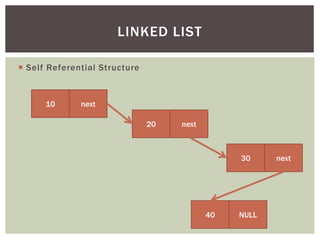
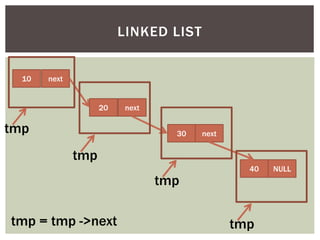
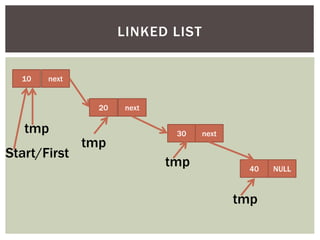
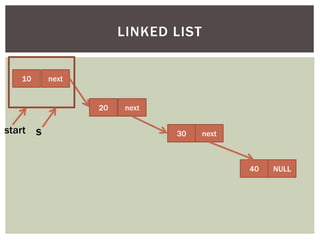
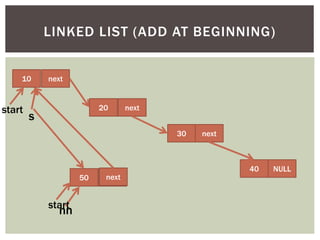
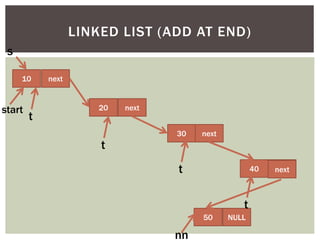
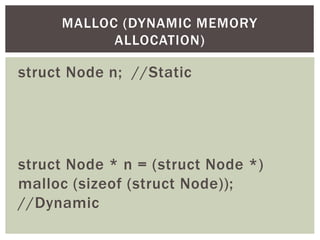
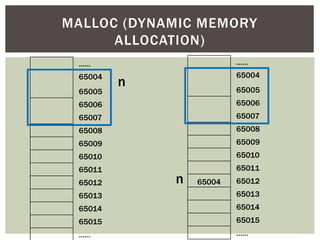
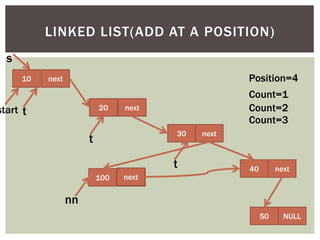
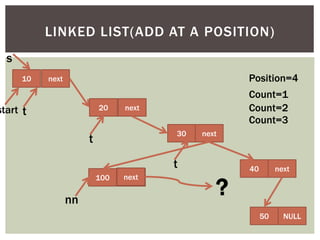
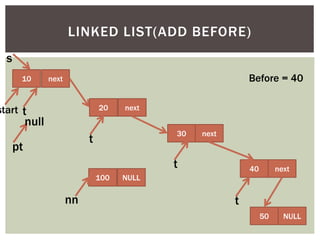
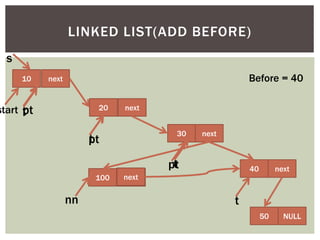
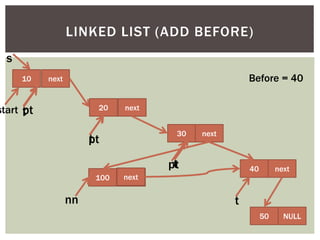
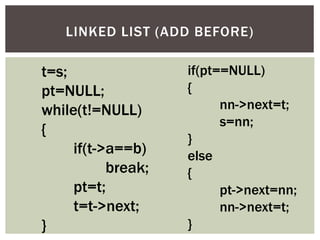
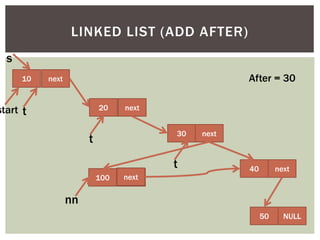
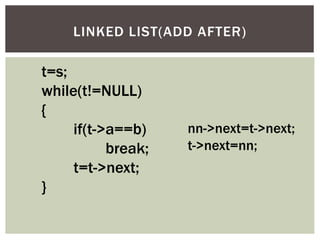
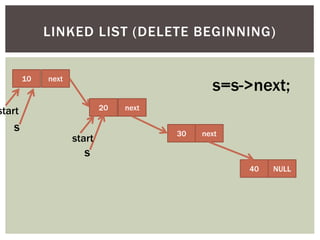
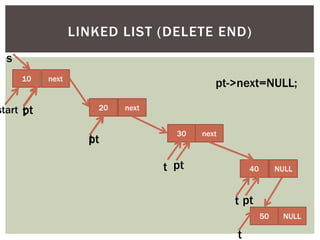
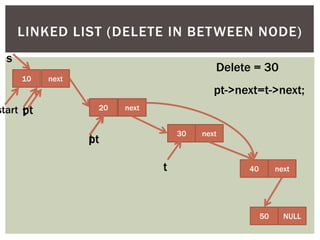
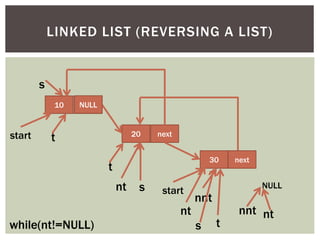
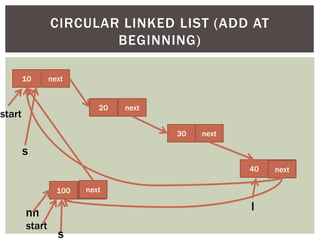
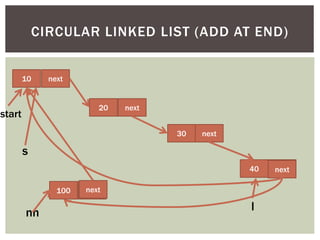
