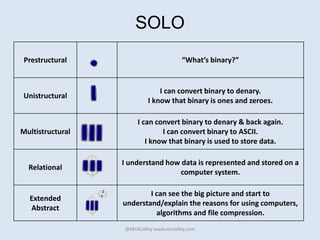
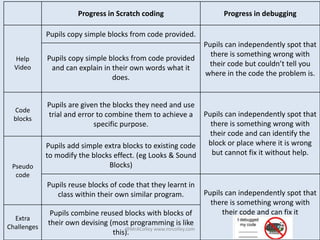
This document contains information from Andy Colley about teaching computing concepts like binary, debugging, and ASCII. It includes lesson plans, differentiation strategies, and progress levels for coding and debugging in Scratch. It also lists additional resources from other educators like websites, hashtags, and materials for teaching computing concepts without computers.