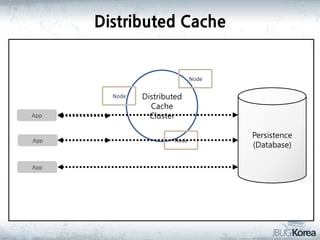
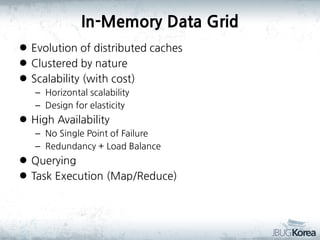
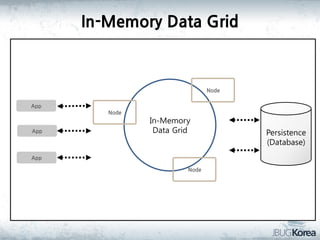
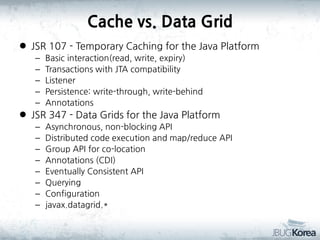
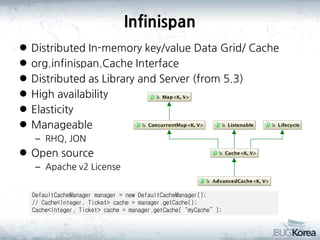
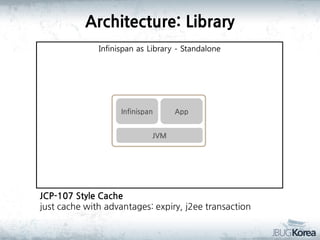
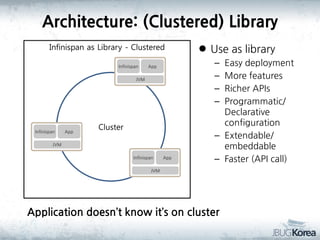
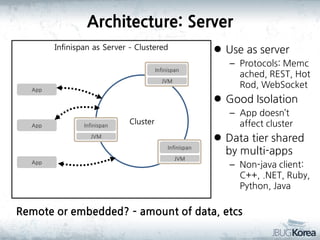
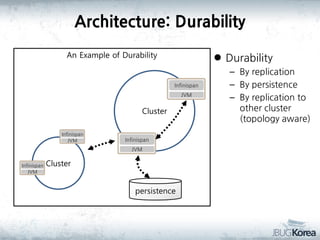
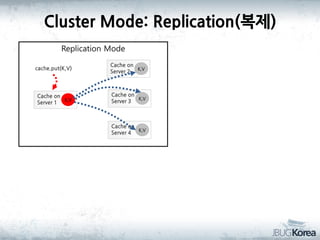
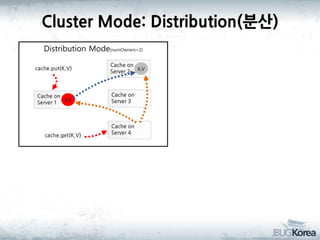
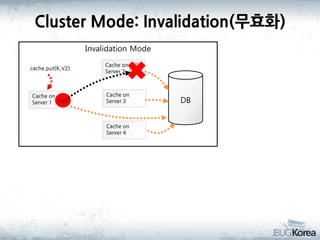
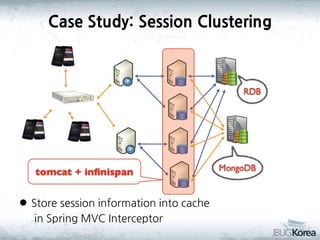
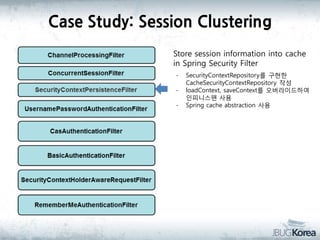
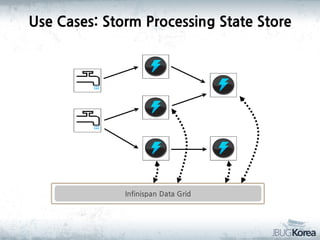
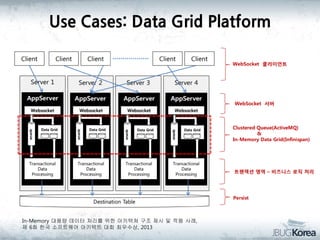
This document discusses in-memory data grids and JBoss Infinispan. It begins with an overview of in-memory data grids, their uses for caching, performance boosting, scalability, and high availability. It then discusses Infinispan specifically, describing it as an open-source, distributed in-memory key-value data grid and cache. The document outlines Infinispan's architecture, features like persistence, transactions, querying, distributed execution, and map-reduce capabilities. It also provides a case study on using Infinispan for session clustering in a web application.