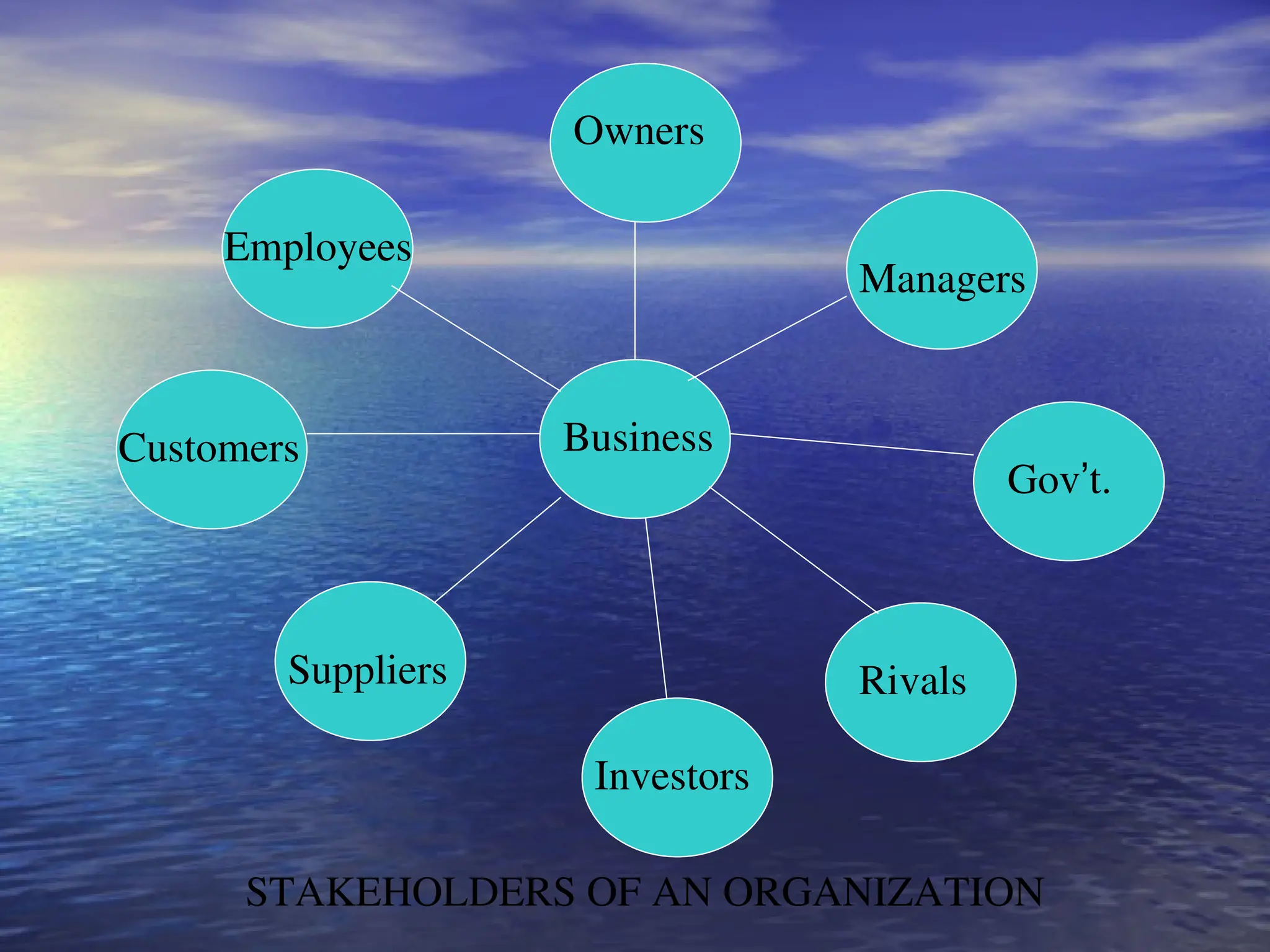
Stakeholders are individuals or organizations with a direct interest in a business's performance, divided into internal stakeholders (employees, shareholders, managers, directors) and external stakeholders (customers, suppliers, government). Conflicts can arise among stakeholders due to differing interests and objectives, particularly regarding director remuneration. Resolving these conflicts requires leaders to consider the organization type, business aims, and the power of each stakeholder group.