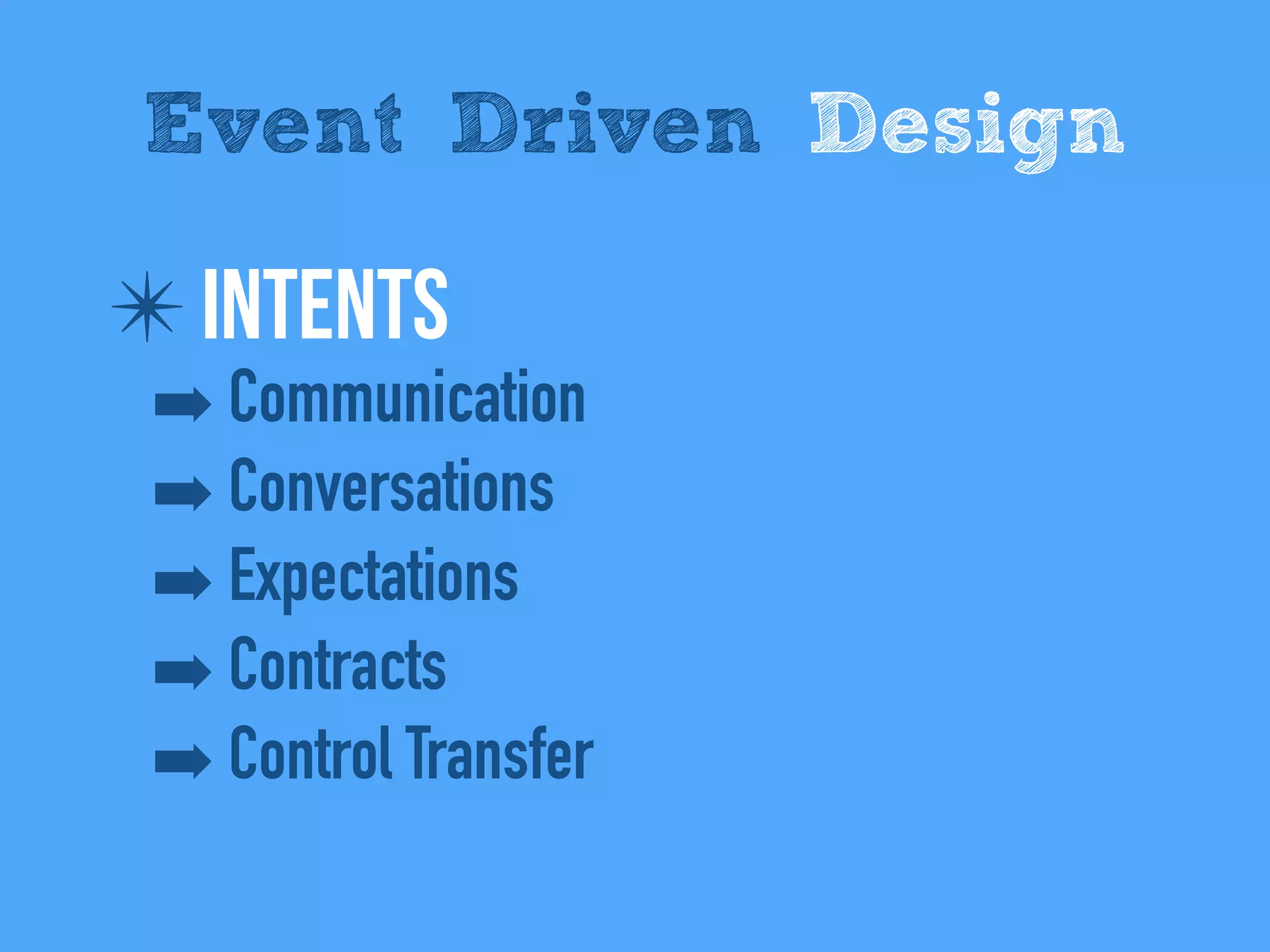
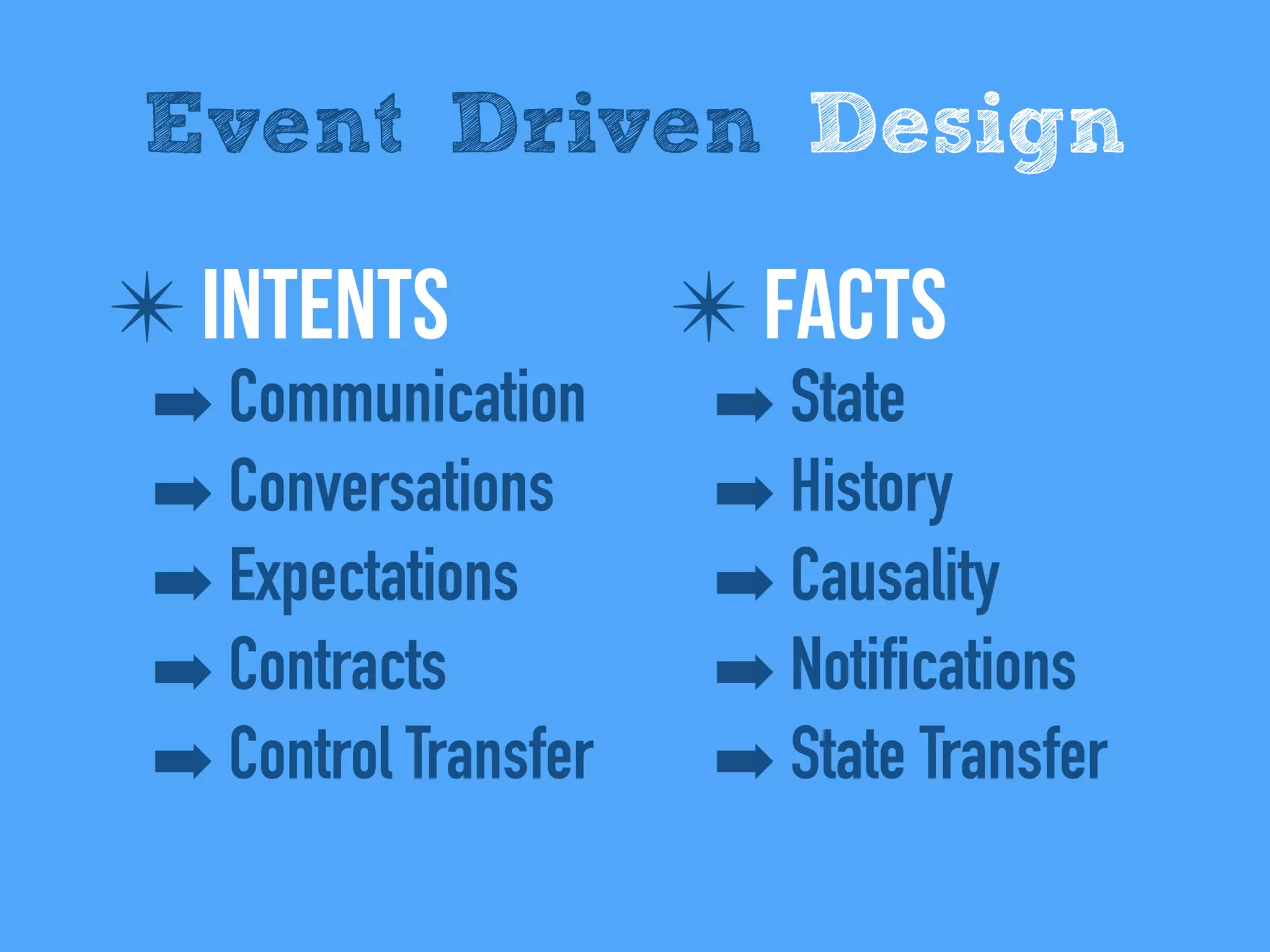
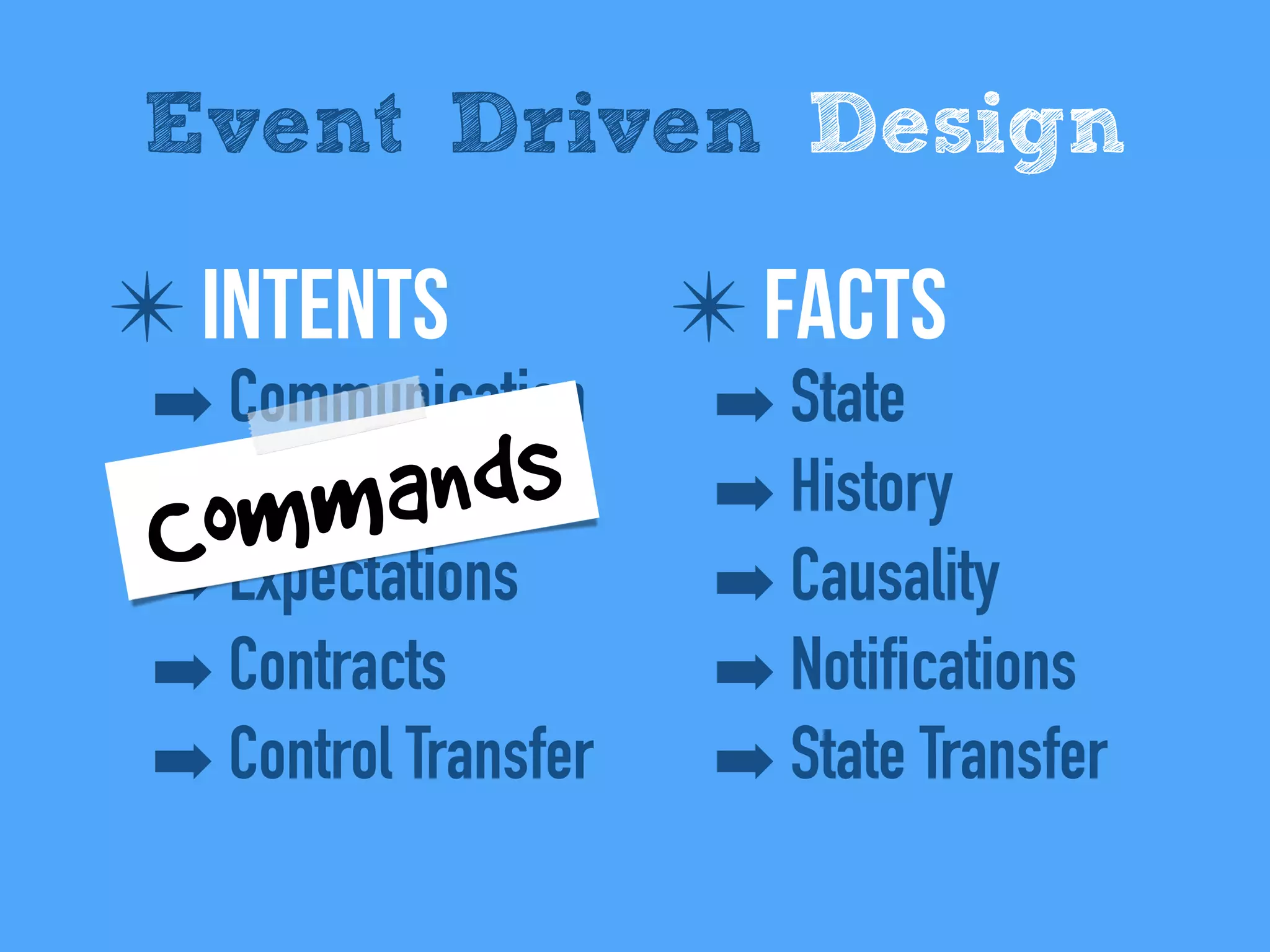
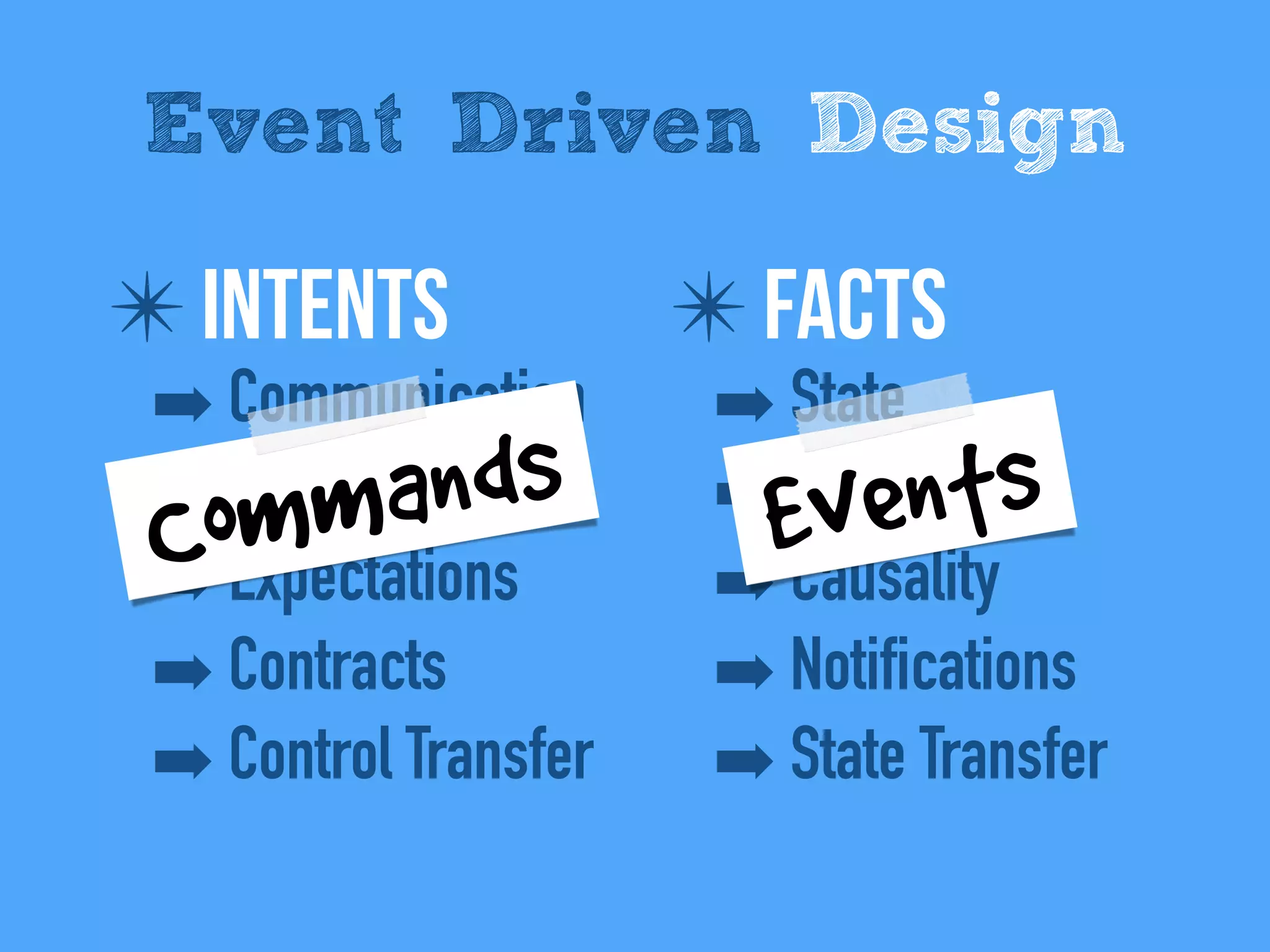
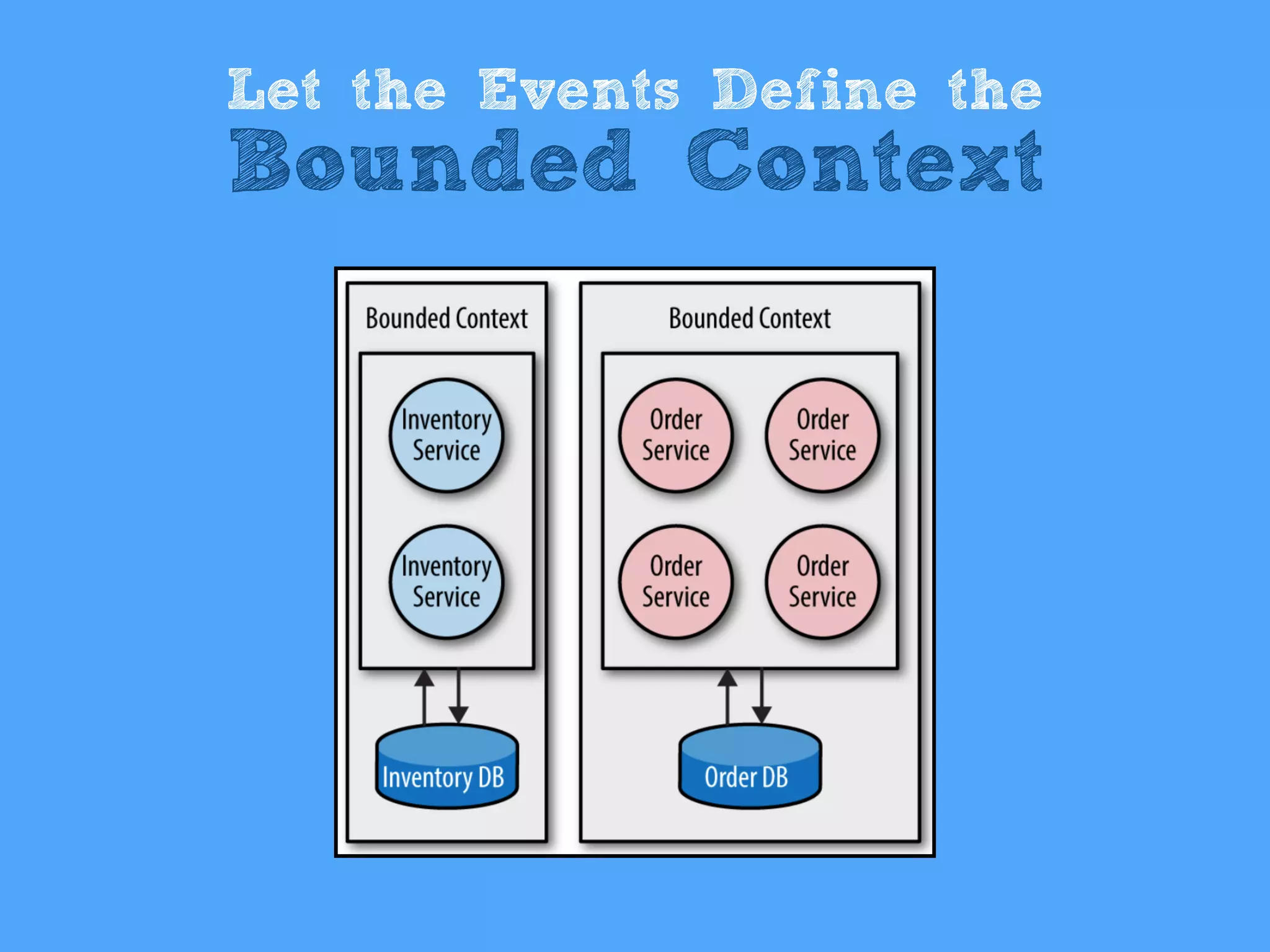
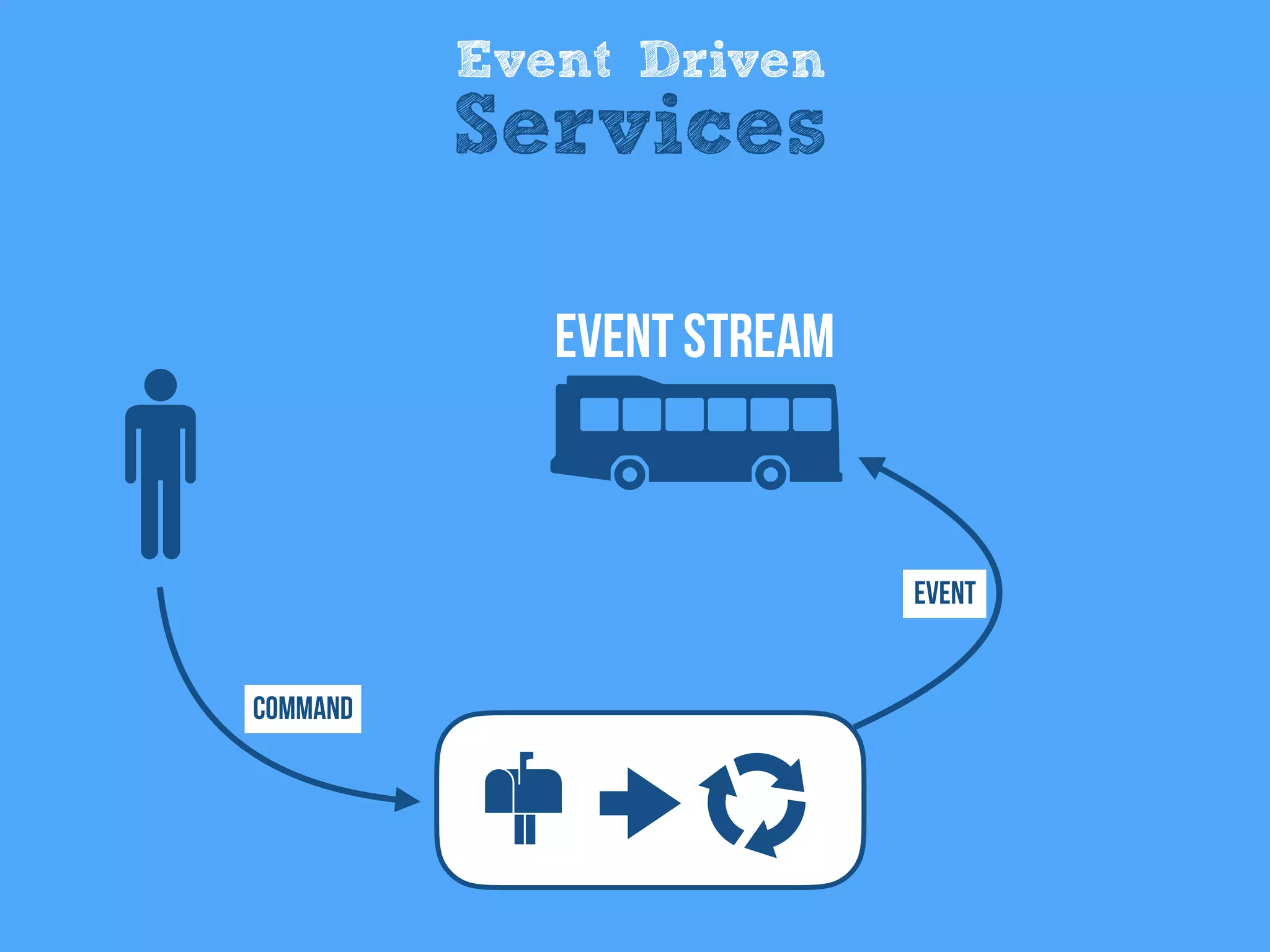
