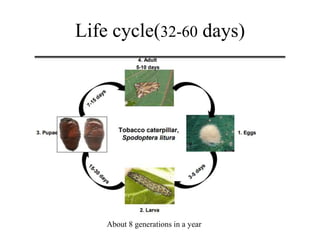
The document provides a comprehensive overview of the tobacco caterpillar (Spodoptera litura), its life cycle, host plants, and the damage it inflicts on crops like tomatoes. It discusses various management practices including cultural, mechanical, and ecological strategies to mitigate the pest's impact. Additionally, it mentions biological control methods involving parasitoids, pathogens, and companion planting with attractant or repellant crops.