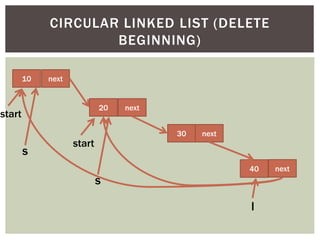
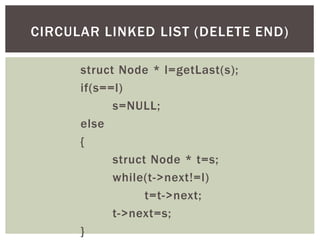
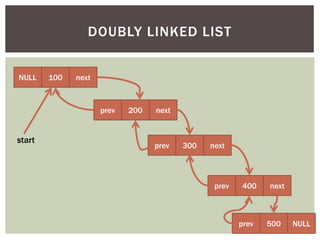
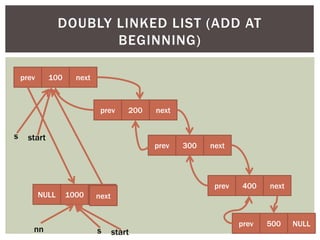
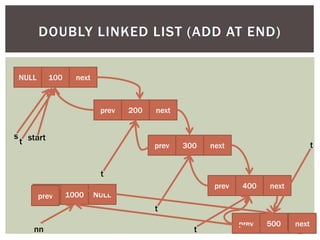
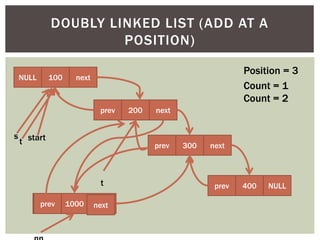
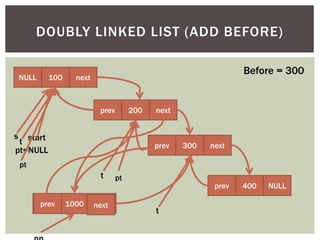
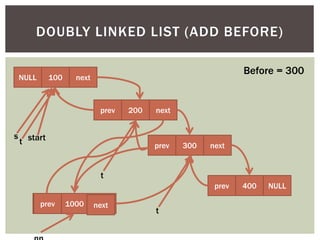
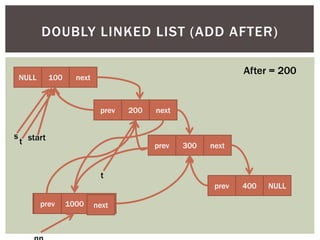
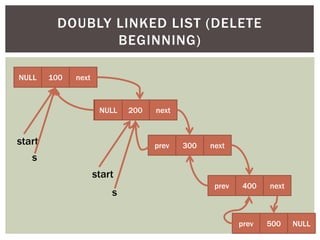
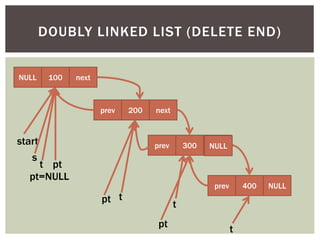
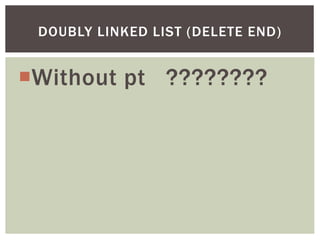
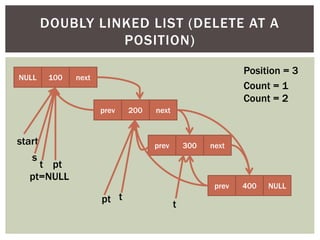
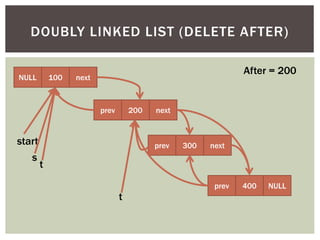
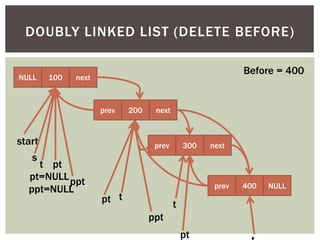
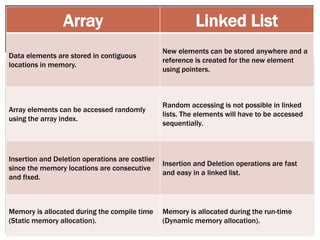
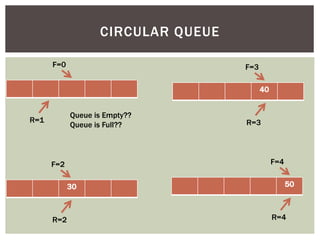
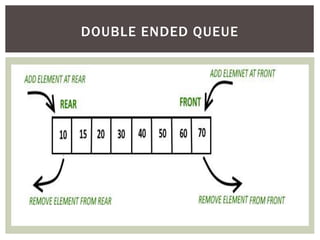
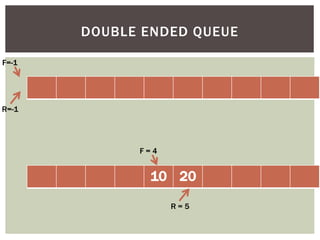
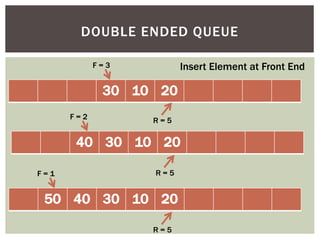
