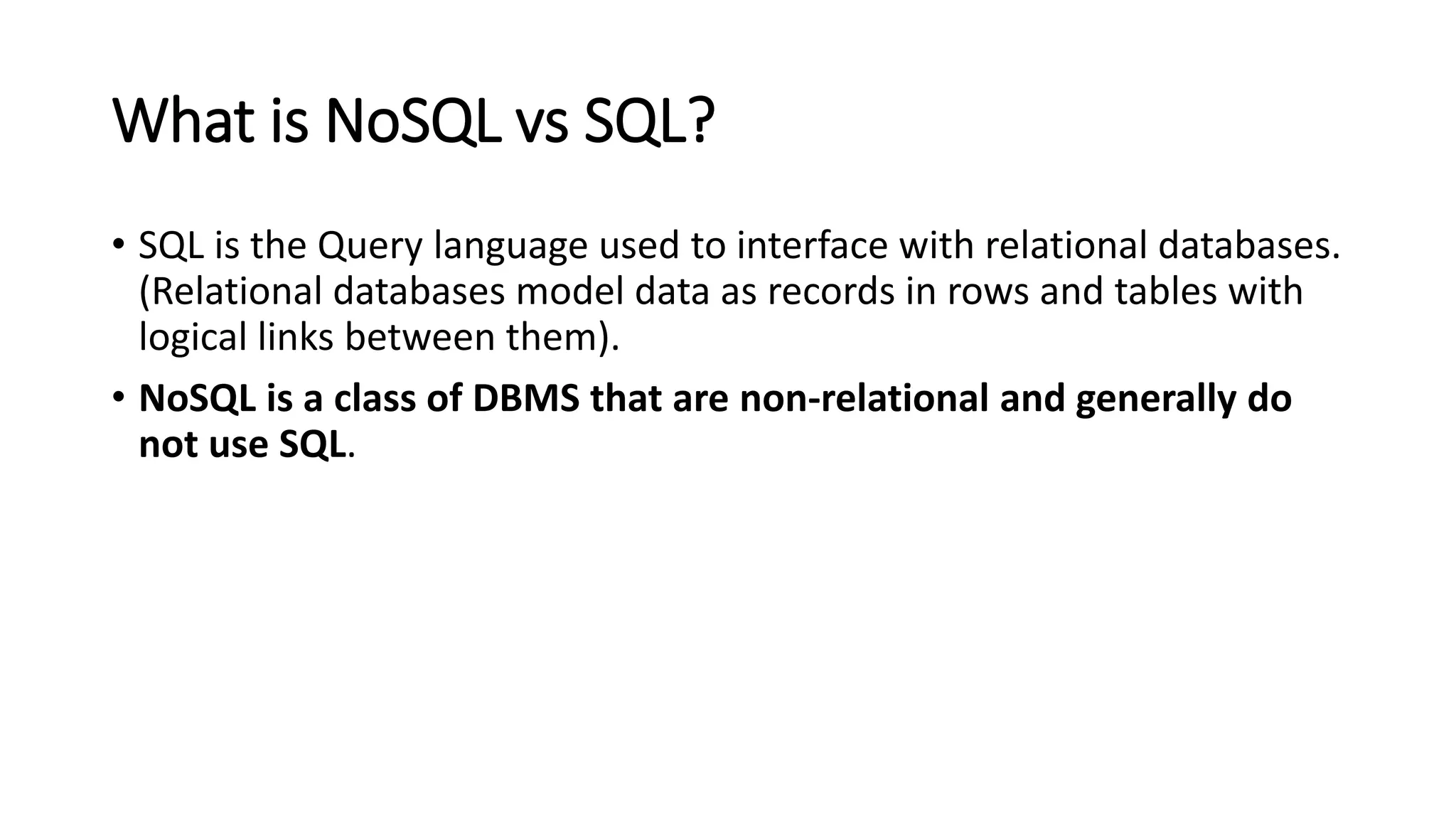
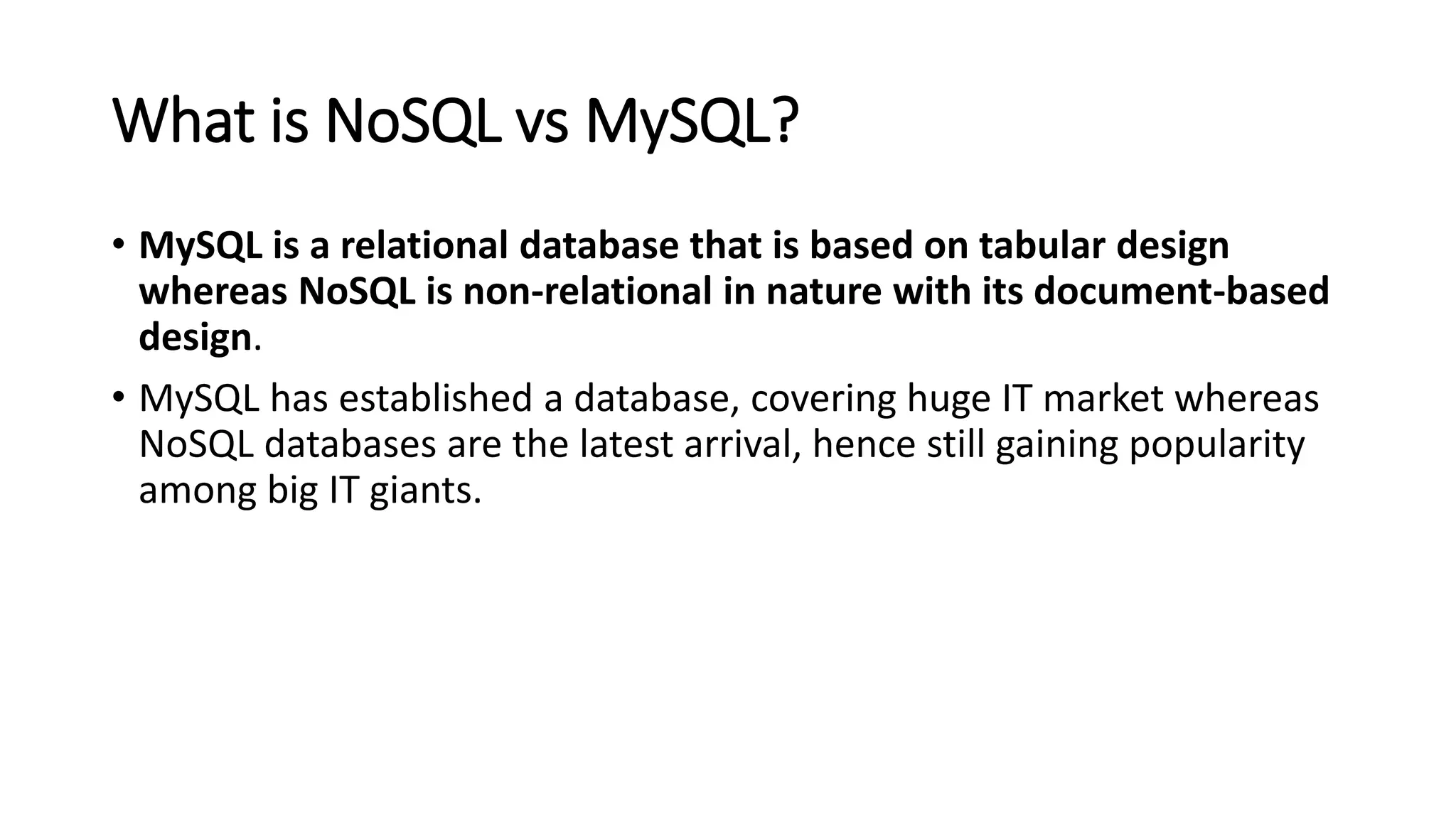
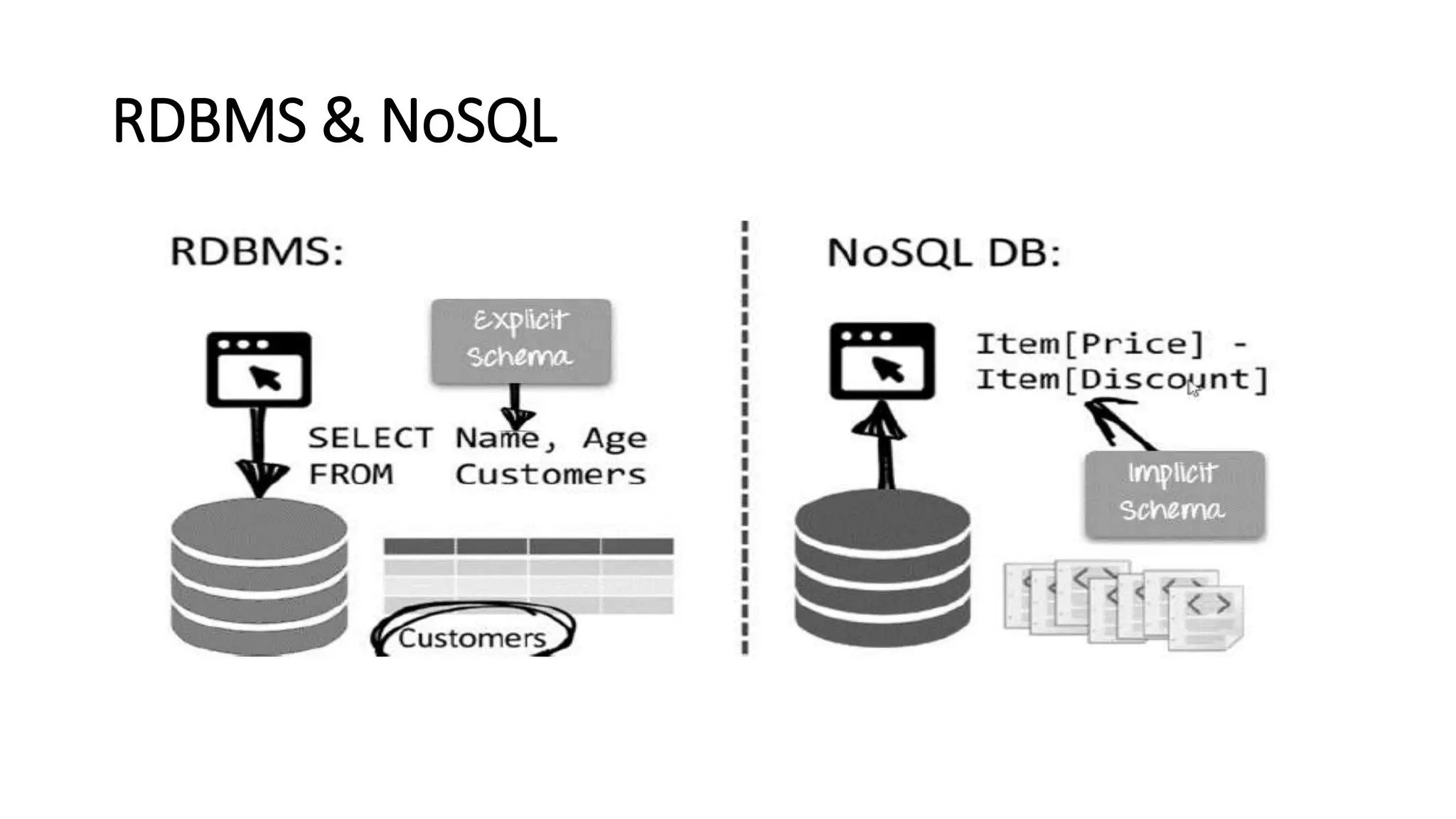