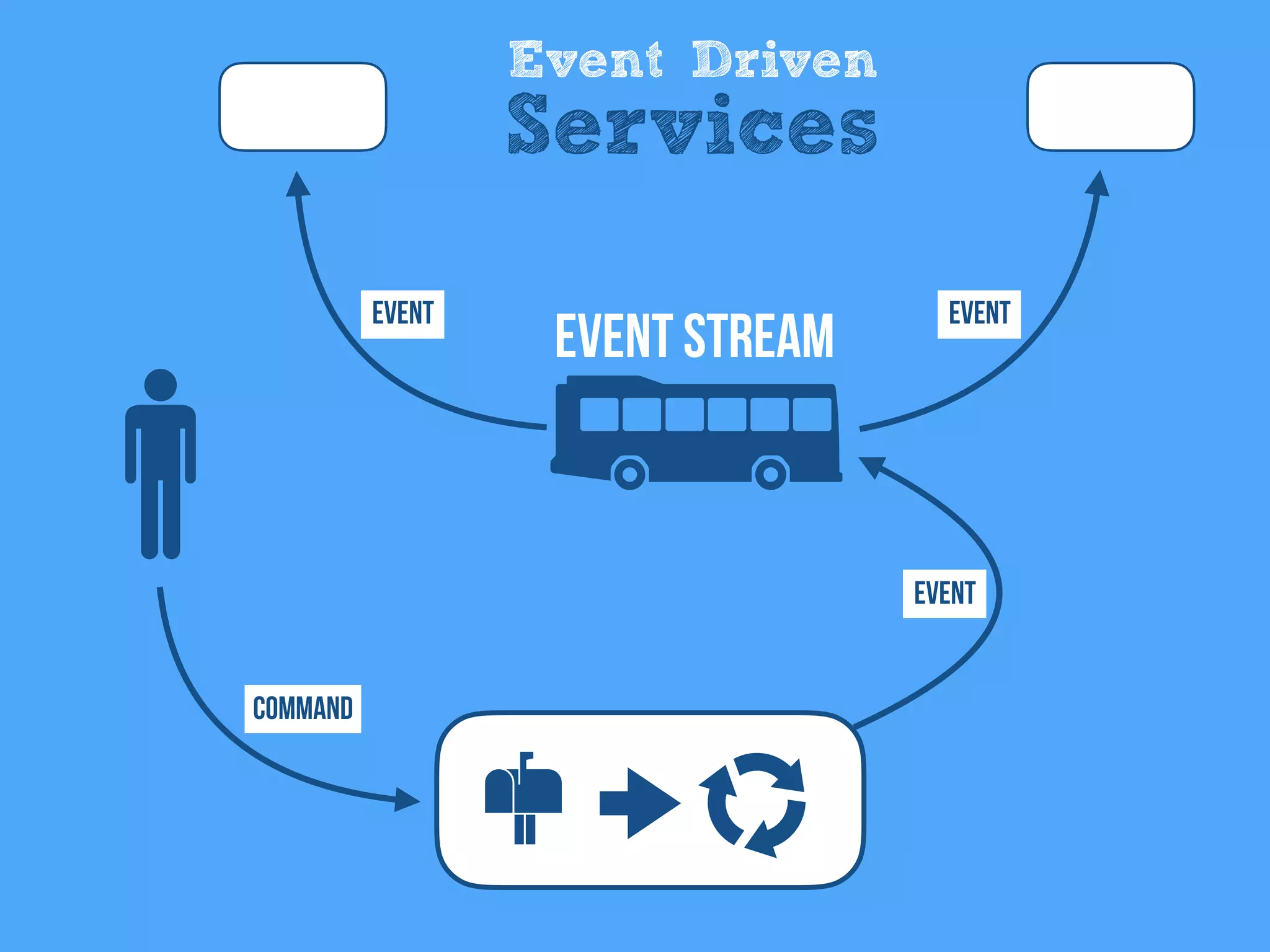
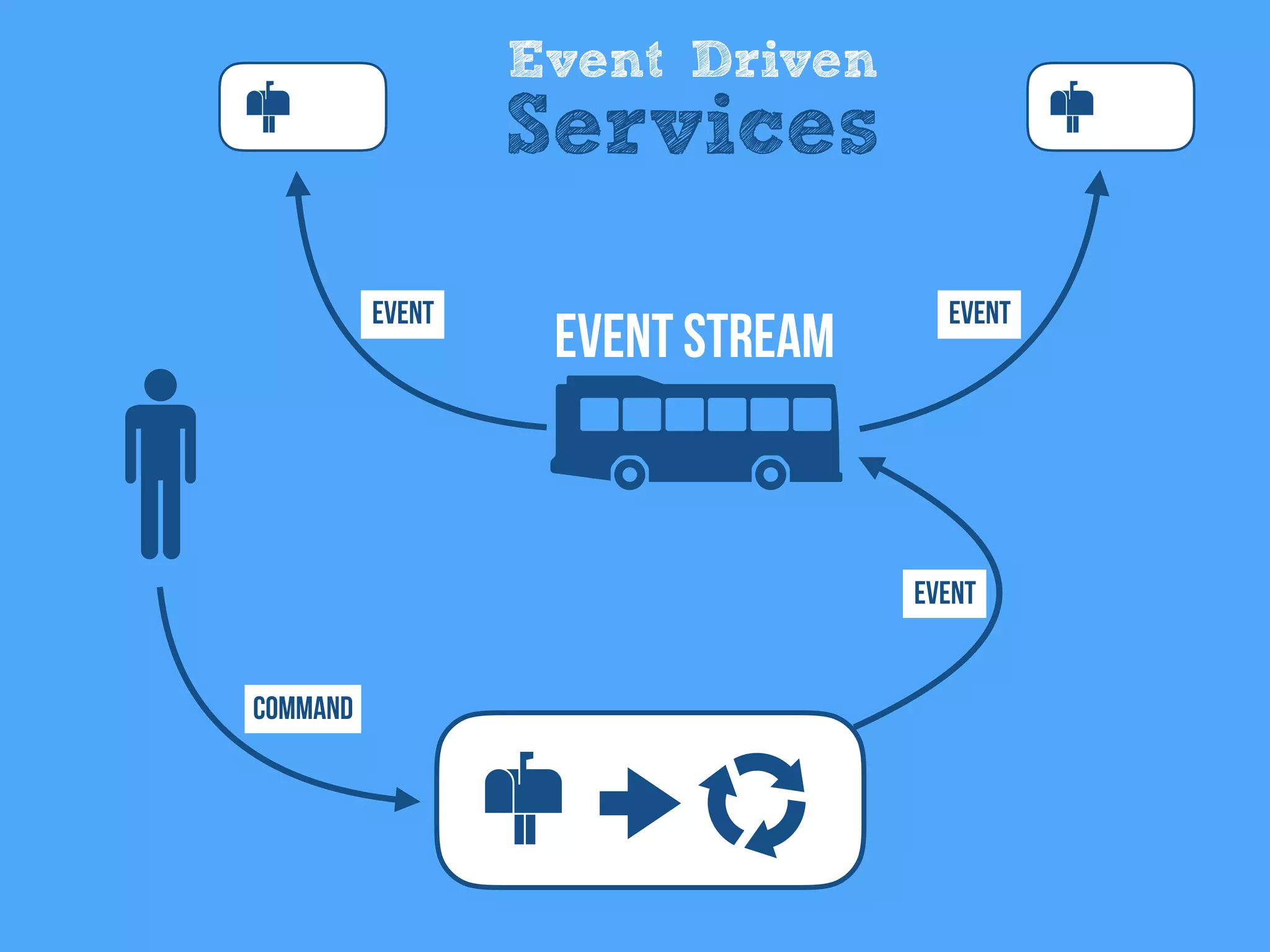
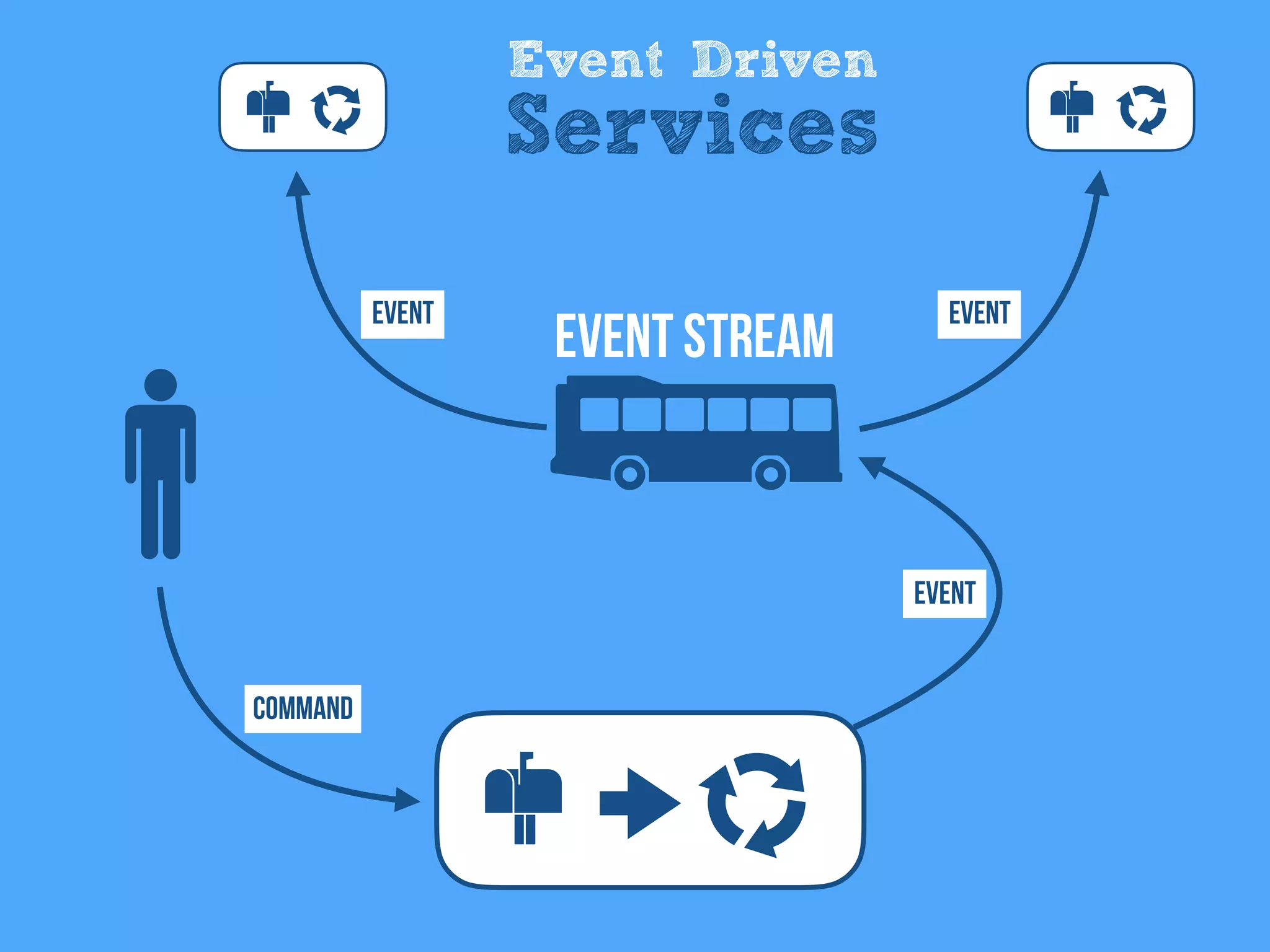
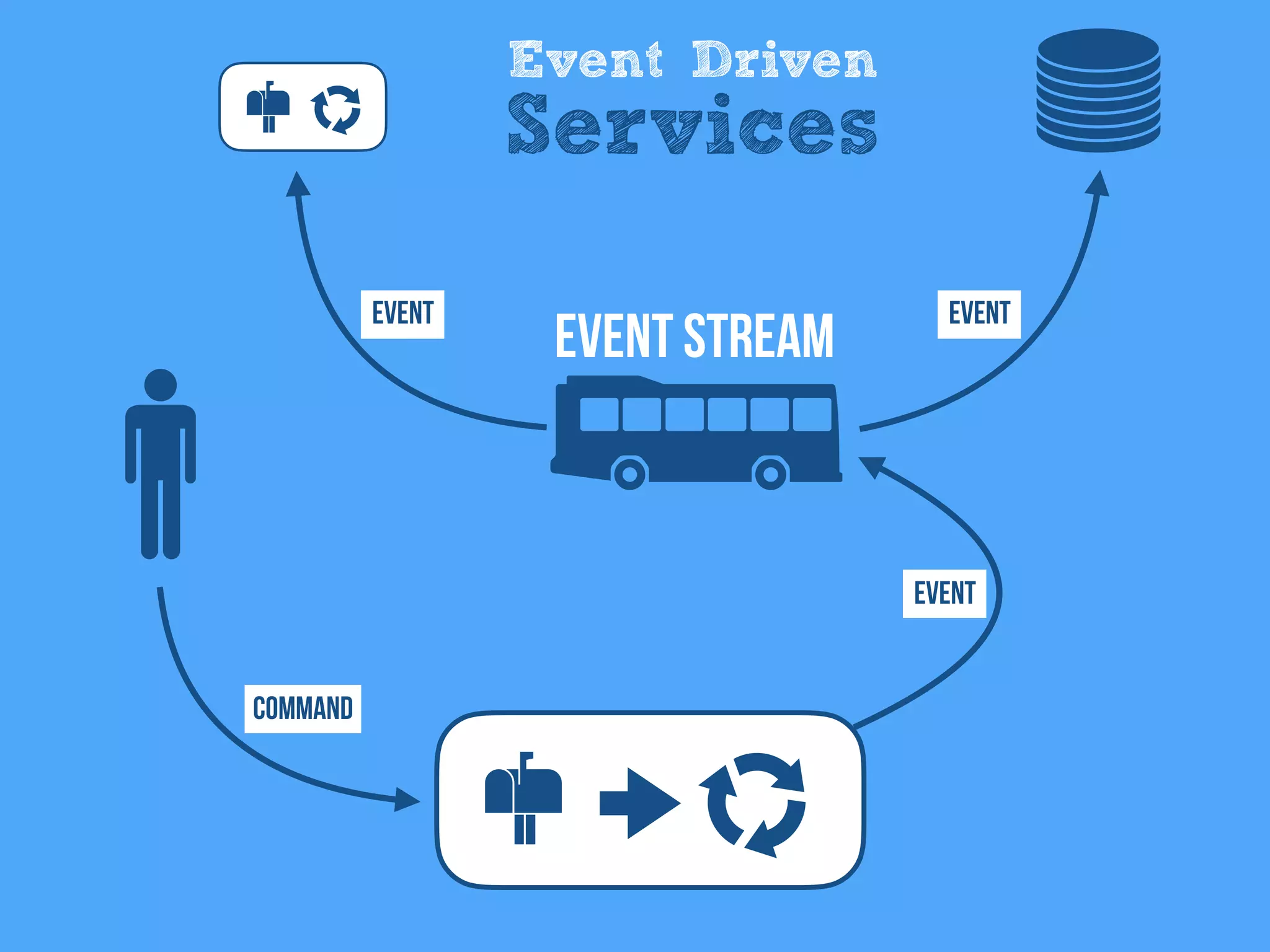
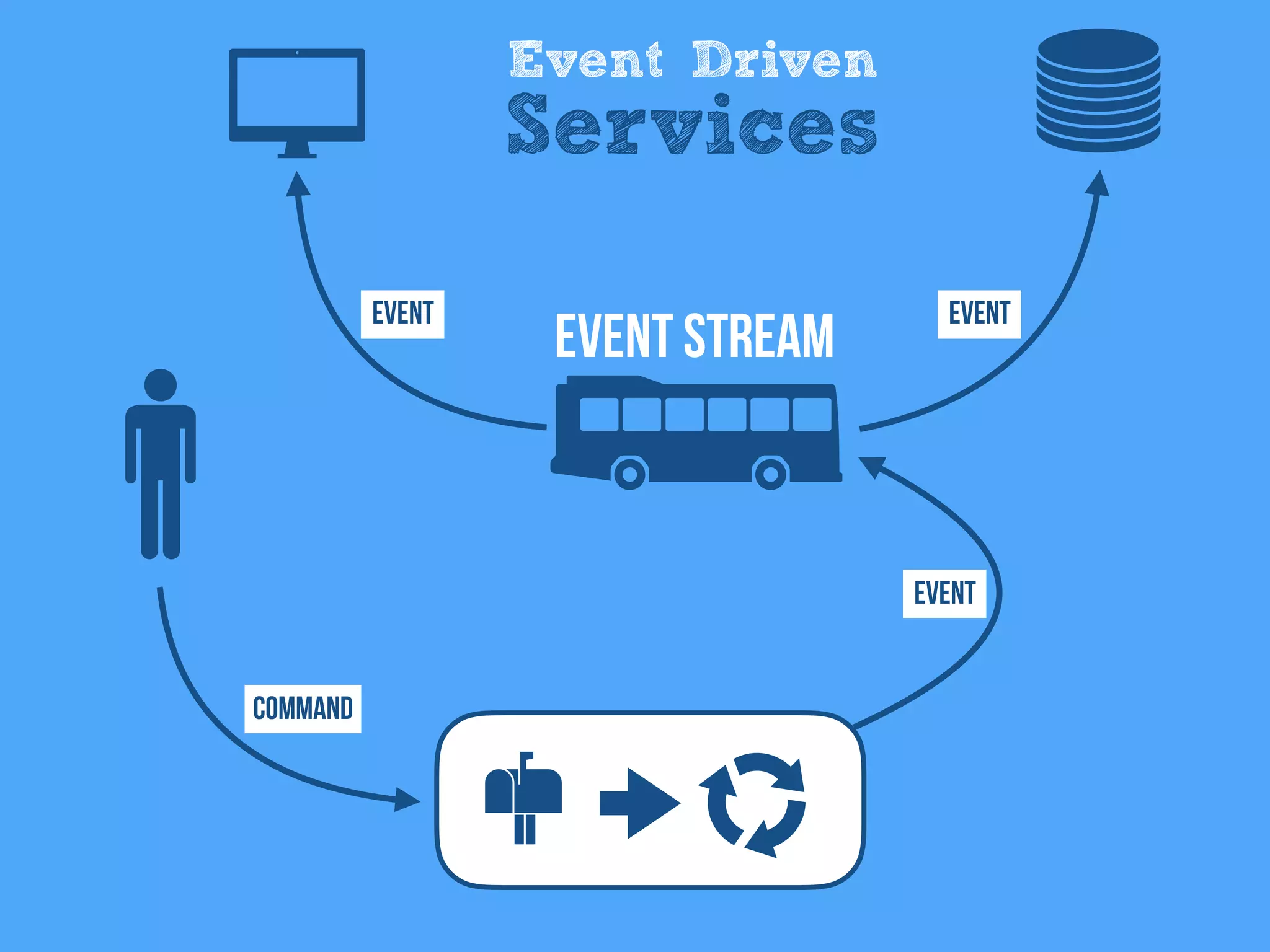
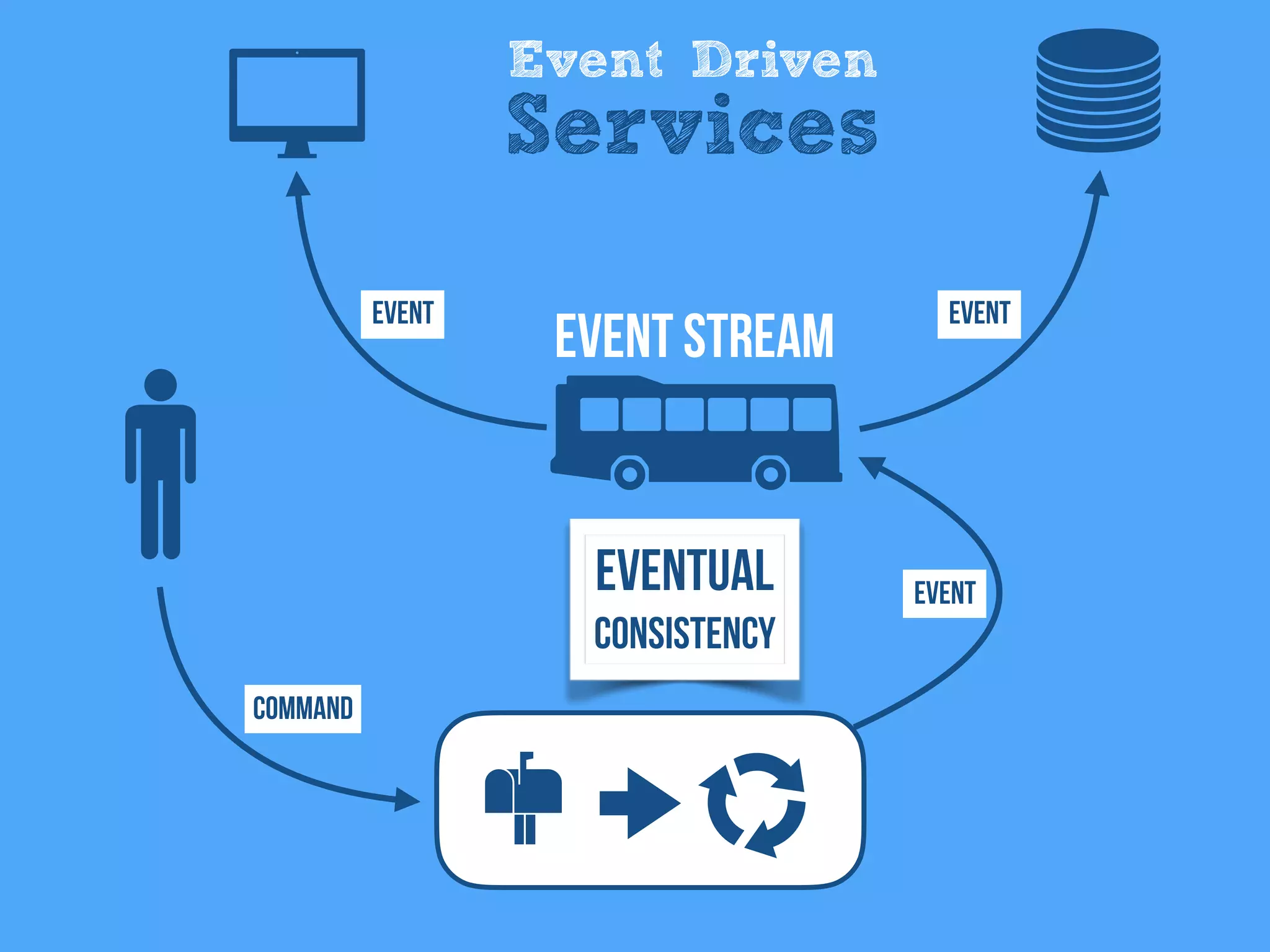
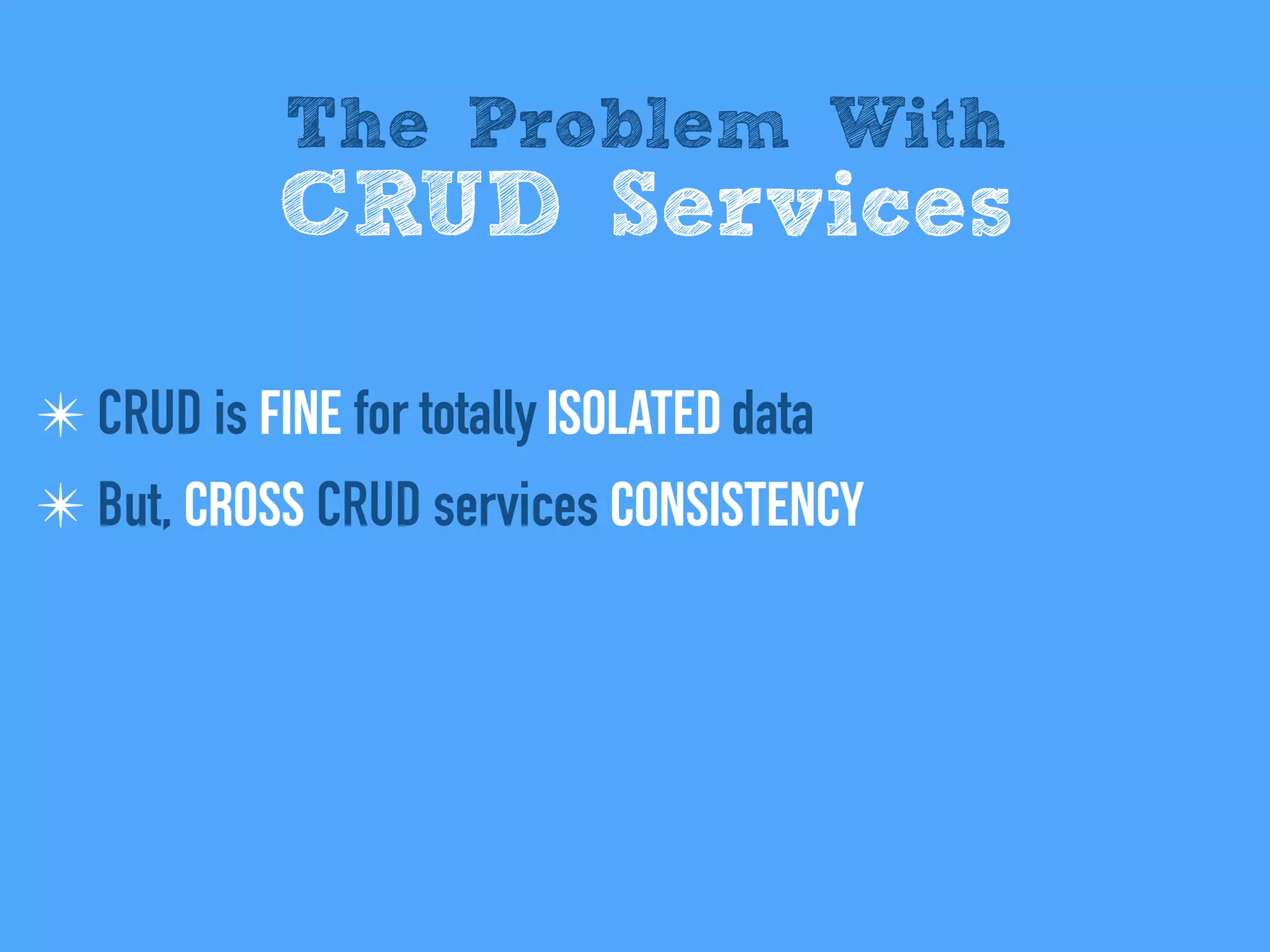