The document discusses various data structures and algorithms. It begins with an overview of common data structures like arrays, lists, stacks, queues, and linked lists. It then provides detailed explanations of stack, queue, circular queue, priority queue, double ended queue, and various linked list implementations including singly linked lists, doubly linked lists, and circular linked lists. For each data structure, it discusses operations like insertion, deletion, traversal, and implementations in C/C++ using structures and pointers.







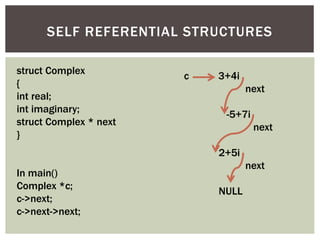
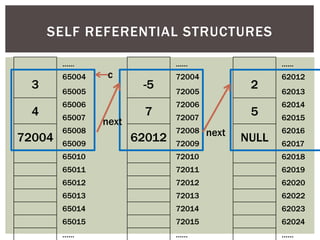
![SELF REFERENTIAL STRUCTURES
struct Complex
{
int real;
int imaginary;
}
In main()
Complex c[3];
3
4
-5
7
2
5
……
65004
65005
65006
65007
65008
65009
65010
65011
65012
65013
65014
65015
……
c[0]
c[1]
c[2]
c[0]= 3+4i
c[1]= -5+7i
c[2]= 2+5i](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stackqueuelinkedlist-220707092852-e4b0beff/85/Stack-Queue-Linked-List-pptx-32-320.jpg)