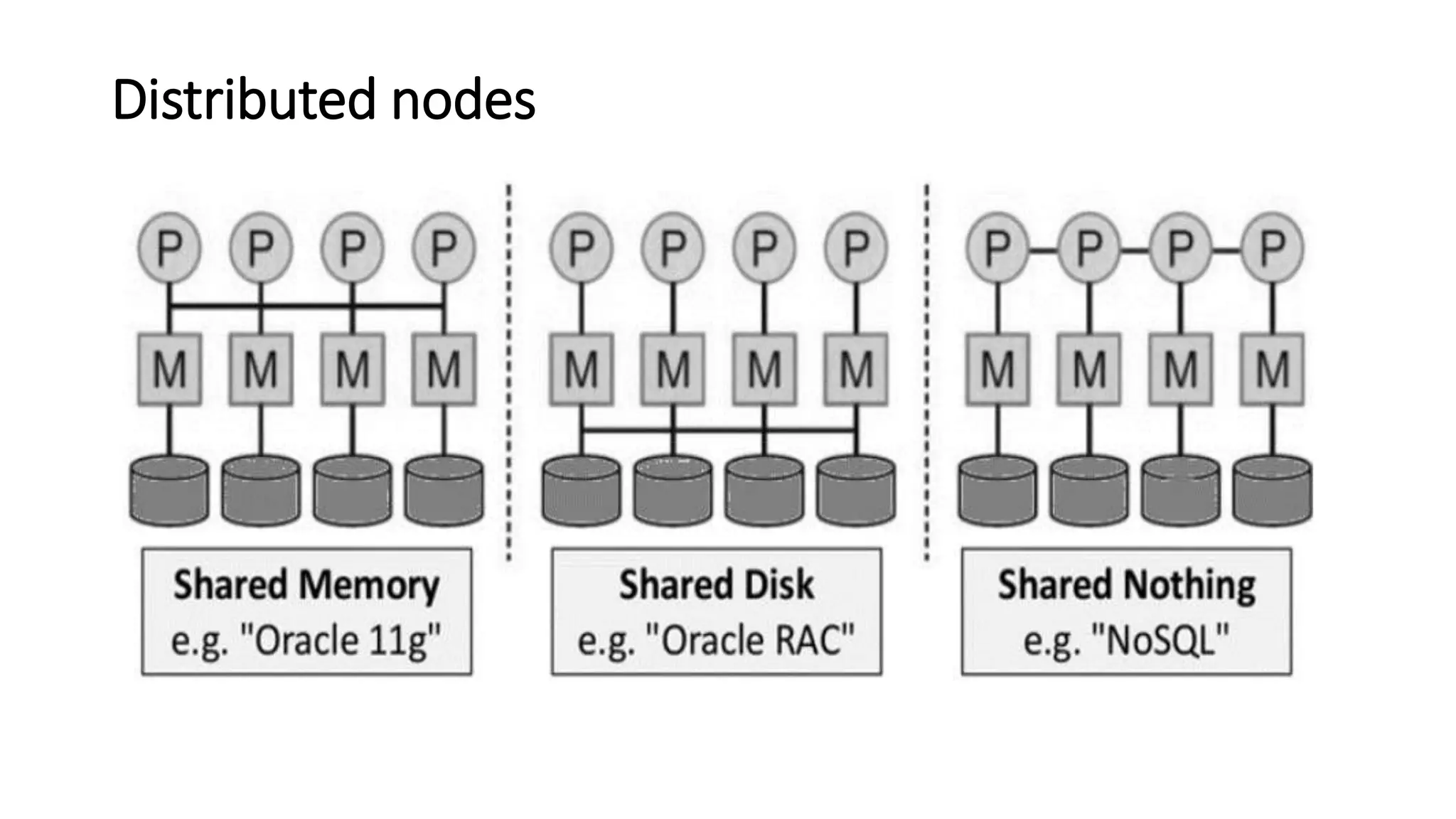
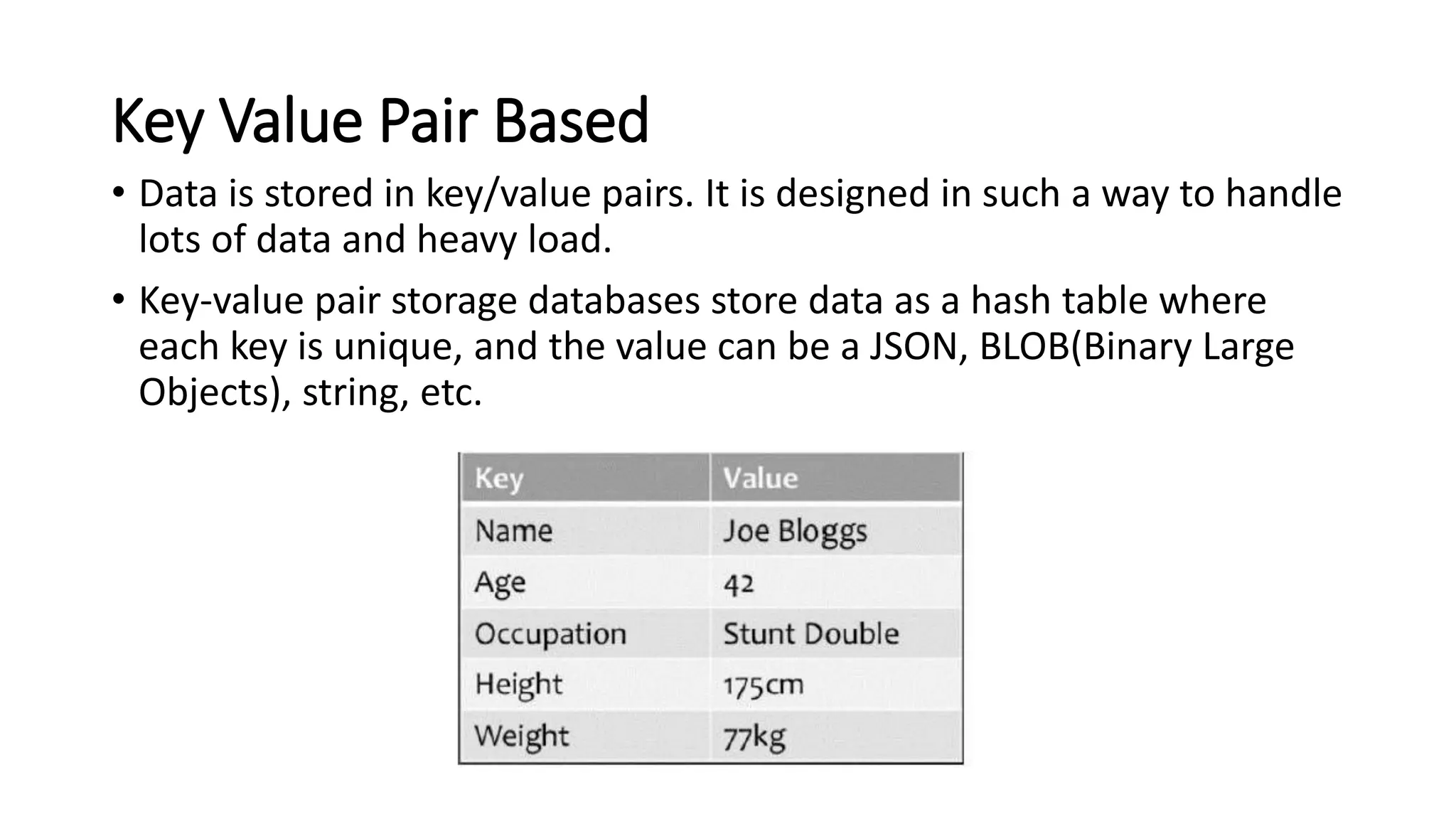
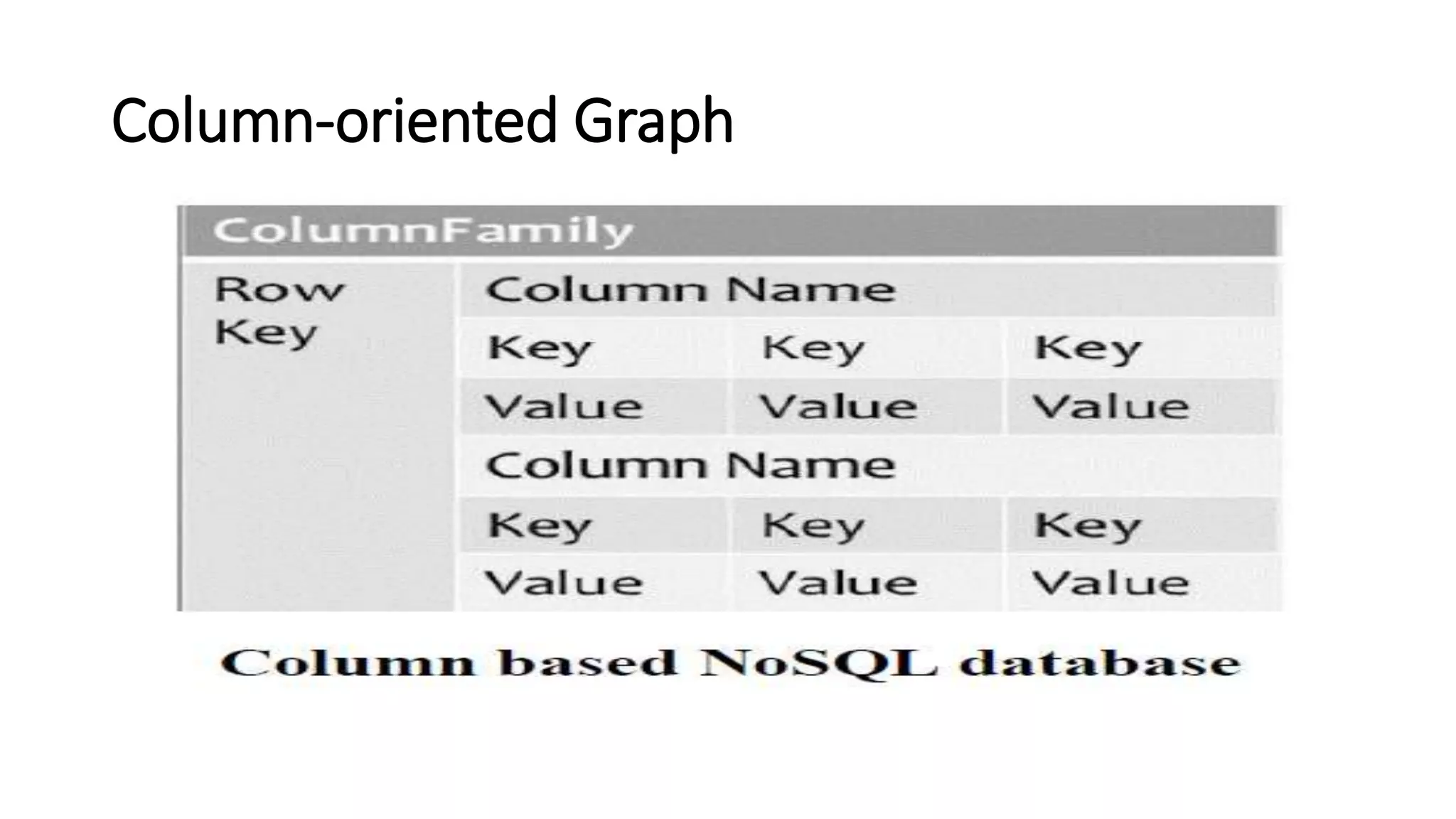
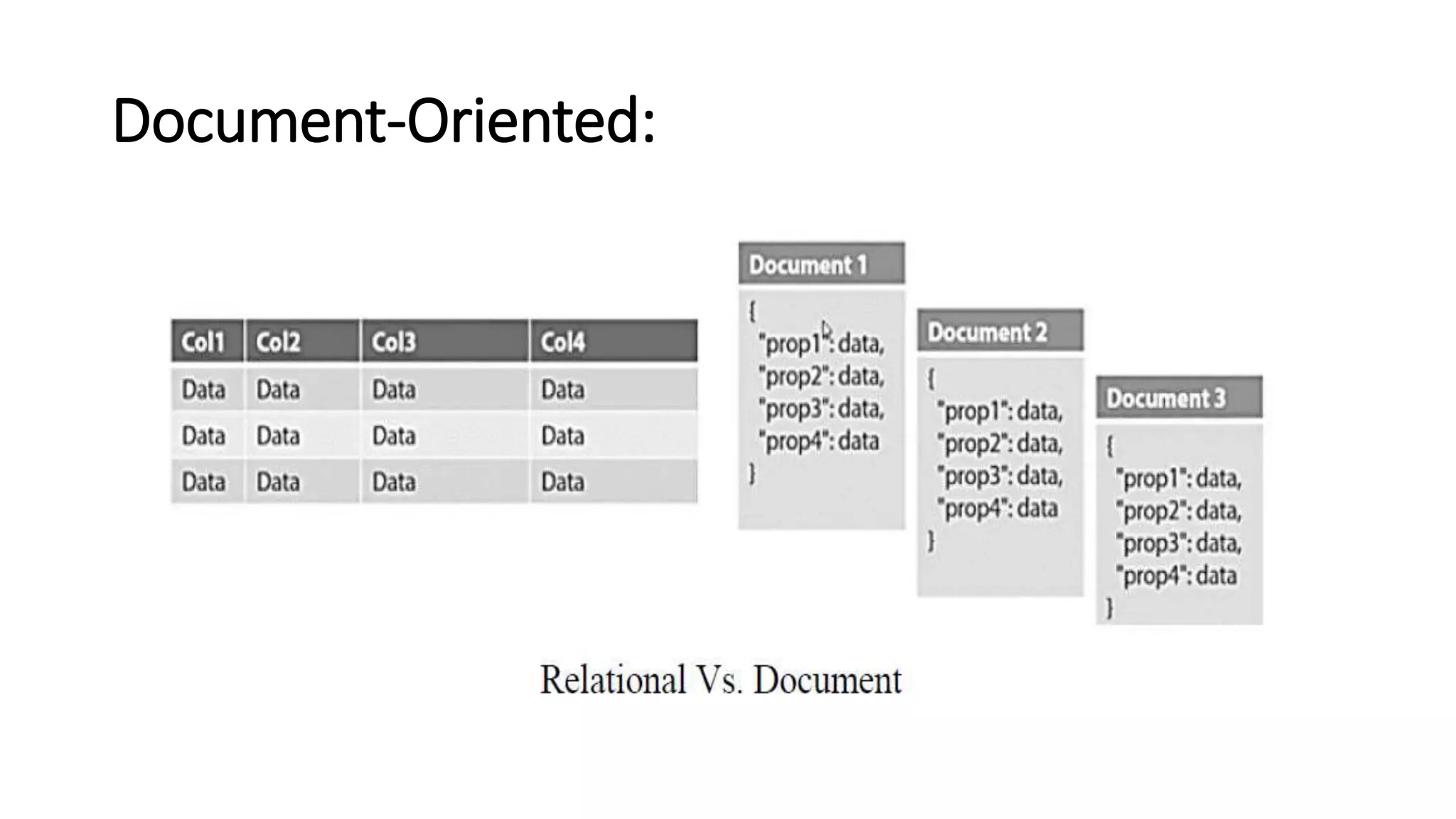
