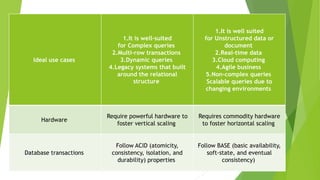
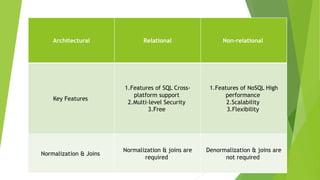
The document compares SQL and NoSQL databases, outlining their definitions, structures, and ideal use cases. SQL is a traditional, structured database suited for consistent data, while NoSQL is flexible and caters to large volumes of unstructured or semi-structured data. It highlights key differences in schema, scalability, transaction management, and performance of both database types.