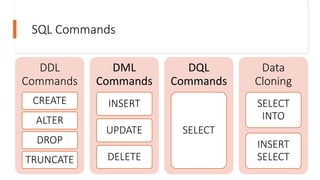
The document outlines training content for SQL Server 2019, focusing on SQL commands including DDL (Data Definition Language), DML (Data Manipulation Language), and DQL (Data Query Language). It includes syntax for creating and modifying databases, schemas, and tables, as well as lab sessions and assignments related to practical SQL applications. The document serves as a comprehensive guide for understanding and executing basic SQL commands and data management techniques.



![DATABASE Commands
For creating a new database
SYNTAX: CREATE DATABASE DBNAME;
EXAMPLE: CREATE DATABASE DEMO_DB;
Displaying name of available database
SELECT name FROM sys.databases;
To get details of available database using stored
procedure
EXEC sp_databases;
To rename the database
EXEC sp_renamedb old_name,new_name;
To delete database
Syntax: DROP DATABASE [
IF EXISTS ] database_name [,database_name2,...];
Example: DROP DATABASE DEMO_DB;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sqlbasicmodule3-240527013208-457a70b1/85/SQL-Introduction-and-its-Basic-Commands-5-320.jpg)
![SCHEMA Commands
For creating a new schema
SYNTAX: CREATE SCHEMA schema_name [AUTHORIZATION owner_name]
EXAMPLE: CREATE DATABASE DEMO_S;
Displaying name of available schemas
SELECT name FROM sys.schemas;
To delete schema
Syntax: DROP SCHEMA [IF EXISTS] schema_name;
Example: DROP Schema DEMO_S;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sqlbasicmodule3-240527013208-457a70b1/85/SQL-Introduction-and-its-Basic-Commands-6-320.jpg)
![Table Commands
For creating a new schema
SYNTAX: CREATE TABLE
[database_name.][schema_name.]table_name
( pk_column data_type PRIMARY KEY,
column_1 data_type NOT NULL,
column_2 data_type, ..., table_constraints );
EXAMPLE: CREATE TABLE DEMO_T;
To rename table
EXEC sp_rename 'old_table_name', 'new_table
_name'
EXEC sp_rename 'DEMO_T', 'DEMO_NT'
Displaying name of available table
SELECT * FROM SYS.TABLES;
To delete table
Syntax: DROP TABLE [IF
EXISTS] table_name;
Example: DROP Table DEMO_T;
Syntax: TRUNCATE TABLE
[database_name.][schema_name.]table
_name;
Example: TRUNCATE Table DEMO_T;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sqlbasicmodule3-240527013208-457a70b1/85/SQL-Introduction-and-its-Basic-Commands-7-320.jpg)



![Data cloning
• SELECT Into
• Syntax: SELECT select_list INTO destination FROM source [WHERE
condition]
• Example:
• INSERT INTO SELECT
• Syntax: INSERT [ TOP ( expression ) [ PERCENT ] ] INTO target_table
(column_list) query
• Example:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sqlbasicmodule3-240527013208-457a70b1/85/SQL-Introduction-and-its-Basic-Commands-11-320.jpg)