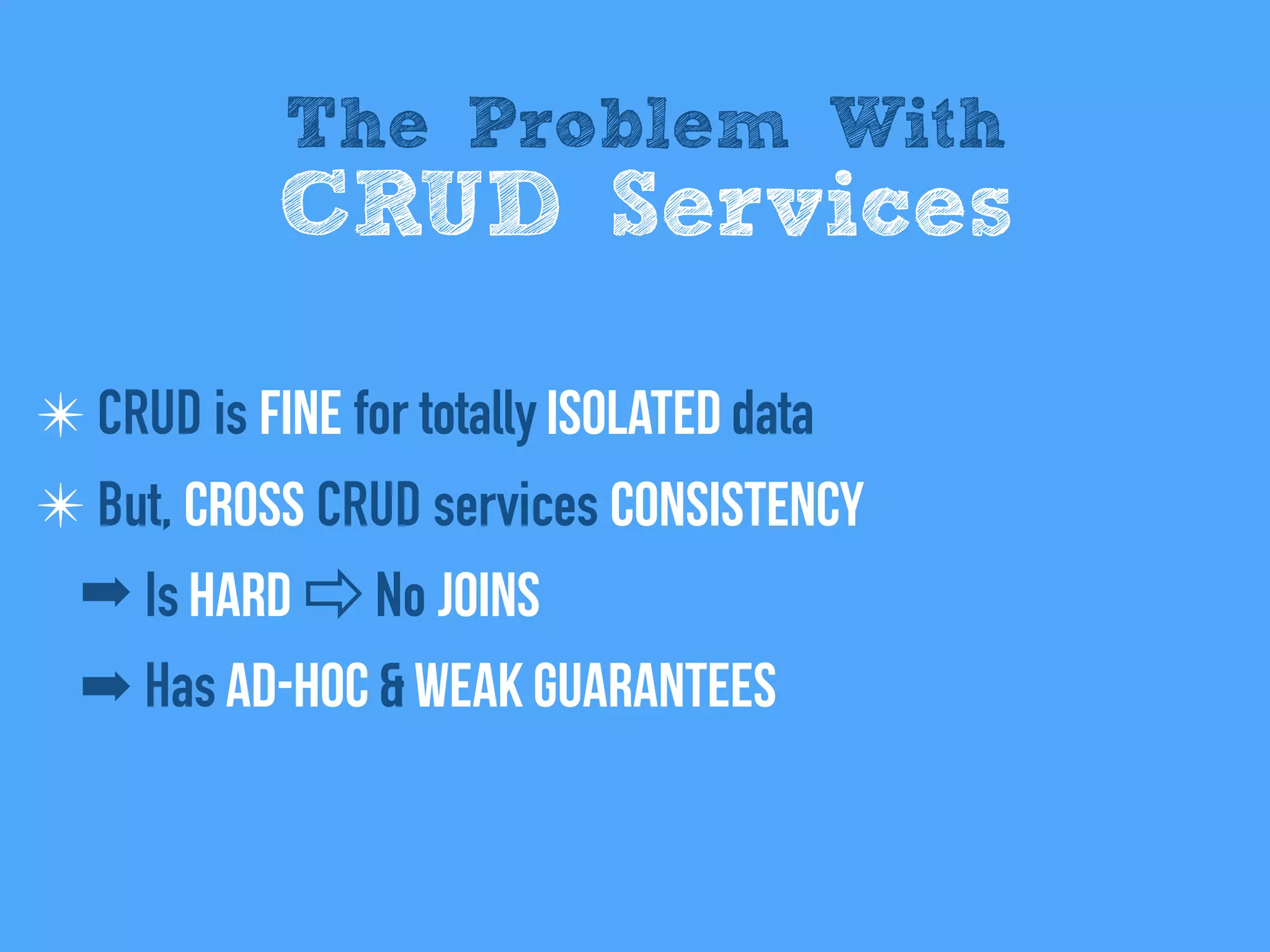
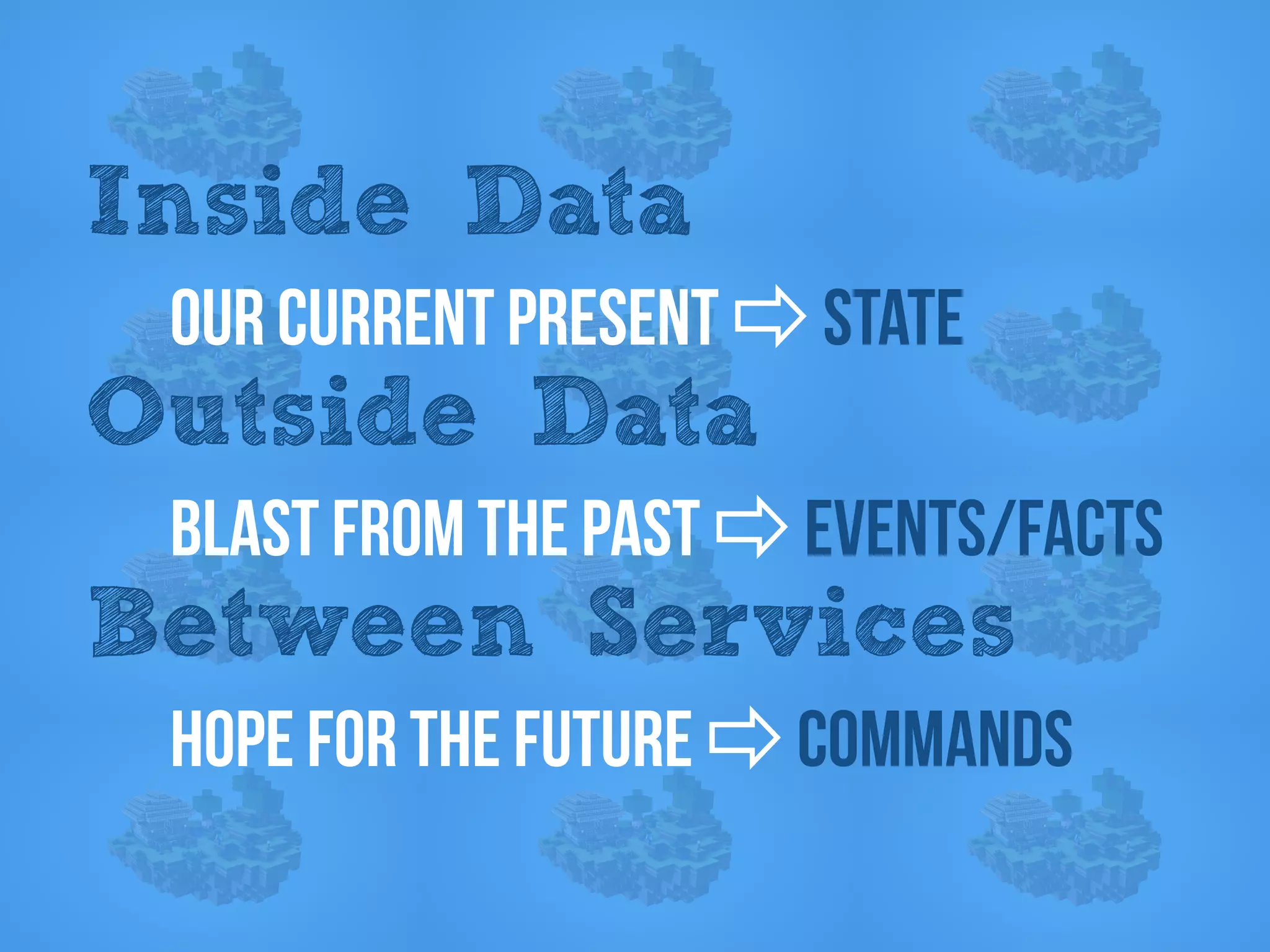
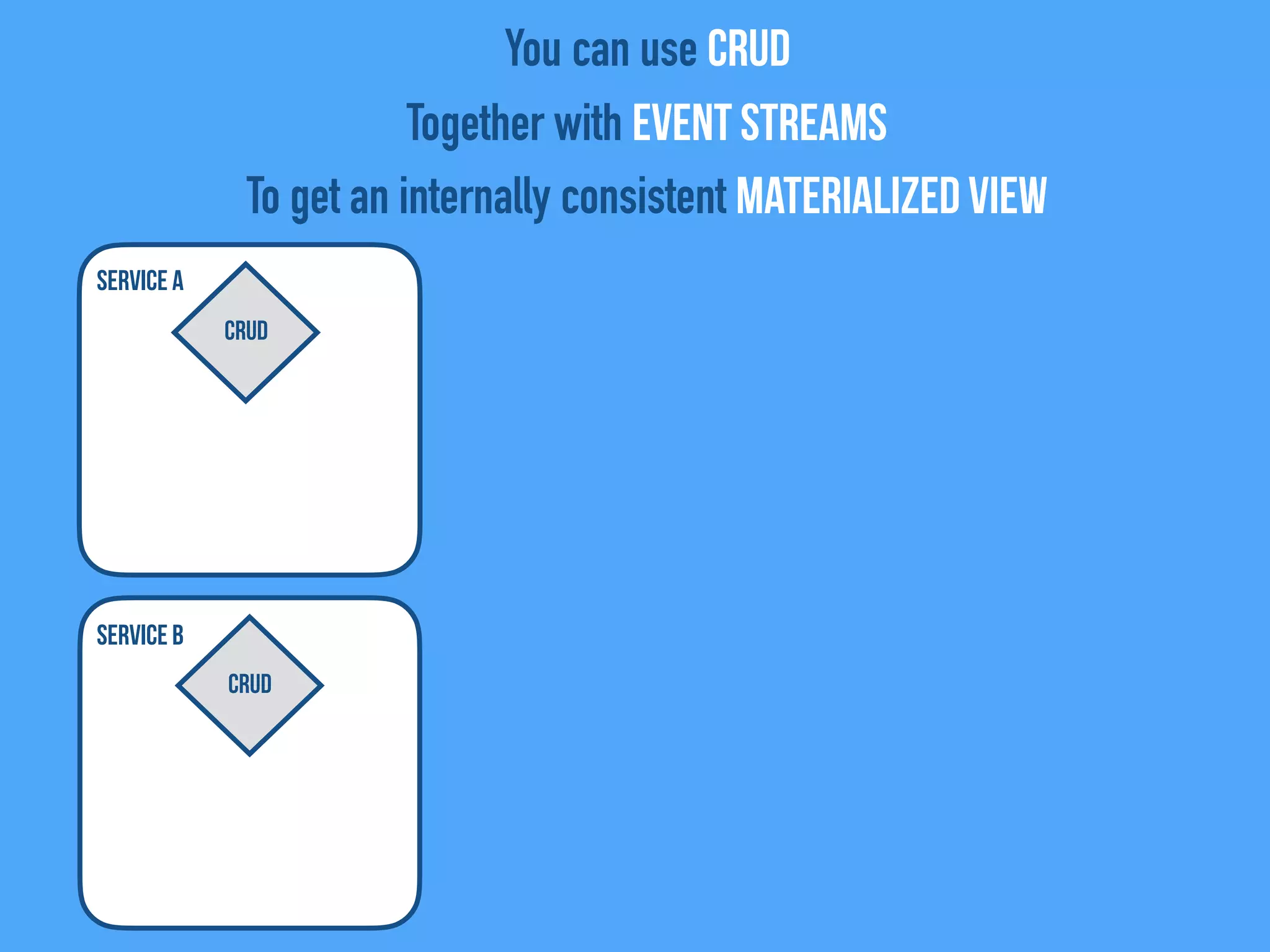
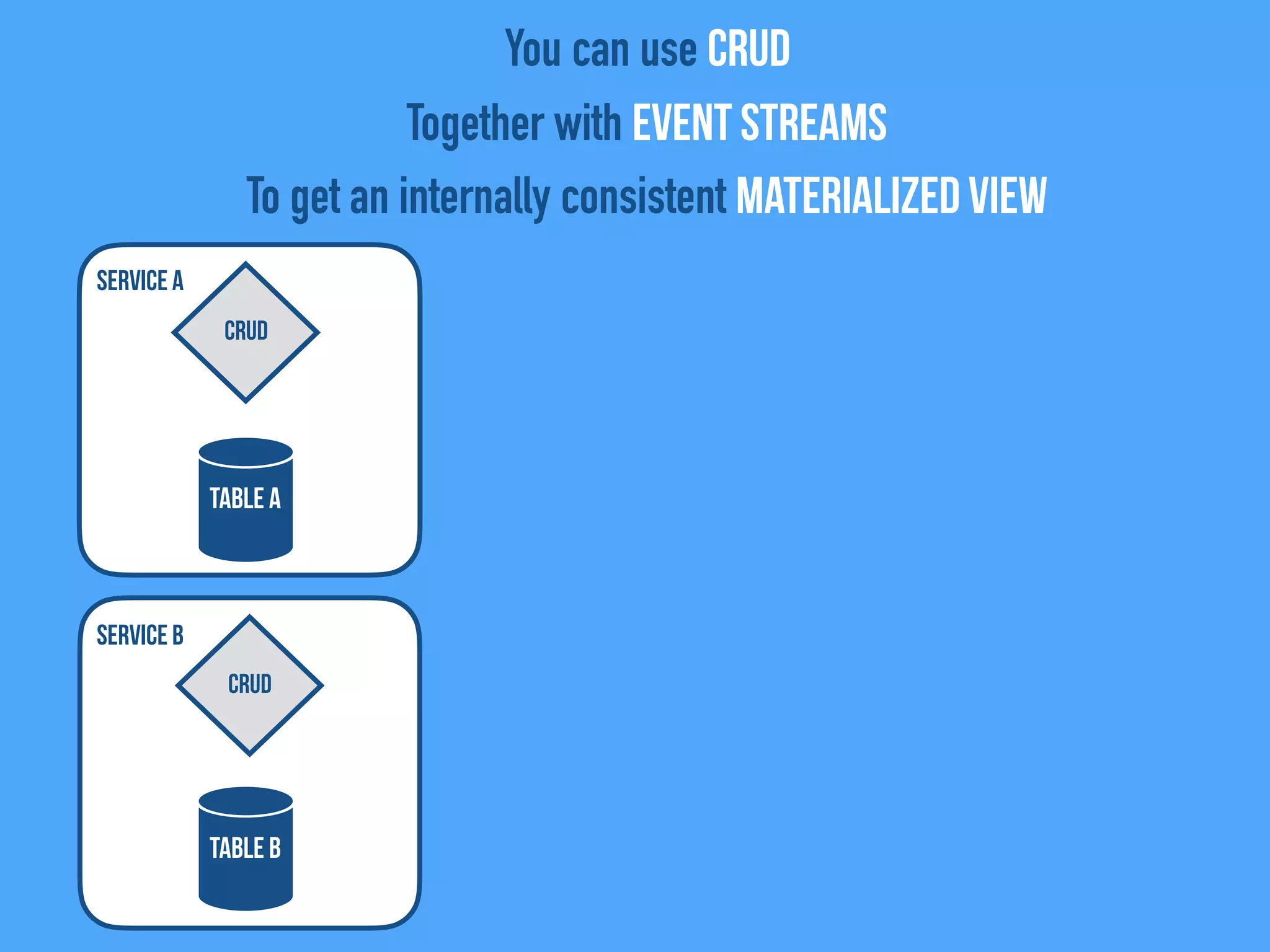
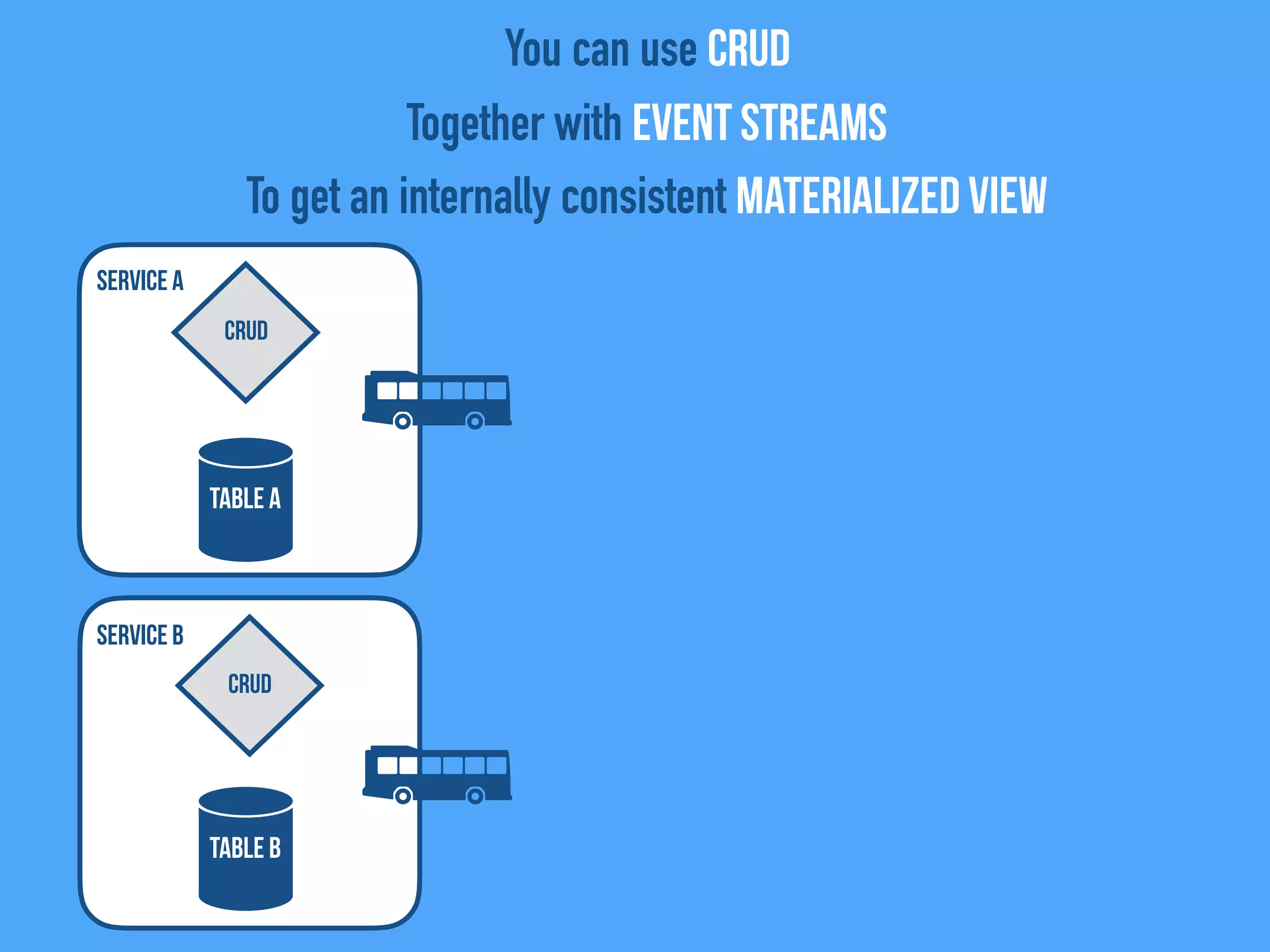
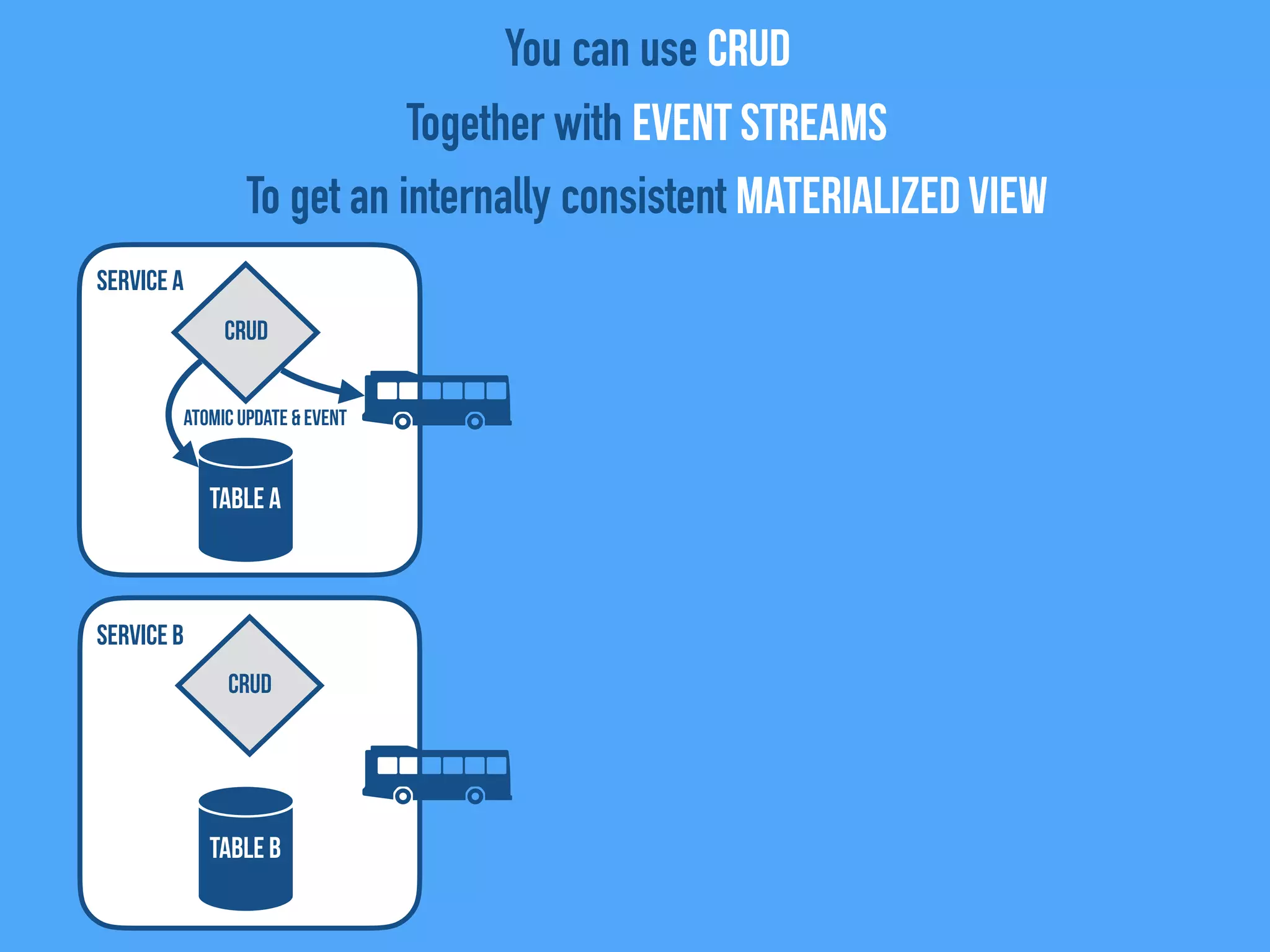
