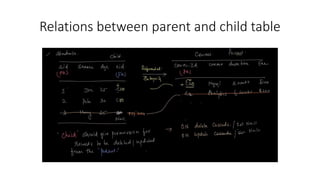
This document provides an overview of SQL concepts including:
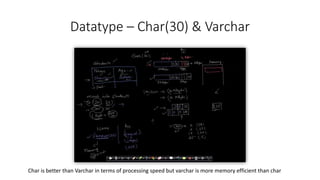
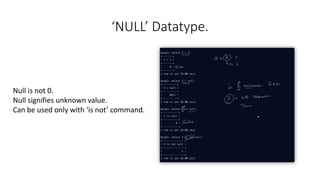
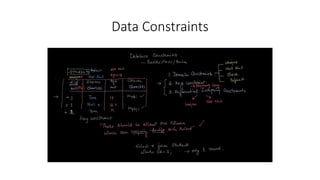
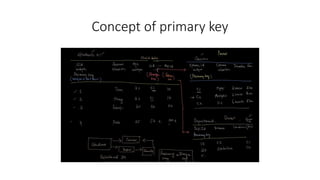
- Data types like char, varchar, and null
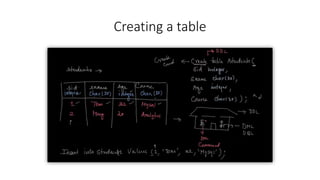
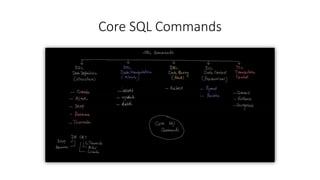
- Core SQL commands like select, update, delete, truncate, and alter
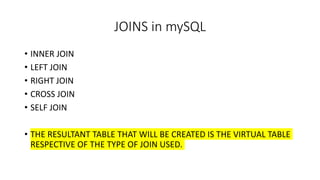
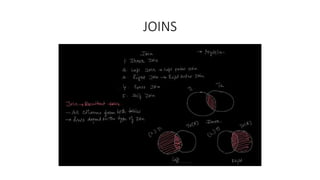
- Joins like inner, left, and cross joins
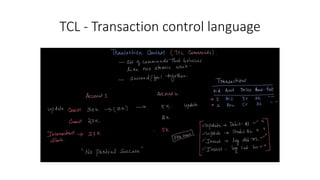
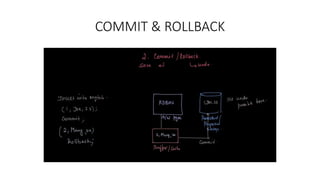
- Transaction control with commit, rollback, and savepoints
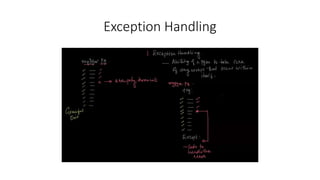
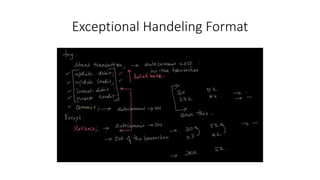
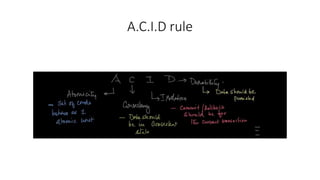
- Exception handling and the ACID properties of transactions
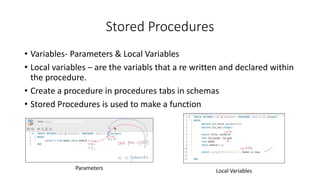
- Other objects like views, sequences, indexes, and stored procedures