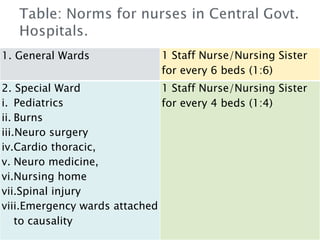
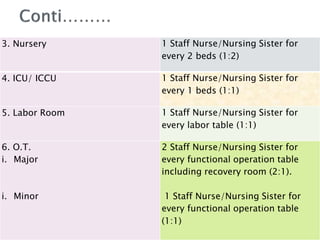
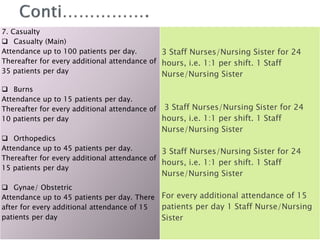
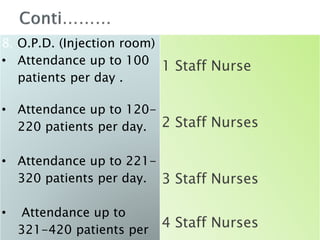
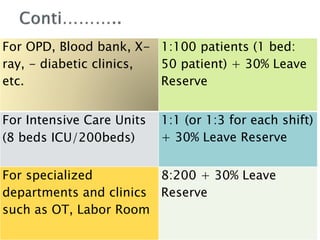
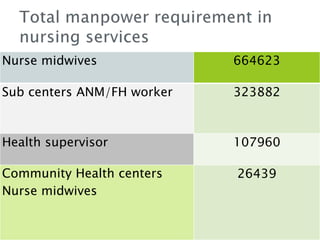
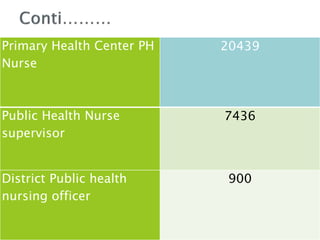
1. The Staff Inspection Unit recommended nursing norms in 1991-1992 that determined nurse-patient ratios in central government hospitals.
2. The Bajaj Committee recommended establishing vocational training programs and health science universities to improve health manpower production and management.
3. A High Power Committee reviewed nursing roles, functions, preparation, services and made recommendations to improve the nursing profession in India.