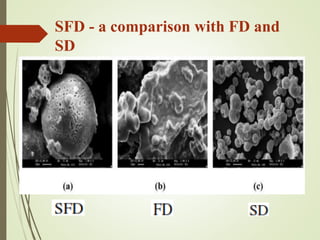
The document provides a comprehensive overview of spray freeze drying (SFD), a technique that combines aspects of spray drying and freeze drying for food and pharmaceutical applications. It discusses the processes involved, advantages, and limitations of SFD, including comparisons with traditional drying methods and case studies on producing soluble coffee and probiotic powders. The technique is highlighted as an effective alternative due to its ability to produce high-quality, shelf-stable products while maintaining the viability of sensitive compounds.