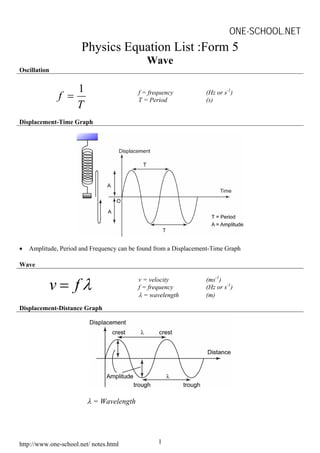
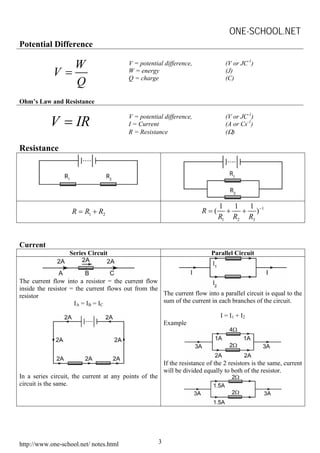
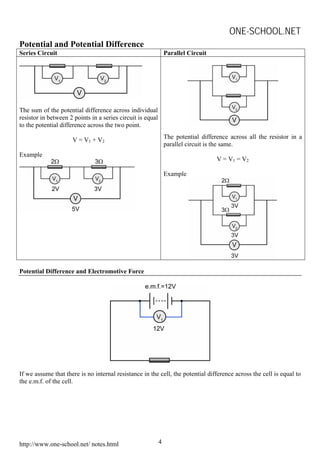
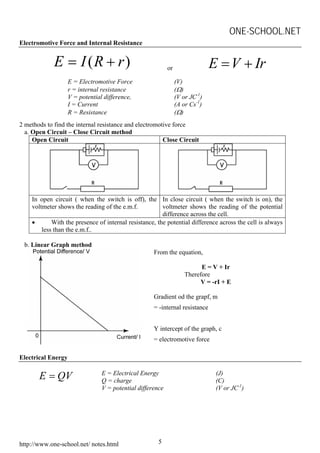
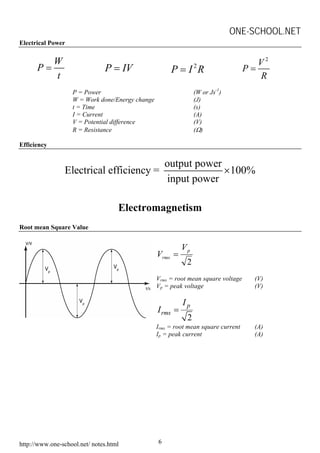
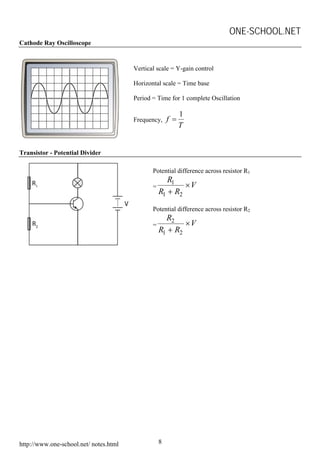
This document contains summaries of various physics concepts and equations related to waves, electricity, electromagnetism, electronics, and radioactivity. It includes definitions and equations for key terms like wavelength, frequency, potential difference, resistance, current, electromotive force, transformer ratios, kinetic energy of electrons, half-life of radioactive particles, and Einstein's mass-energy equivalence formula. The document is a compilation of physics notes intended to be a study guide for a high school physics course.