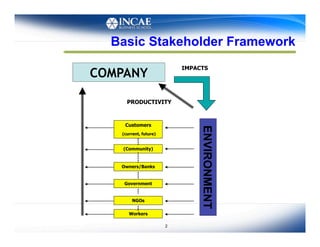
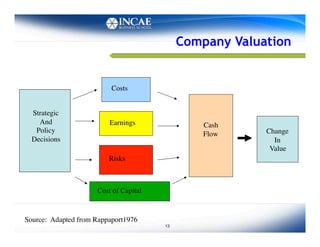
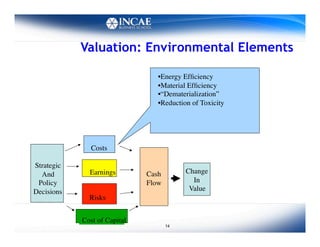
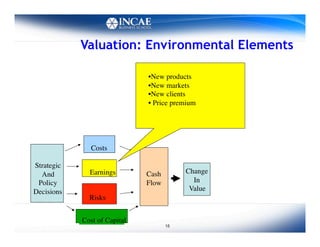
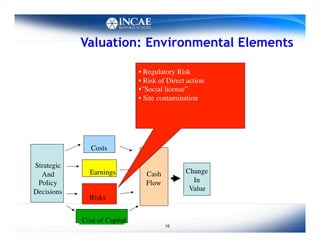
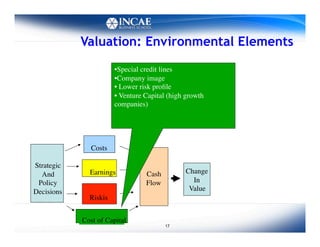
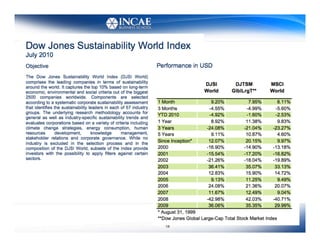
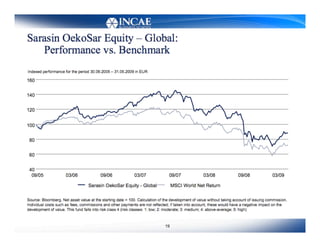
This document discusses the links between competitiveness and sustainability for companies. It outlines seven environmental value drivers that can benefit companies: 1) process efficiency, 2) buyer preferences, 3) access to more ecological international markets, 4) official business relationships, 5) environmental performance and competition in domestic markets, 6) incentive for innovation, and 7) lower risk profiles for funding. The document then examines how environmental performance can be incorporated into company valuation by affecting costs, earnings, cash flows, risks, and cost of capital.