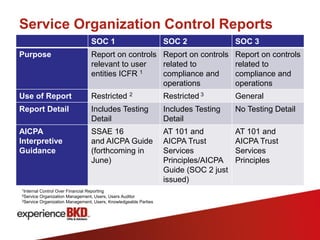
This document provides an overview of Service Organization Control (SOC) reporting, including definitions, background, and types of reports. SOC 1 reports address controls relevant to user entities' internal control over financial reporting, following the new SSAE 16 standards. SOC 2 reports examine controls related to security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality or privacy using the Trust Services Principles. SOC 3 reports also use Trust Services Principles criteria but do not include testing details. The document outlines key differences between SAS 70 and SSAE 16 reporting and transitions to the new standards.