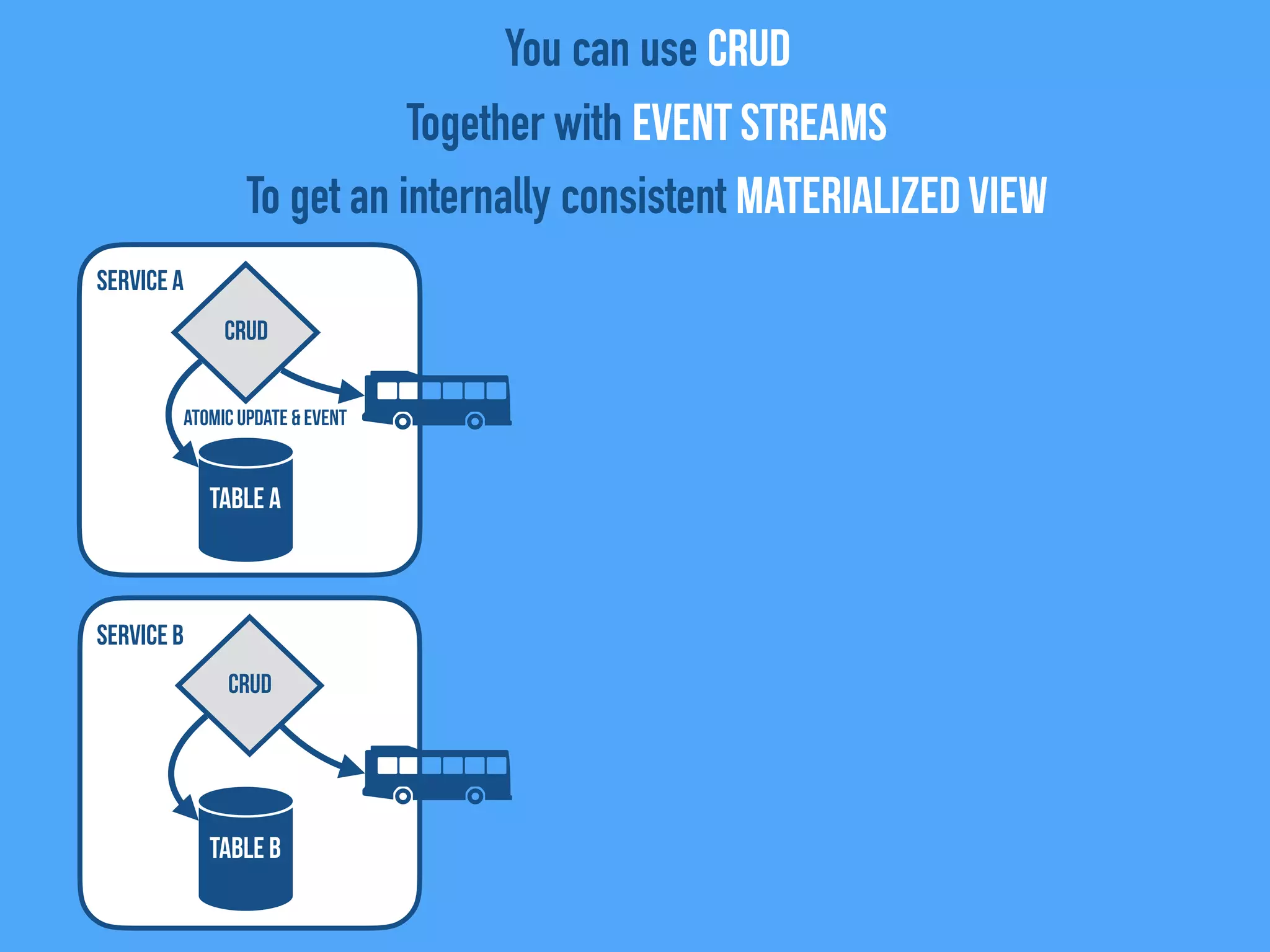
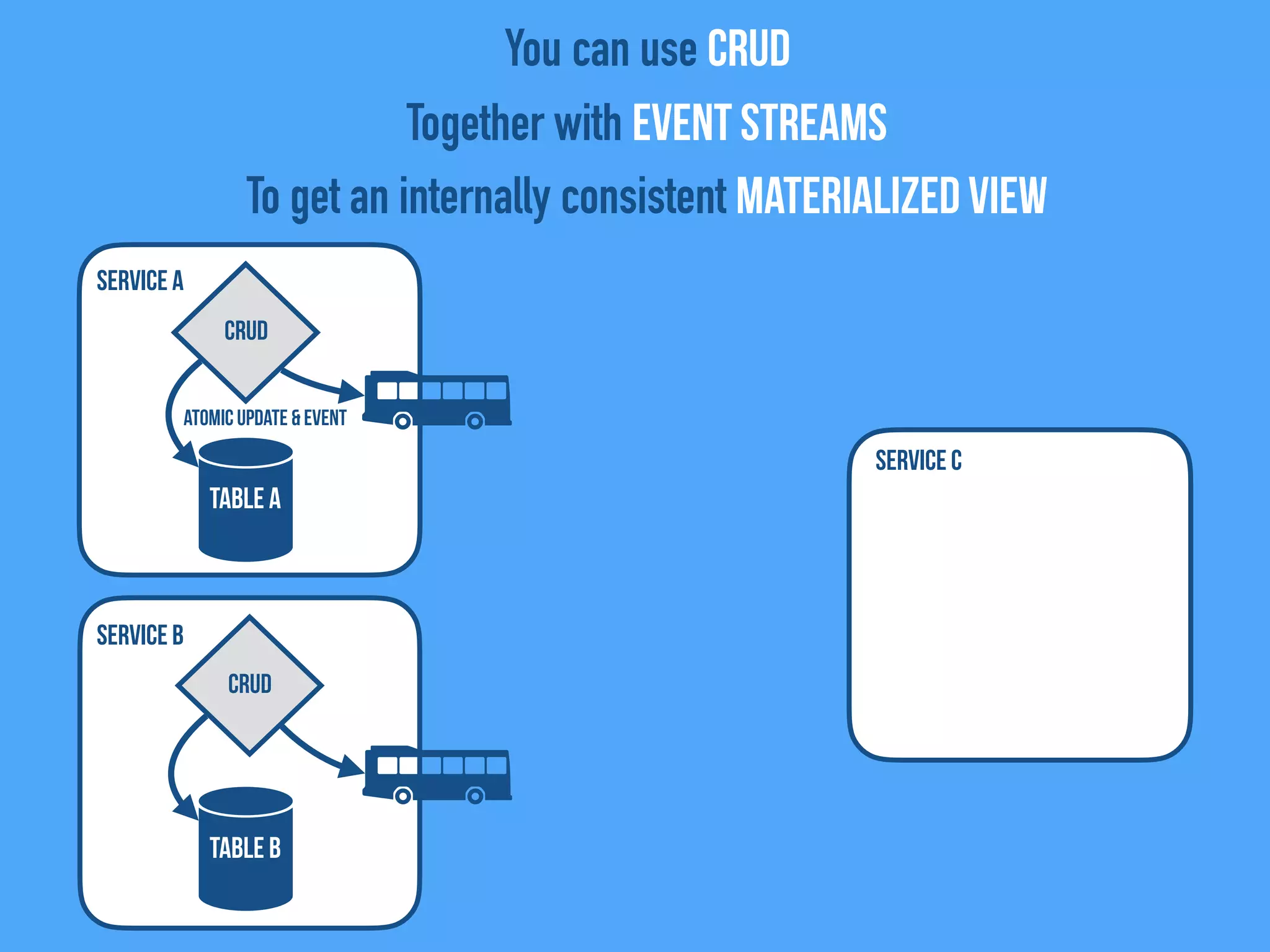
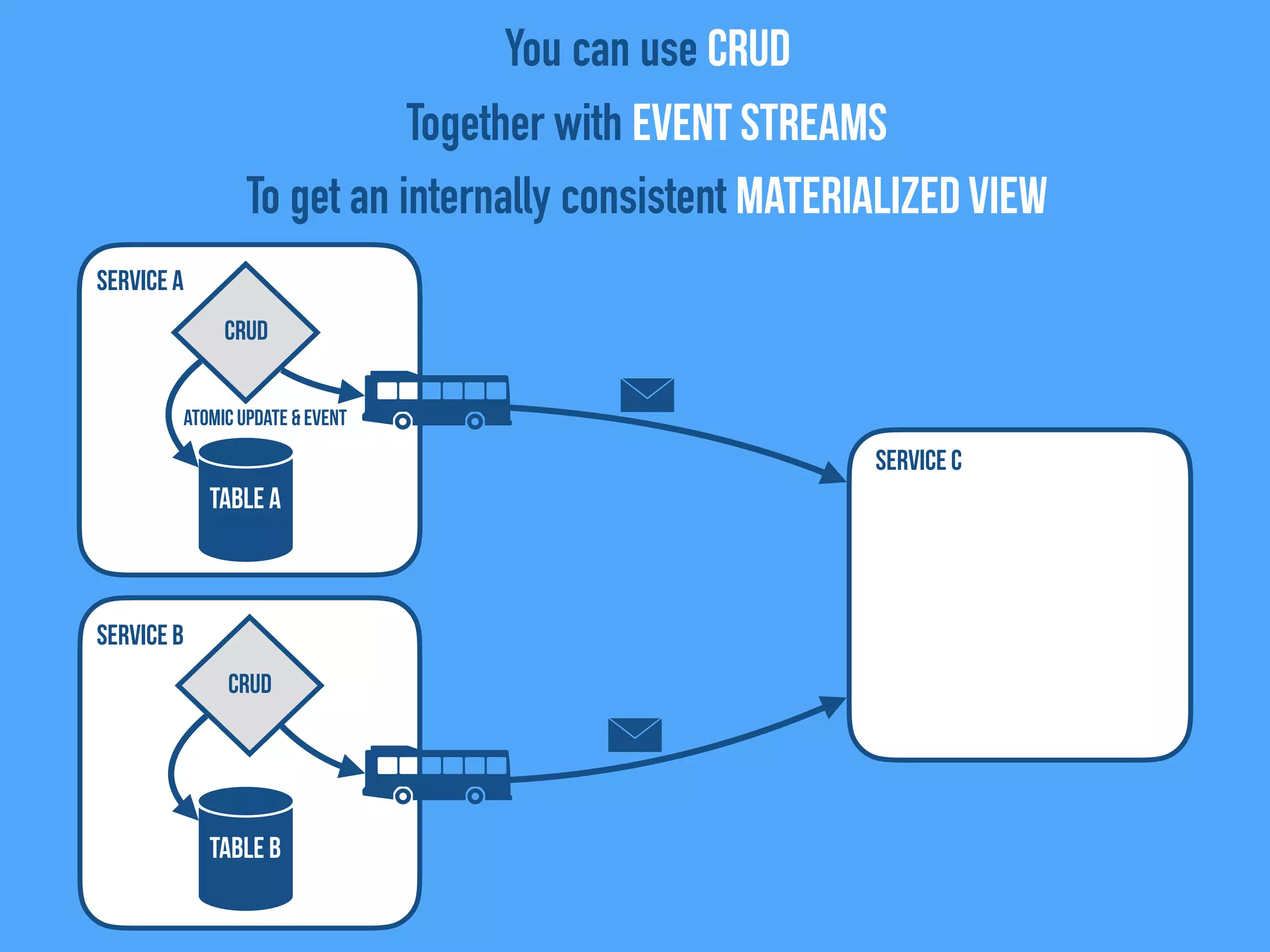
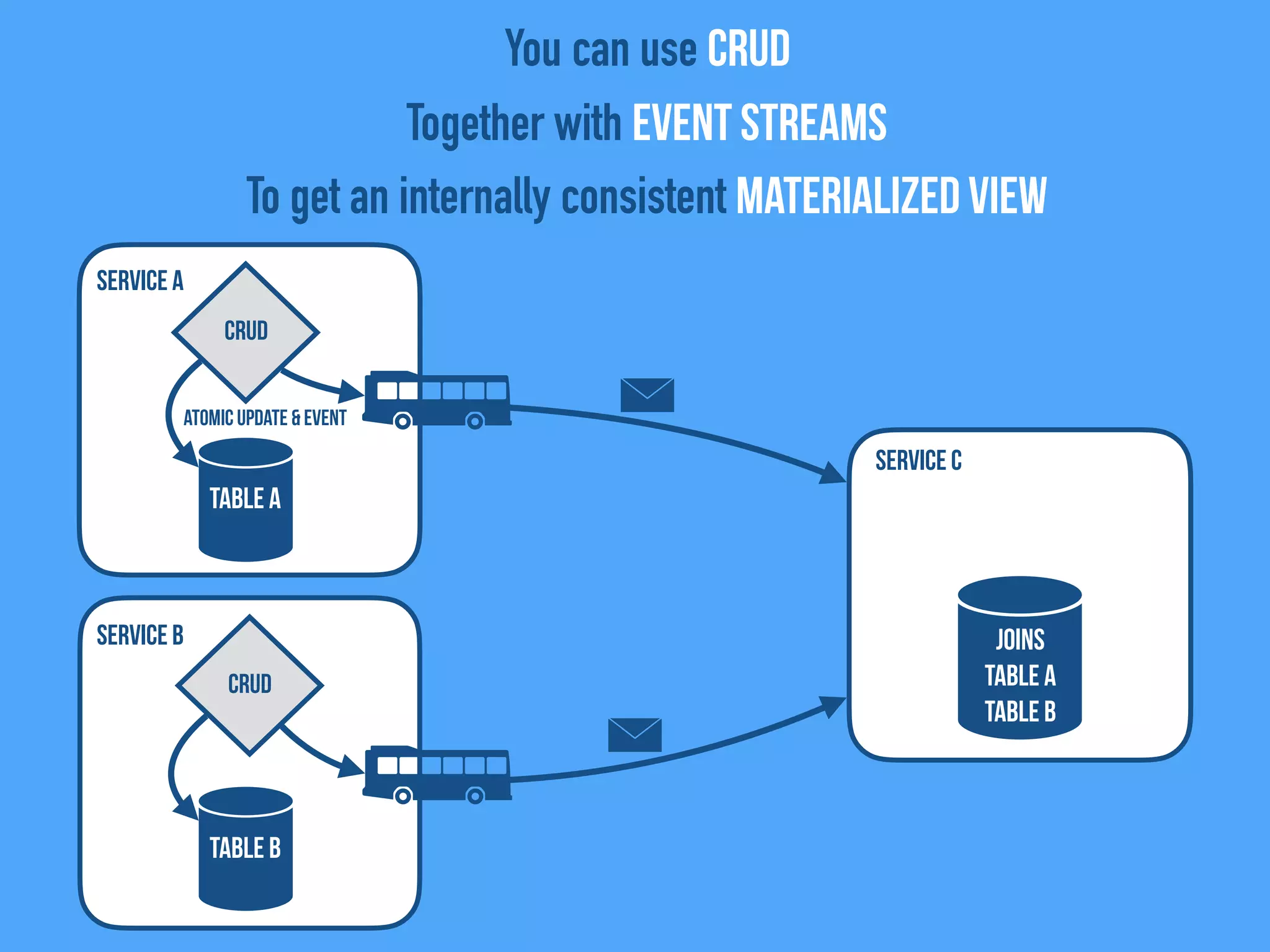
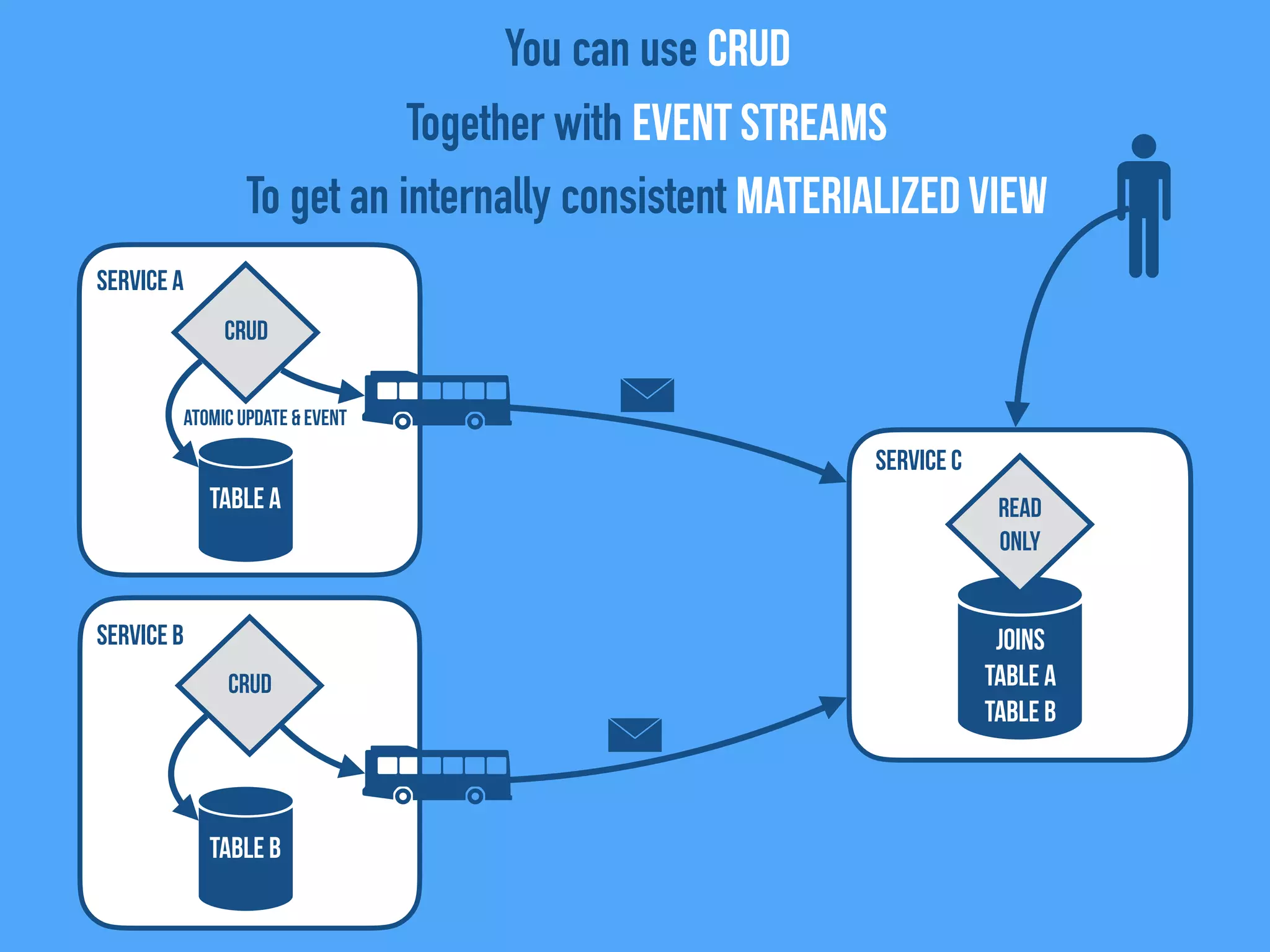
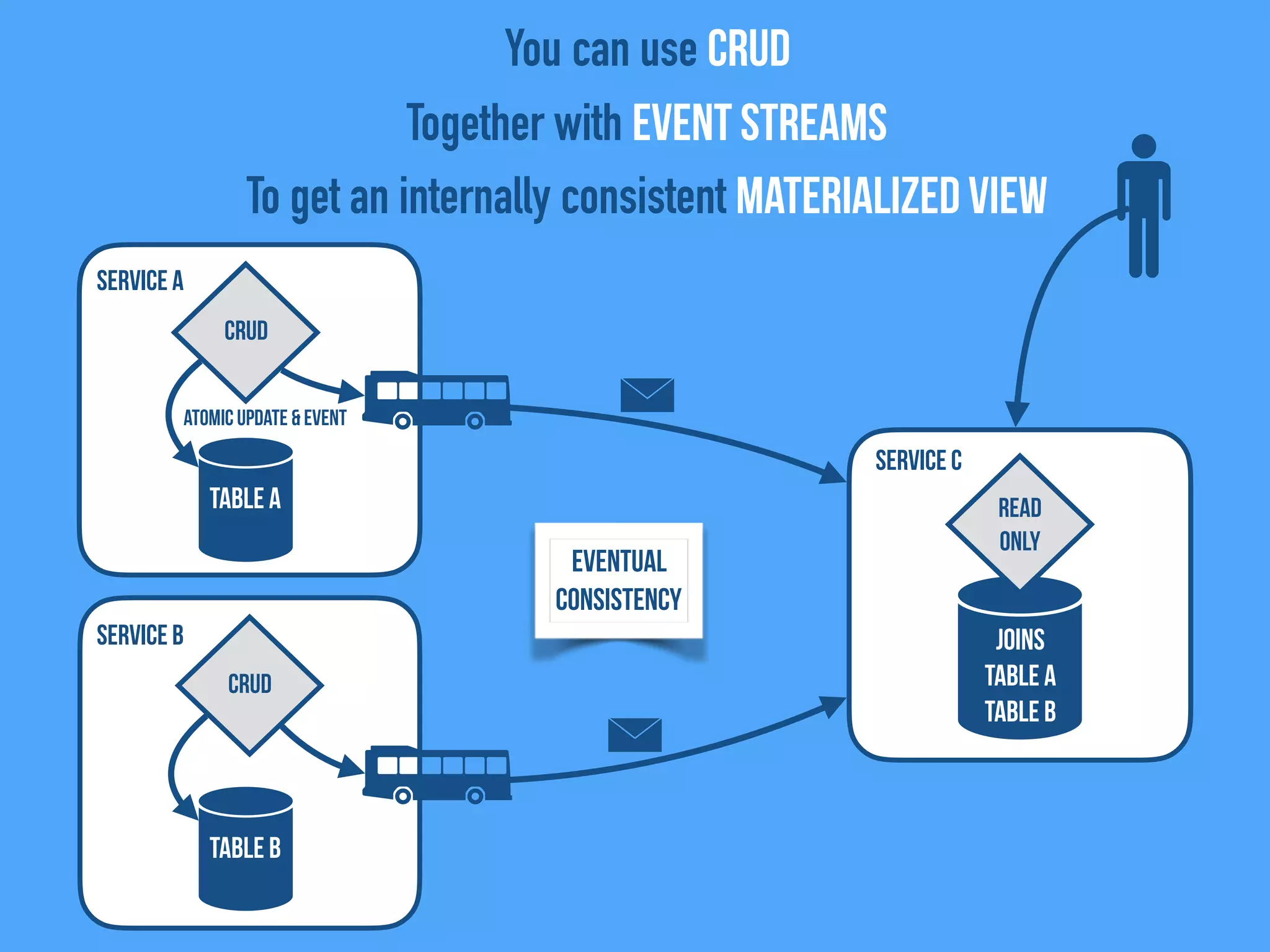
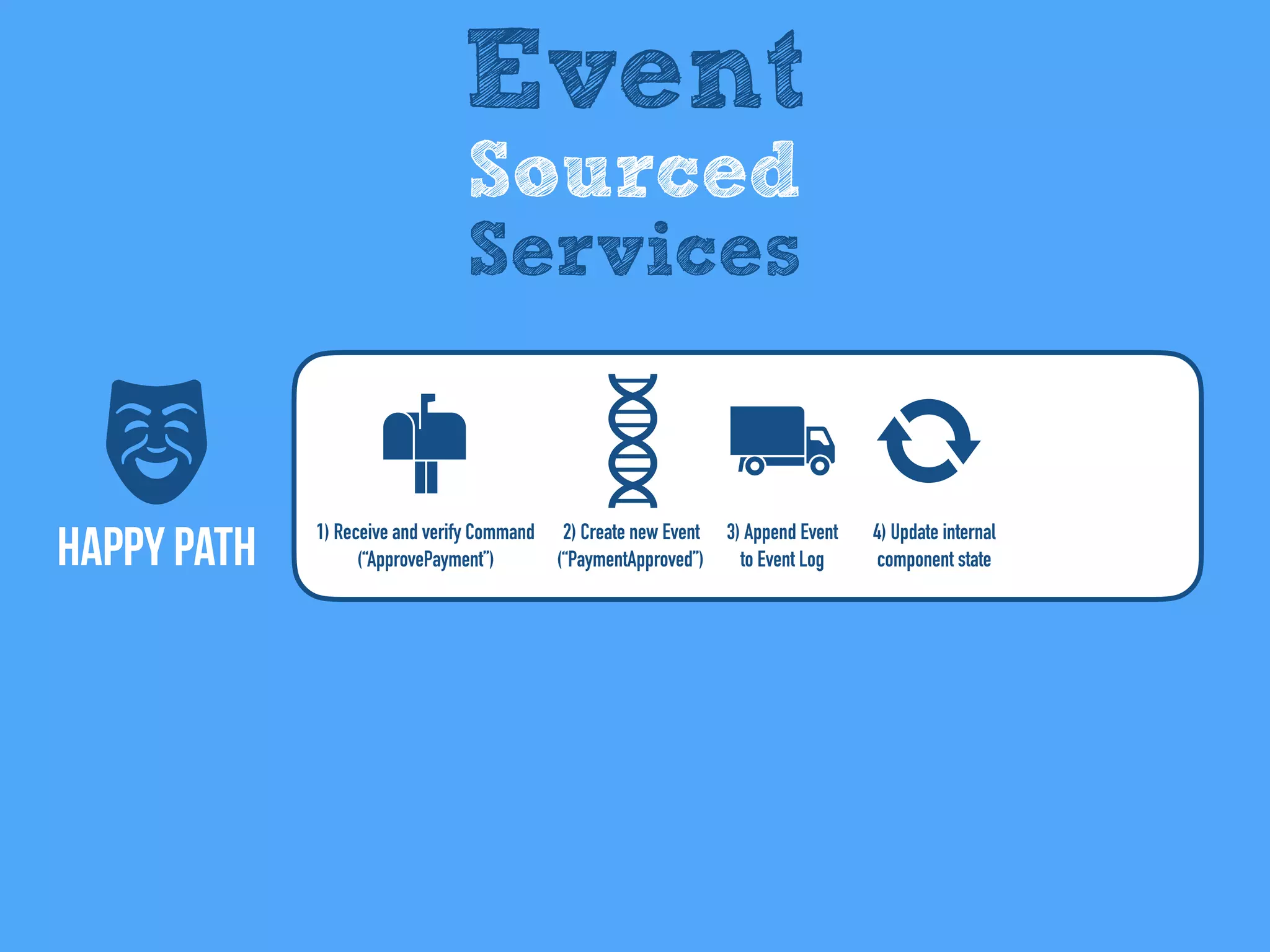