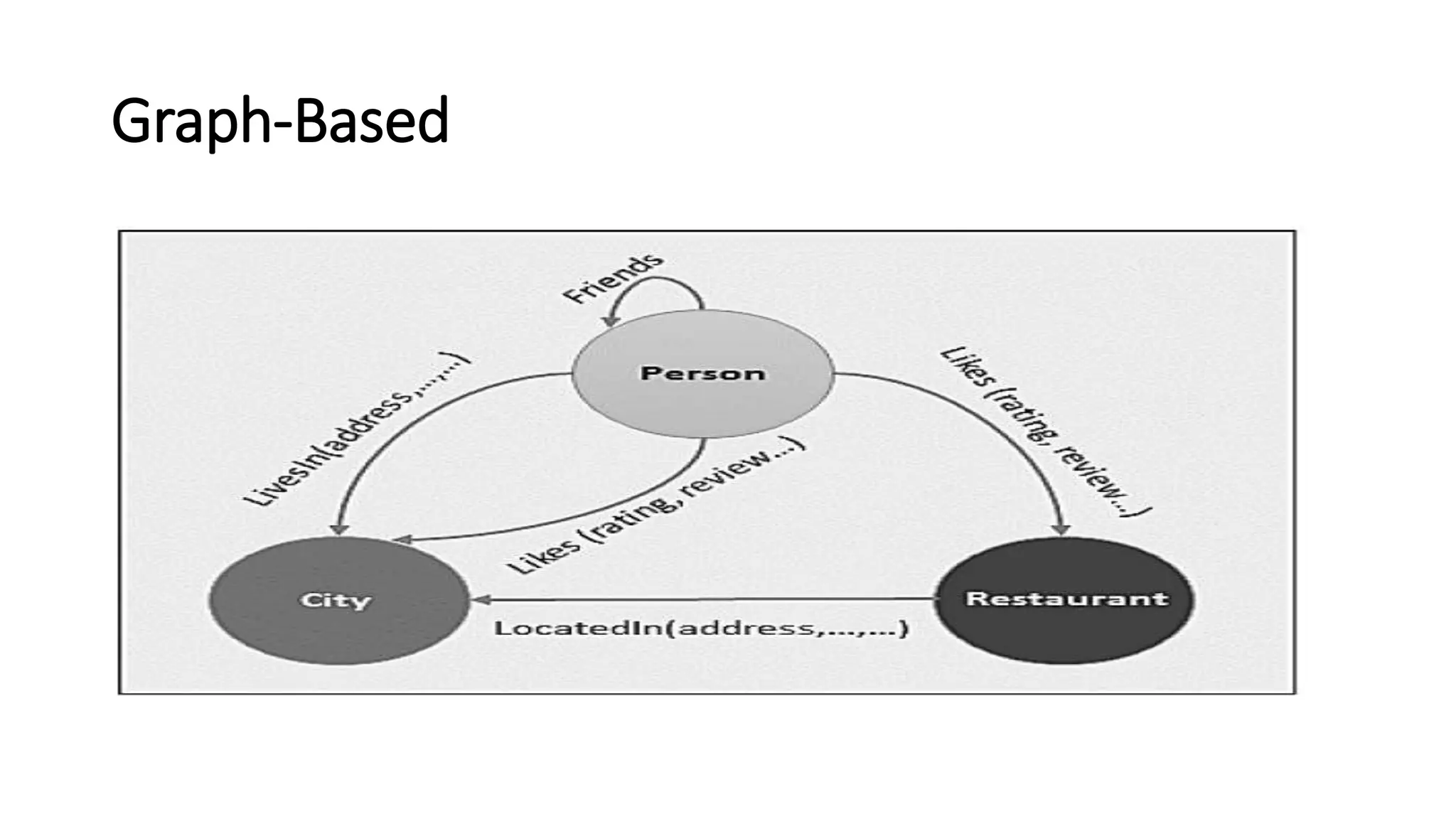
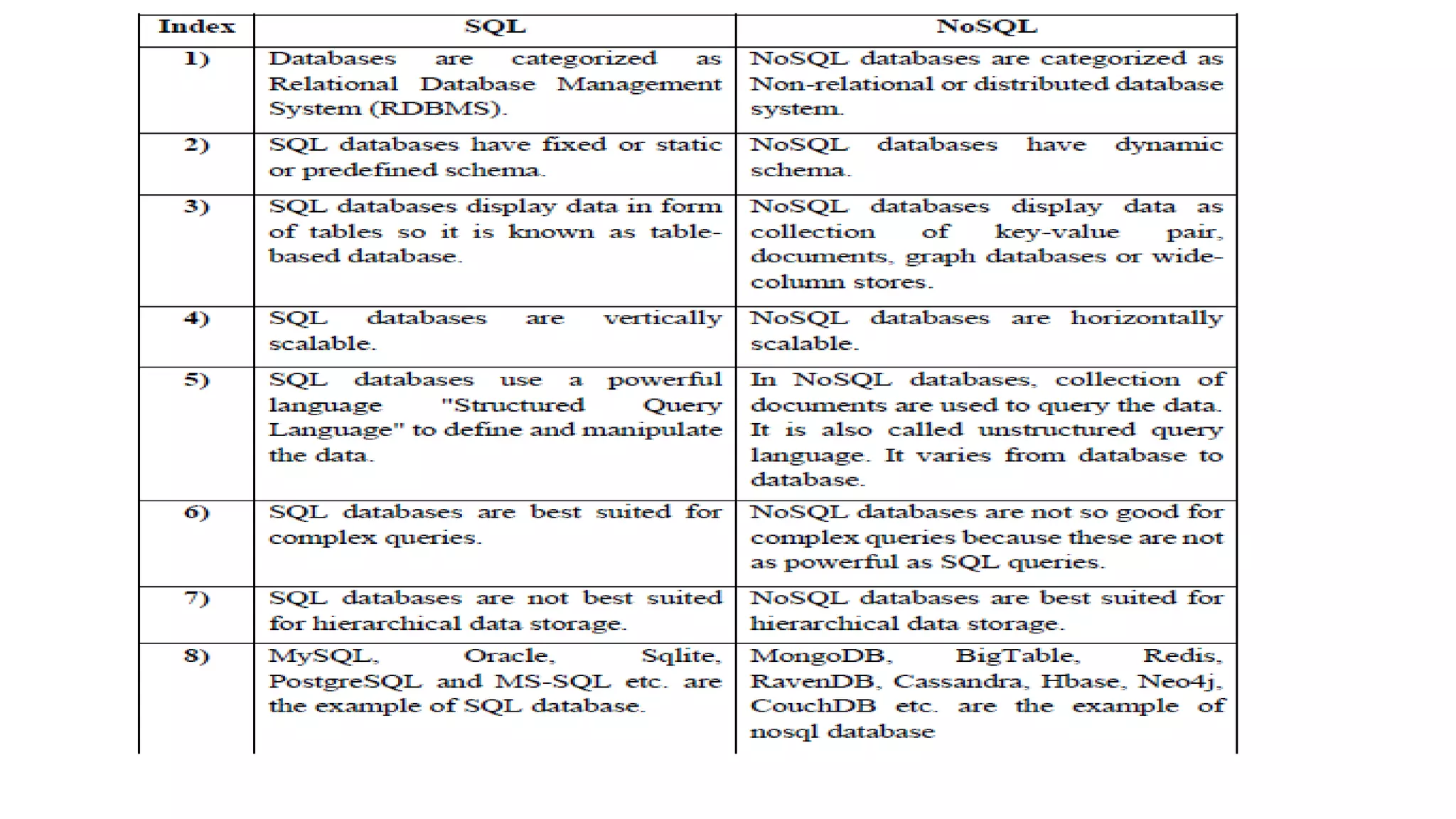
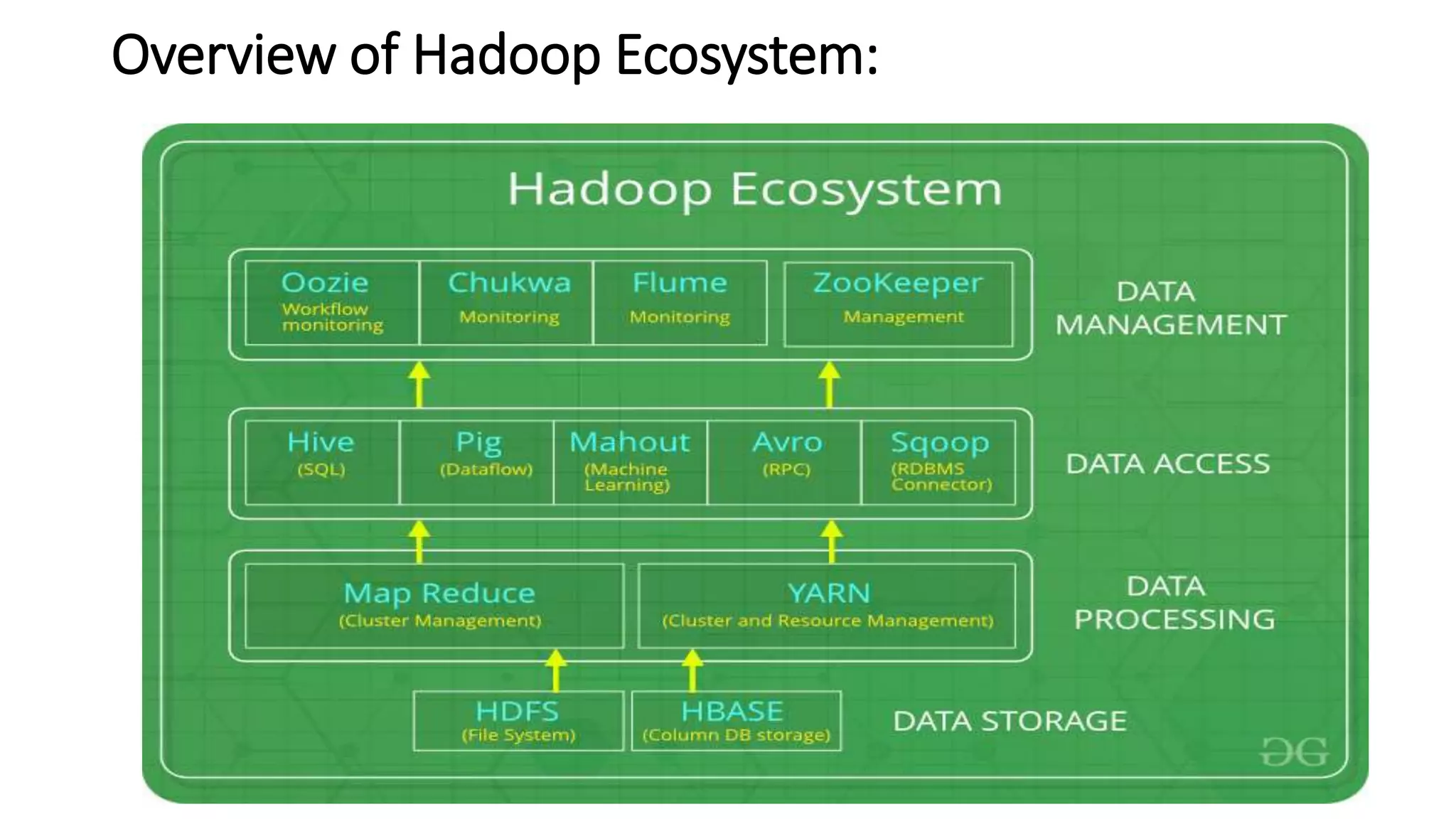
NoSQL is a non-relational database approach that accommodates a wide variety of data models. It is non-relational, distributed, flexible and scalable. The four main types of NoSQL databases are document databases, key-value stores, column-oriented databases, and graph databases. MongoDB is an example of a document-oriented NoSQL database. NoSQL databases offer benefits over relational databases like flexible schemas, horizontal scalability, and fast queries. Hadoop is an open source framework for distributed storage and processing of large datasets across clusters of computers. It uses MapReduce as its parallel programming model and the Hadoop Distributed File System for storage.