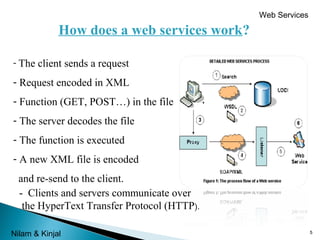
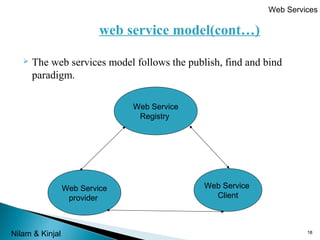
This document provides an overview of web services submitted by Miss. Rachna Kamalia and prepared by Miss. Nilam Radadiya and Miss. Kinjal Kapadiya. It defines web services as a collection of open protocols for exchanging data between applications over a network. The document describes how web services work, why they are used, their components like XML, WSDL, SOAP, and UDDI, as well as their advantages of interoperability and reusability and disadvantages regarding security and quality of service. It concludes with an overview of the web services composition process.