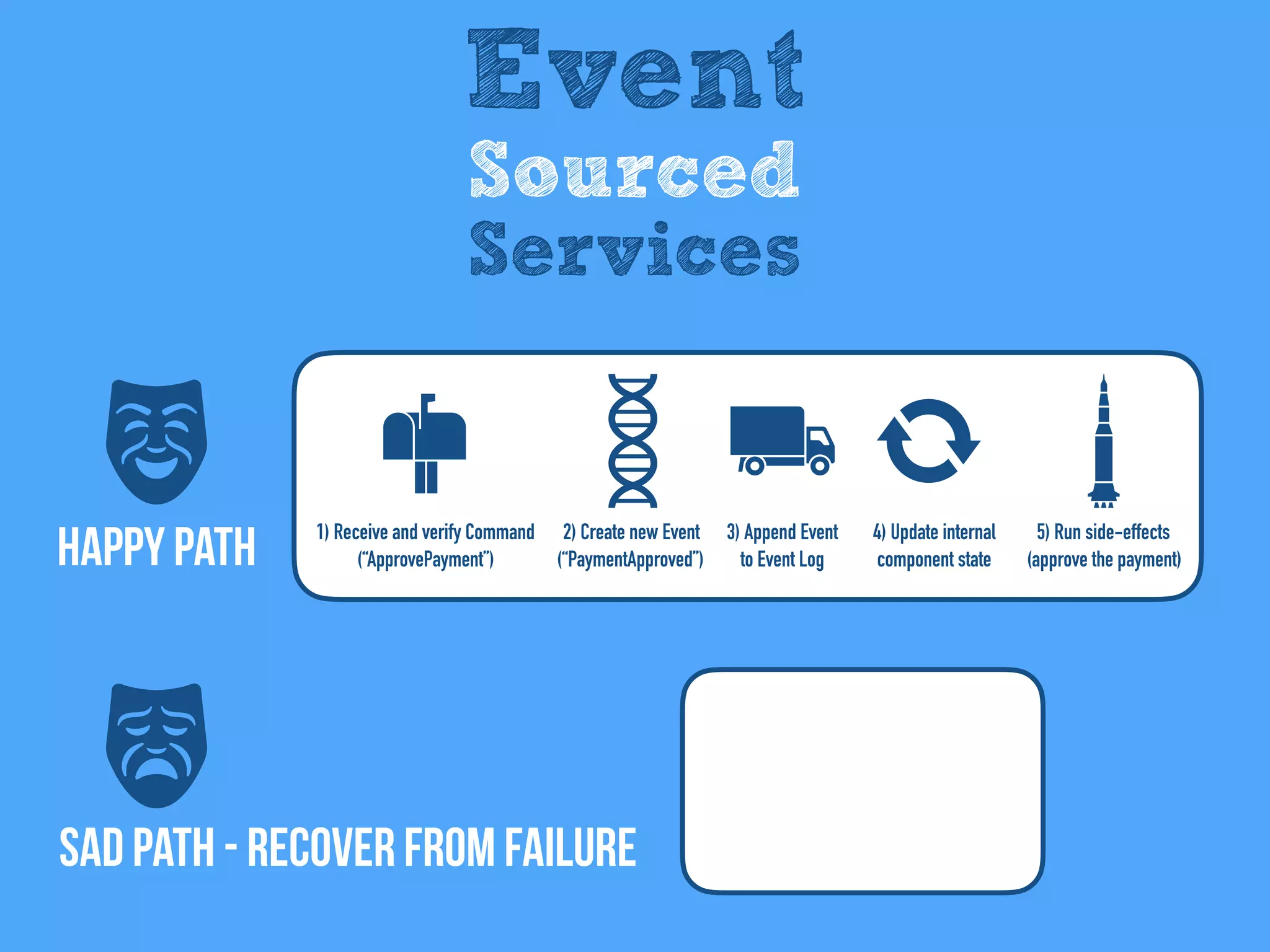
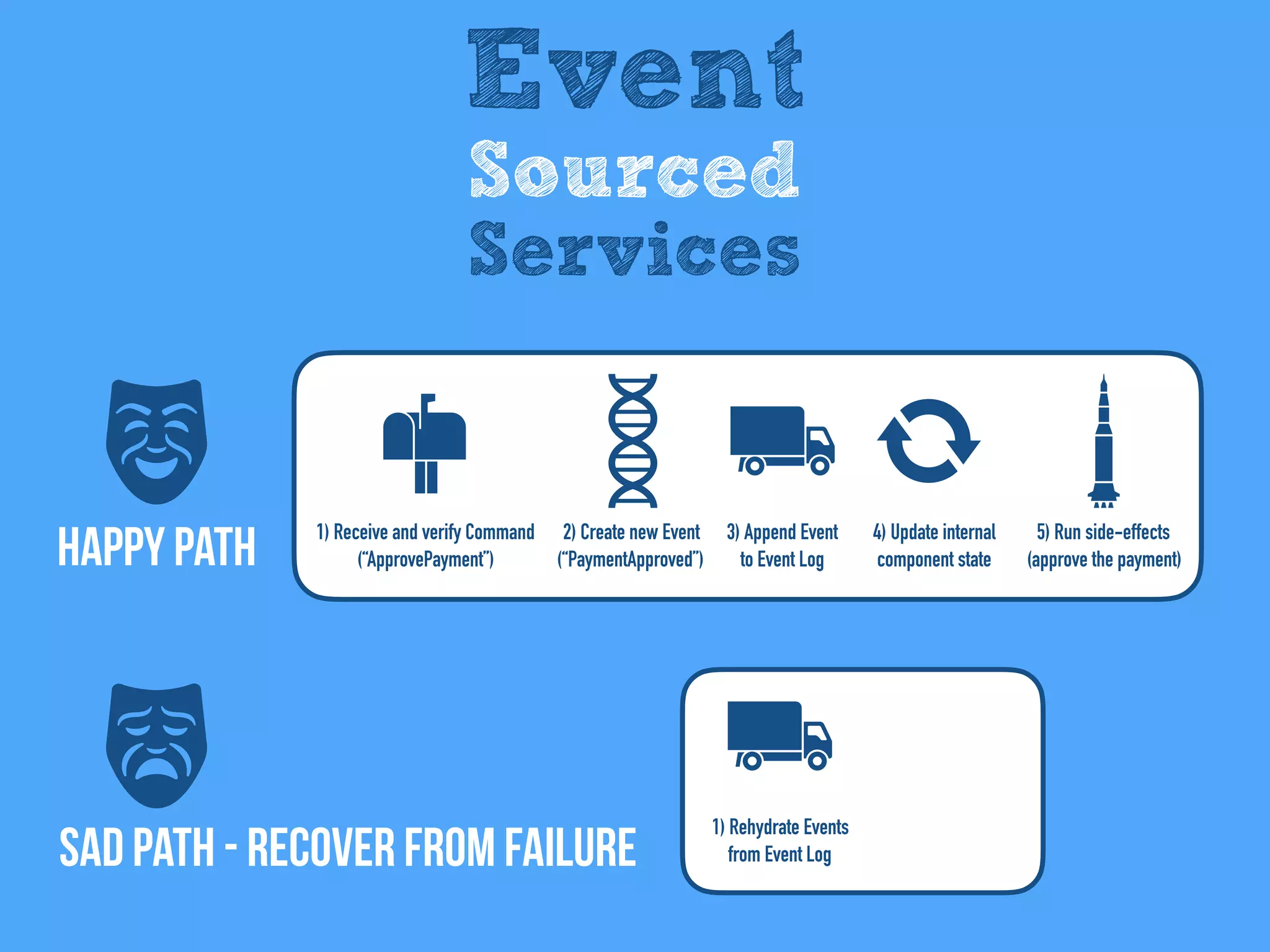
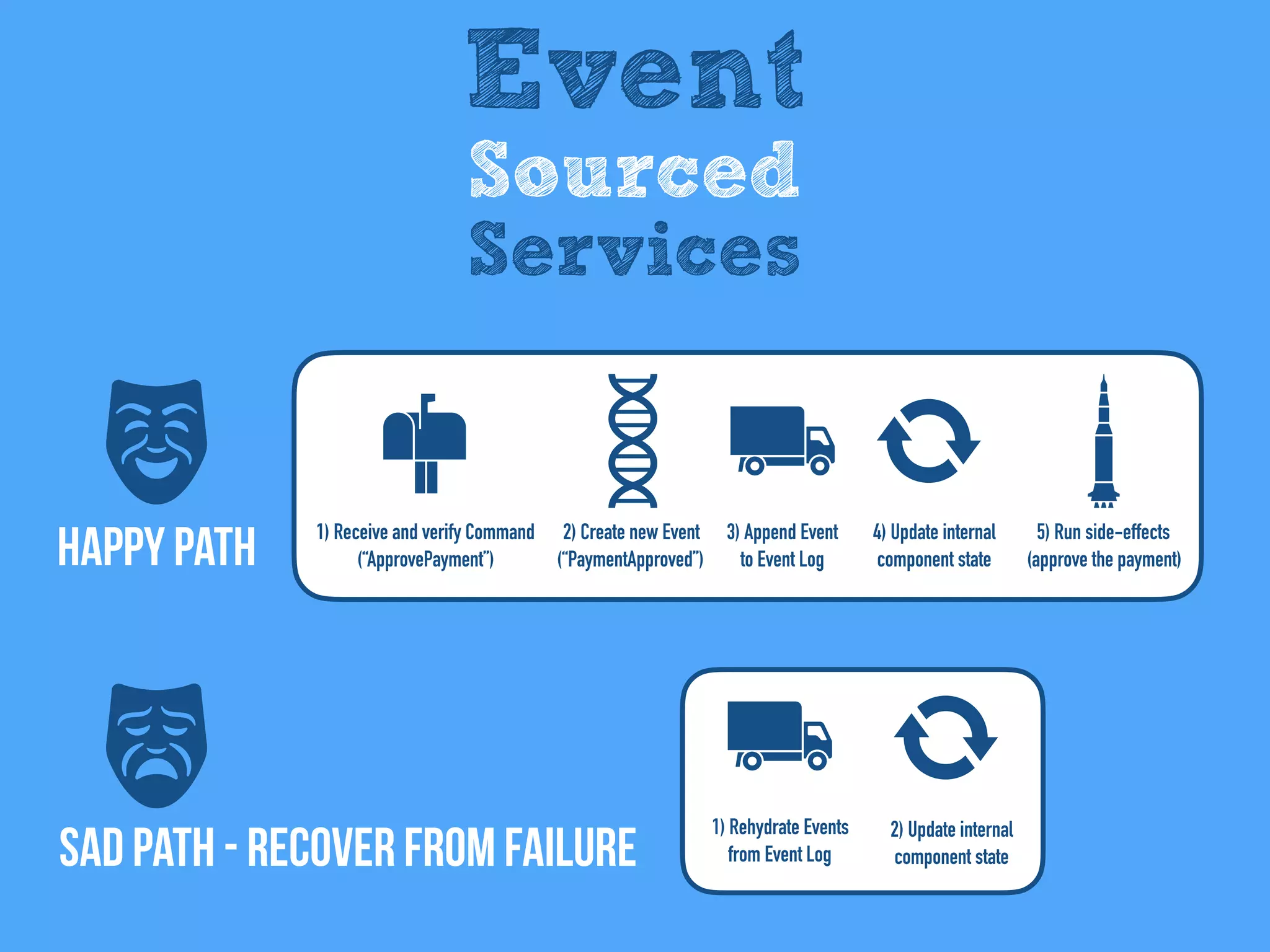
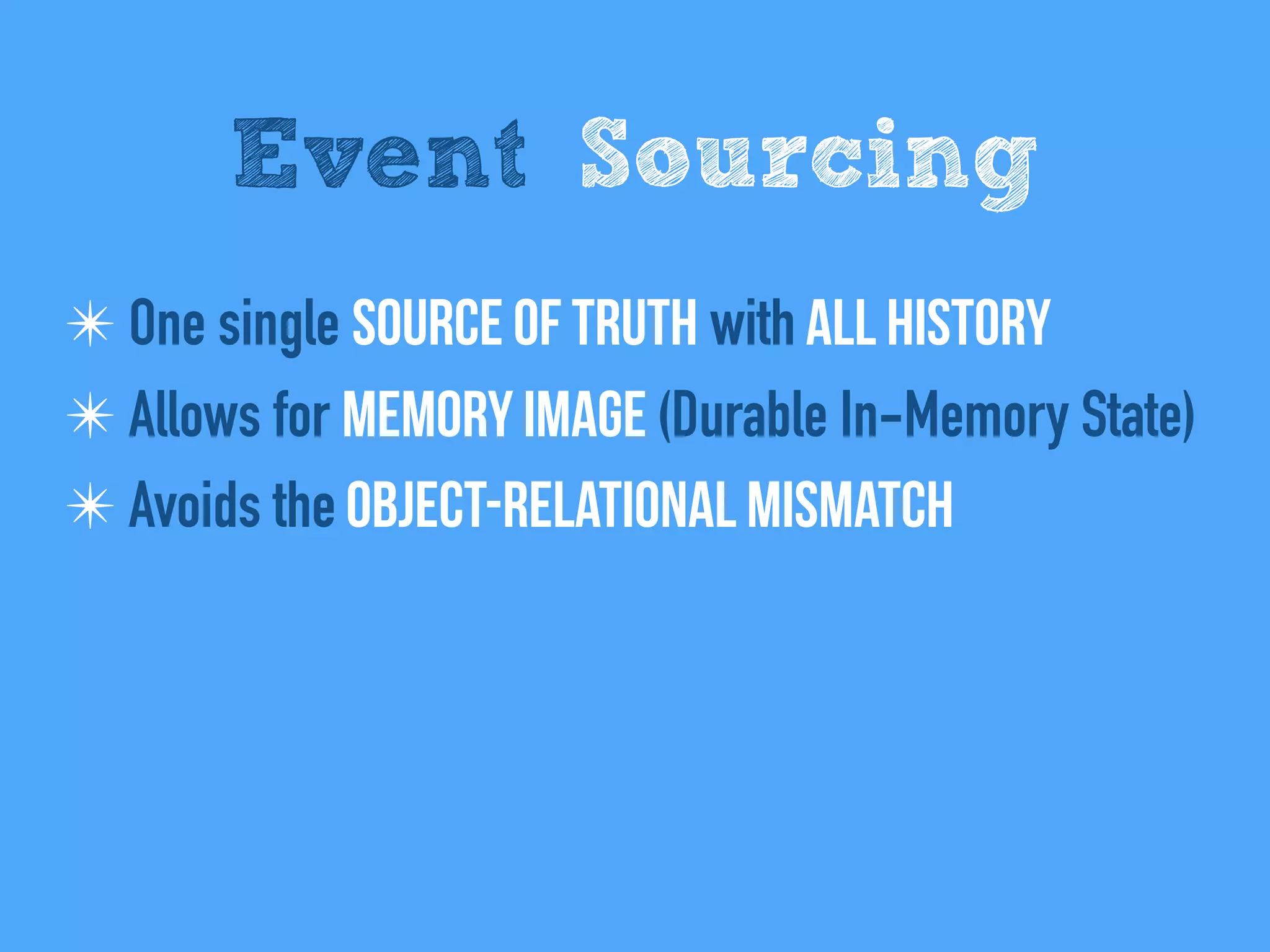
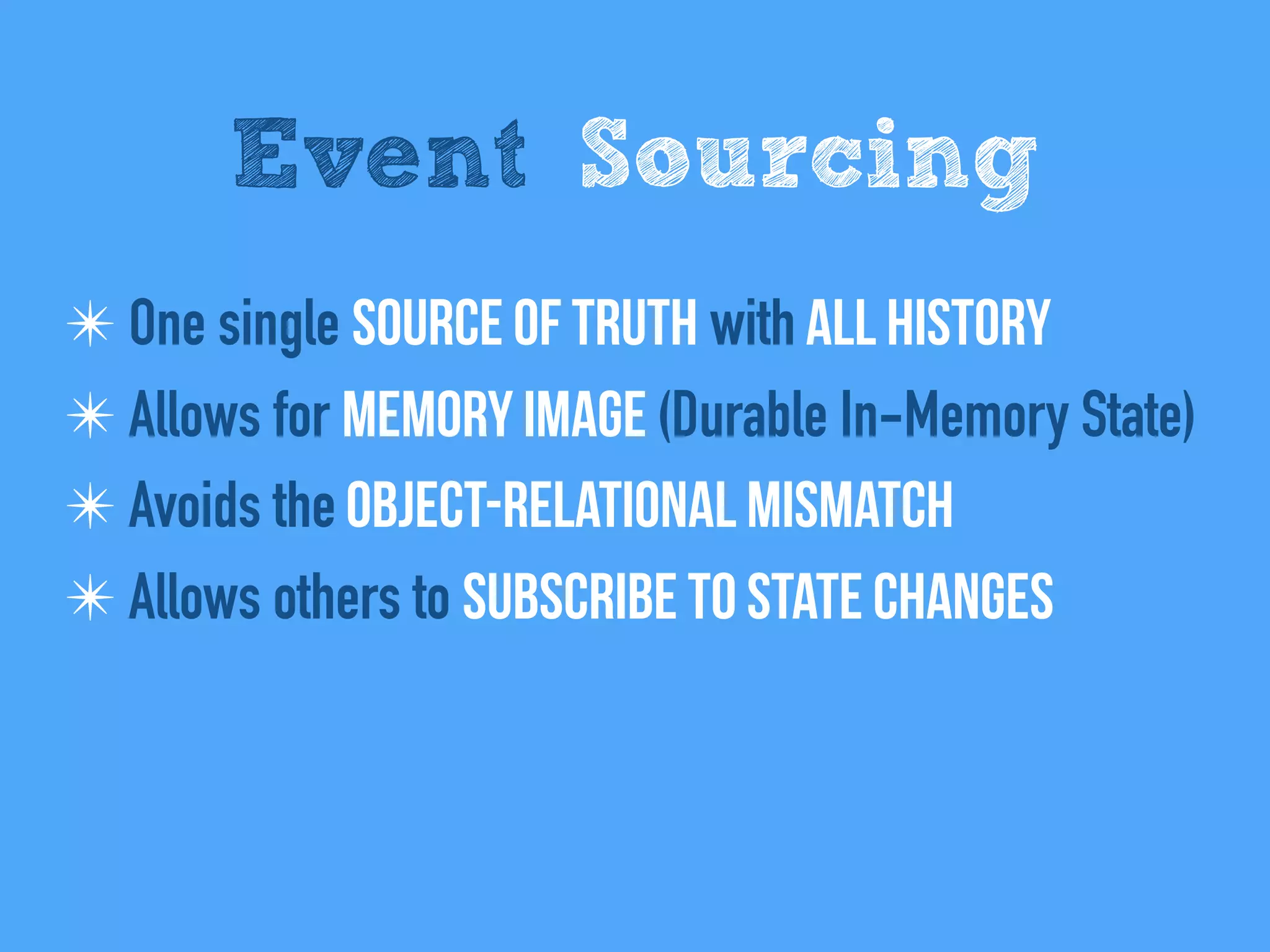
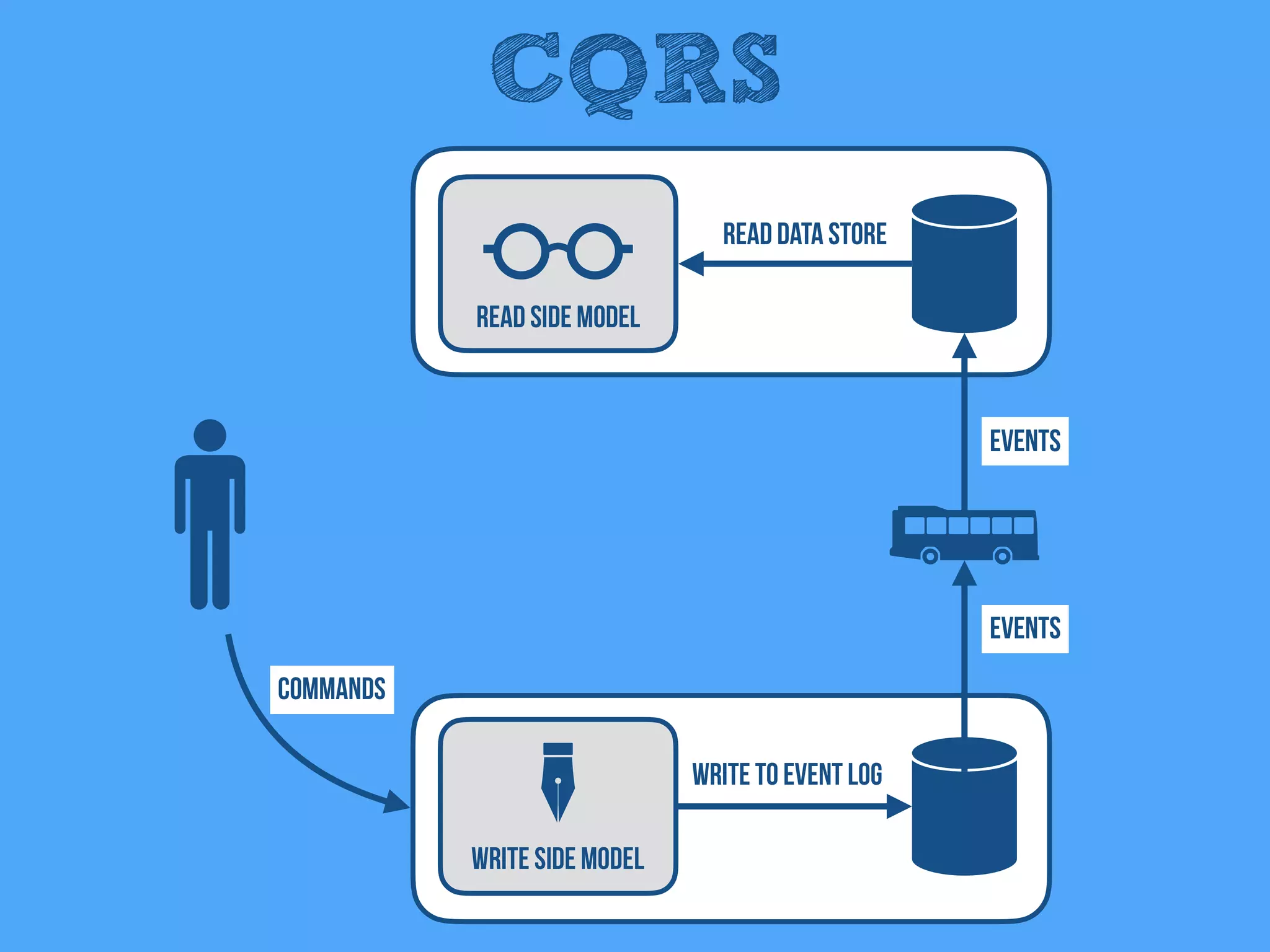
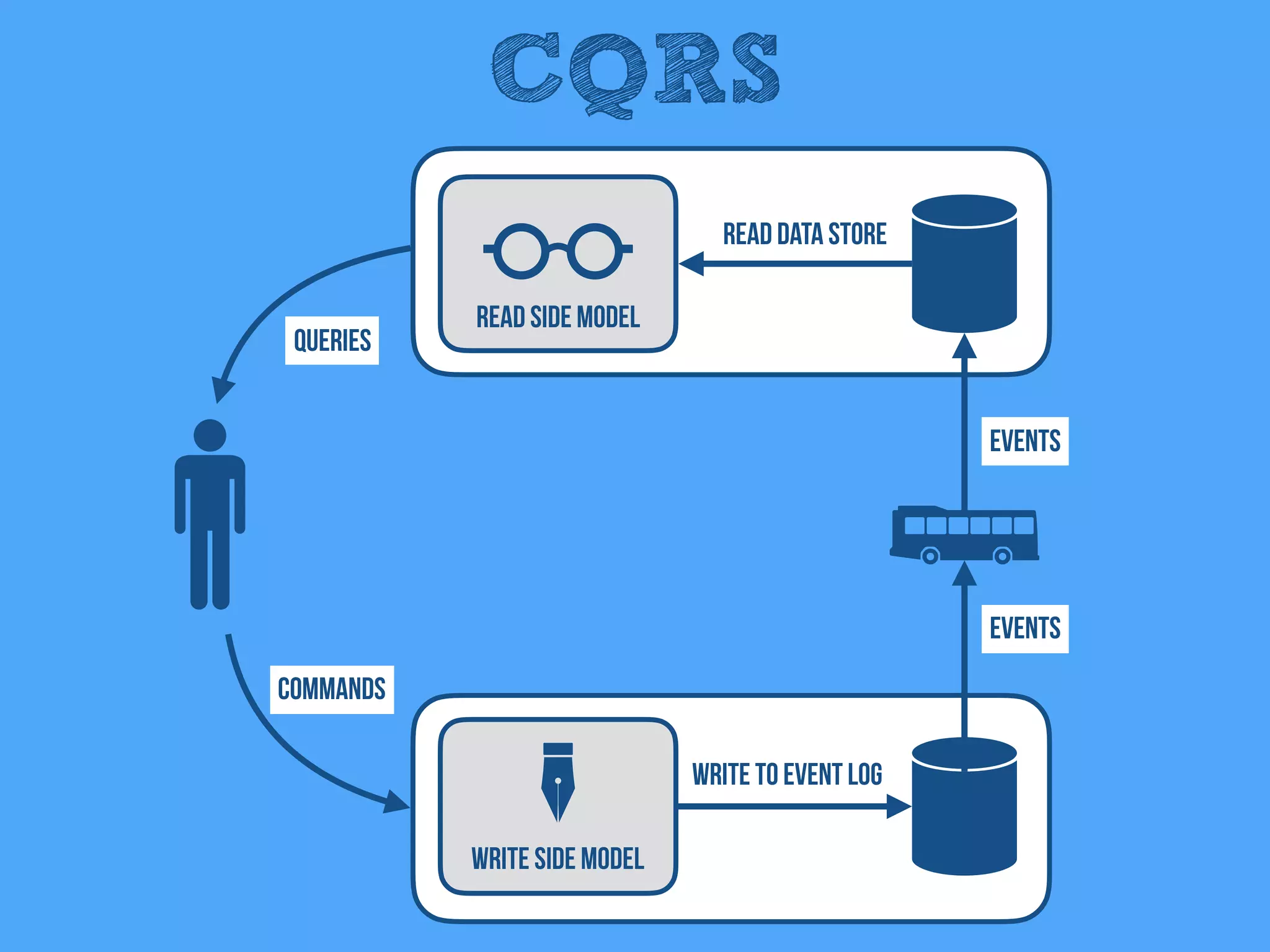
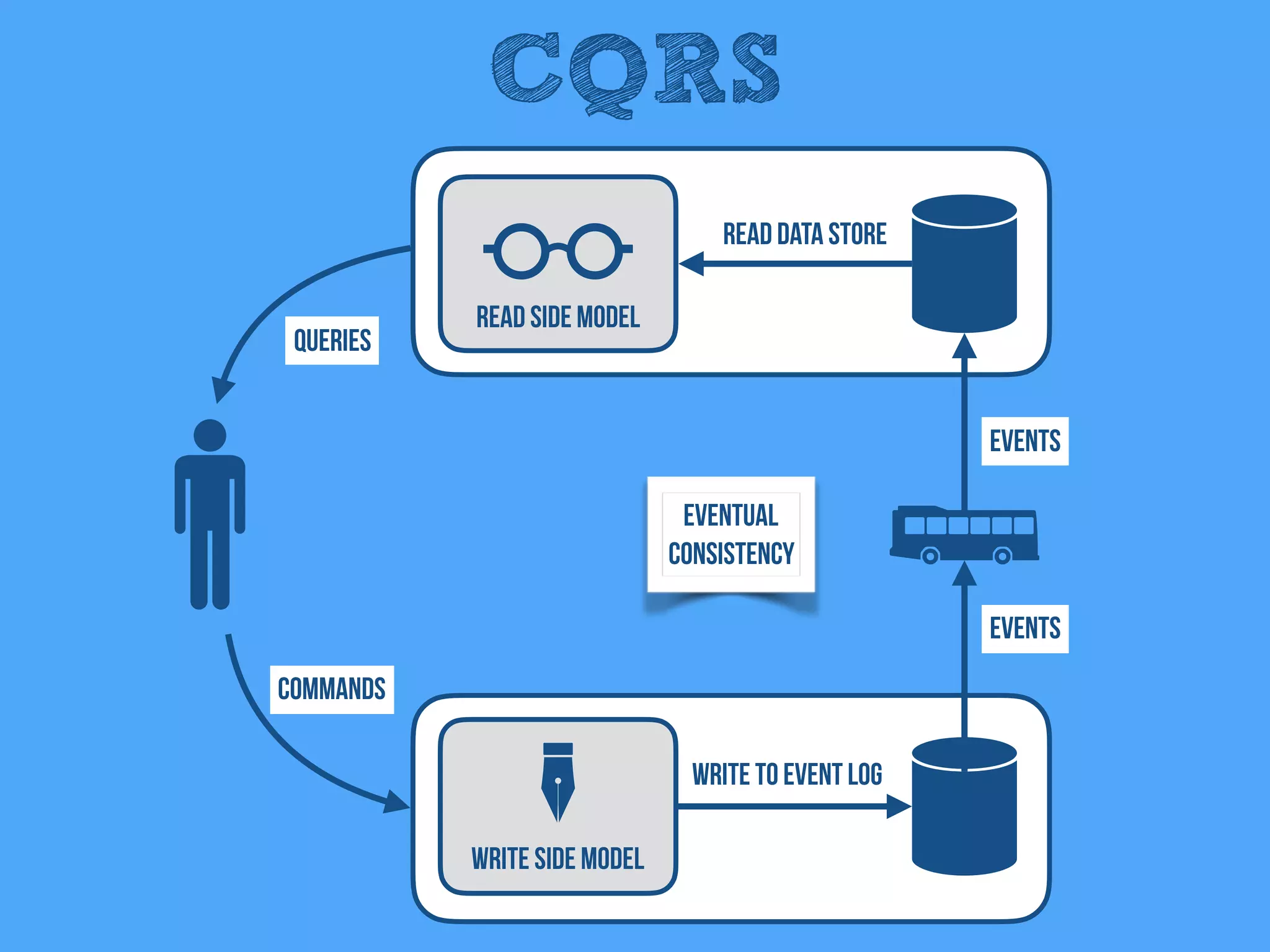
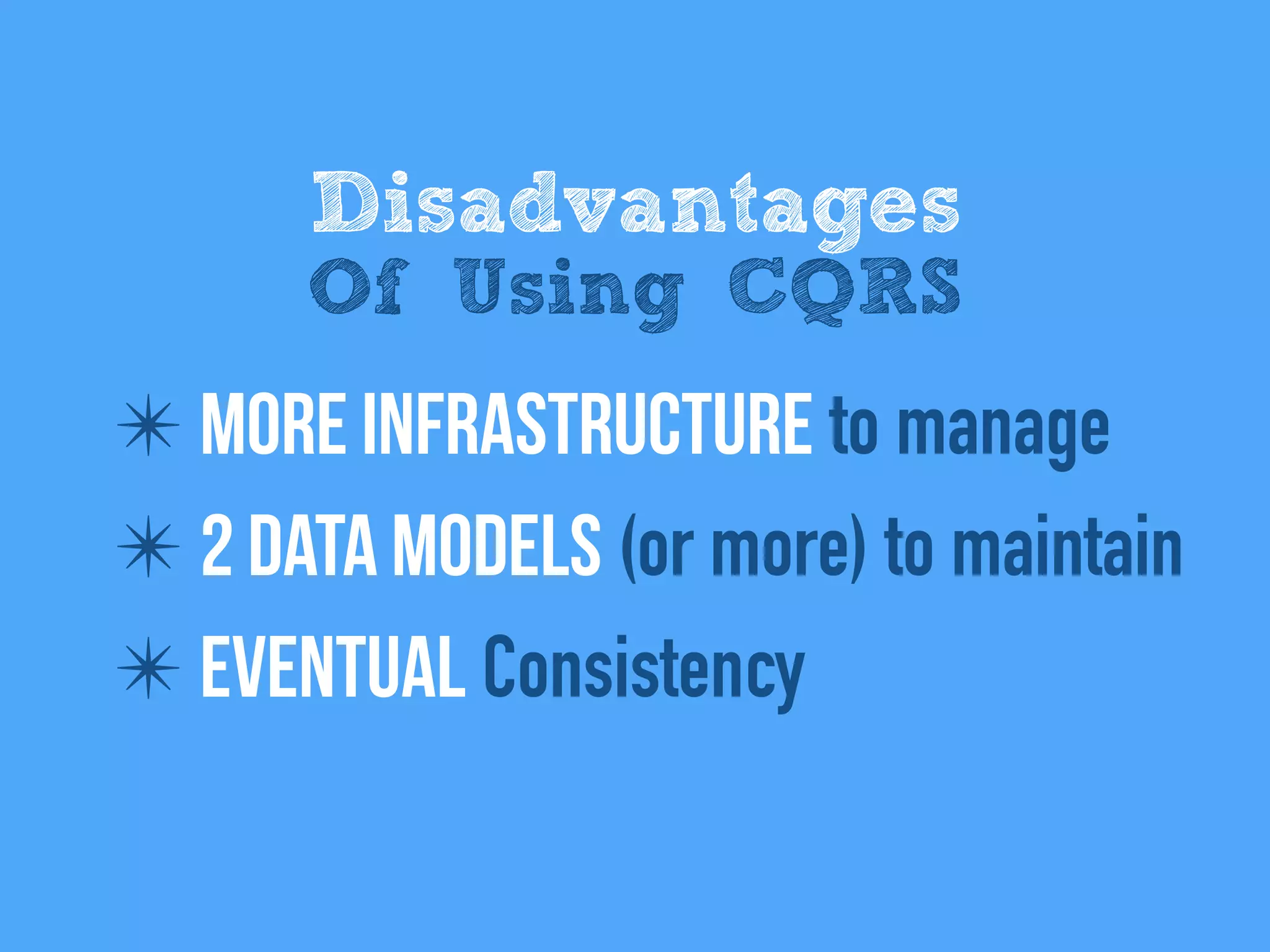
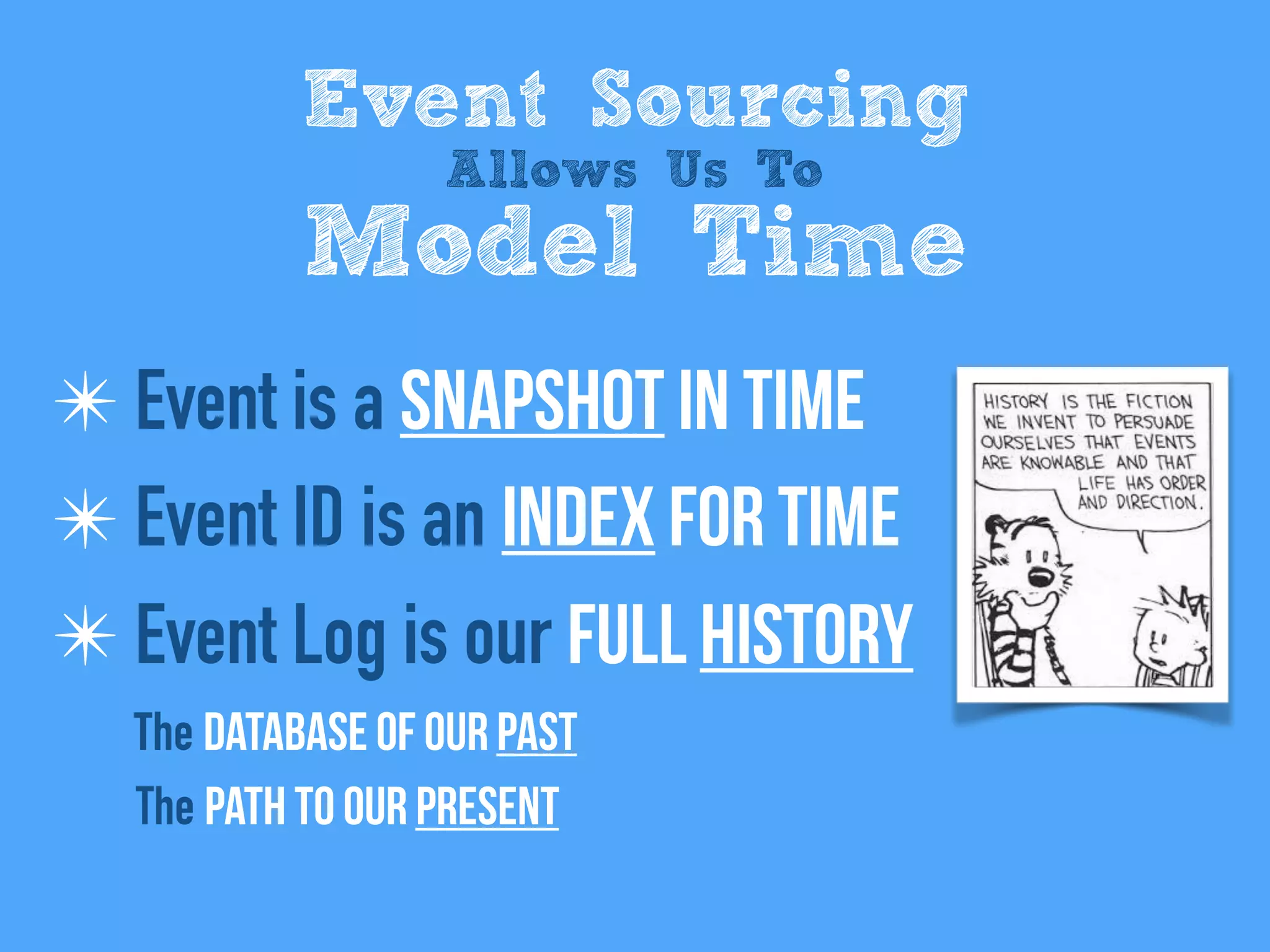
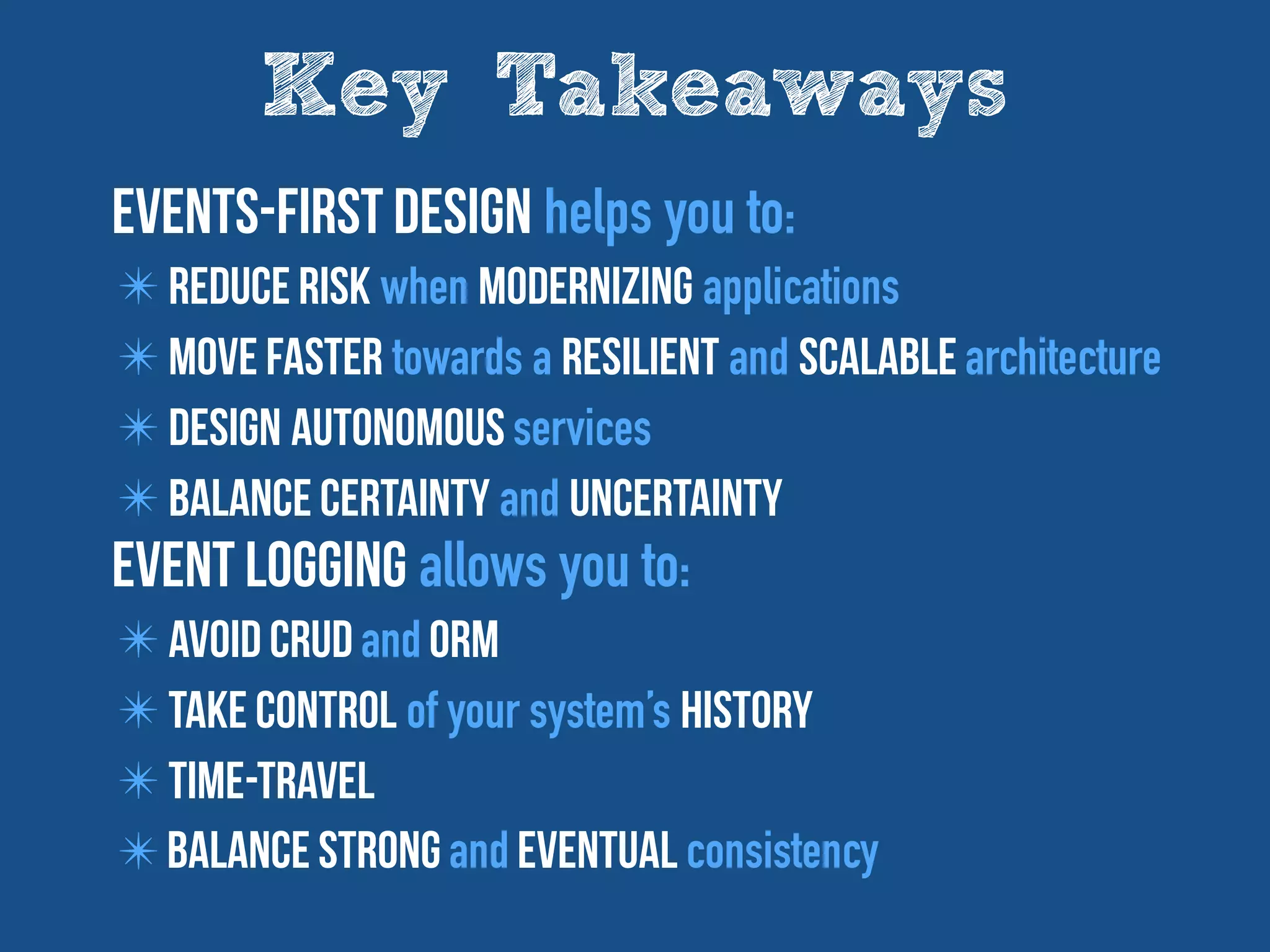
The document discusses the importance of event-driven design in creating modern microservices, emphasizing that events foster autonomy, reduce risk, and enhance scalability and resilience. It highlights key concepts such as the immutability of events, the distinction between commands and events, and the benefits of using event sourcing and CQRS (Command Query Responsibility Segregation) for managing data and system states. Ultimately, it advocates for an events-first approach as a means to improve application modernizations and achieve a more sustainable architectural design.