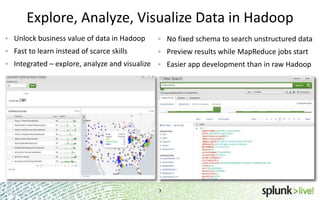
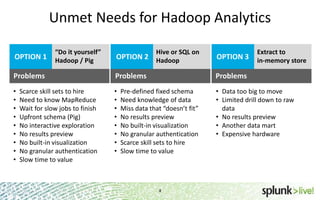
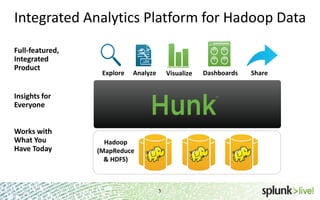
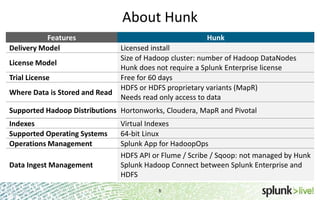
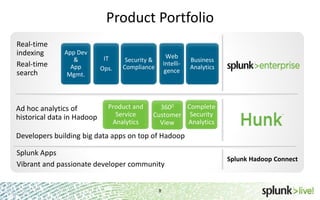
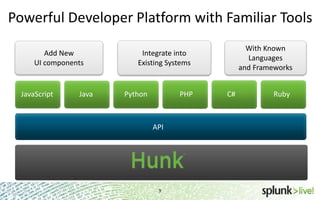
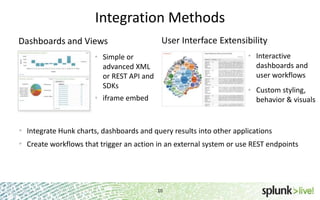
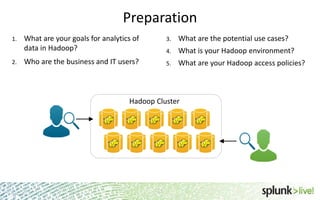
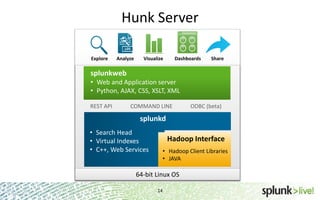
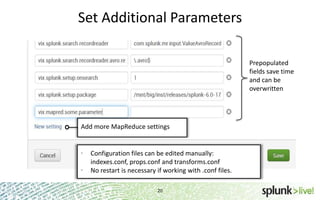
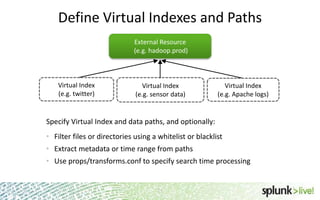
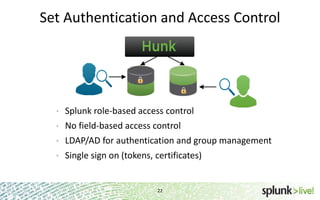
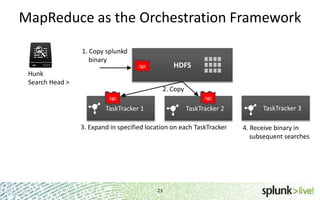
The document provides an overview of Hunk, a product from Splunk that allows users to explore, analyze and visualize data stored in Hadoop. Some key points:
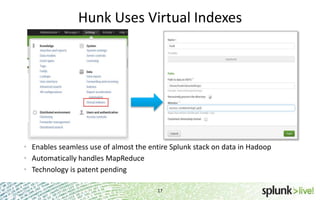
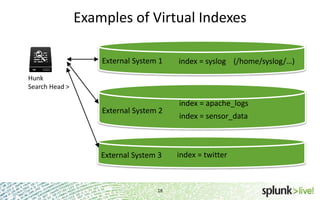
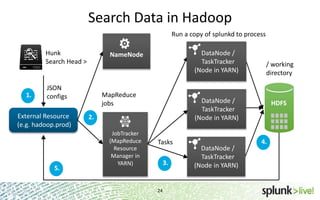
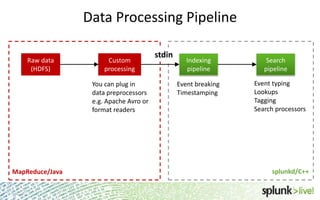
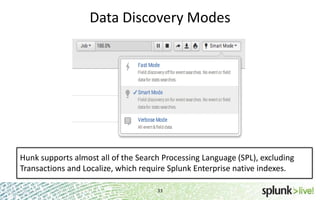
- Hunk uses virtual indexes to enable searching of data in Hadoop using Splunk's interface and capabilities without needing to move the data. It handles MapReduce jobs behind the scenes.
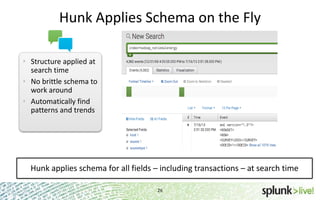
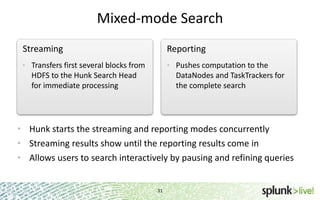
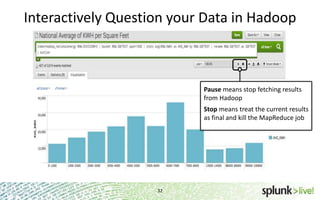
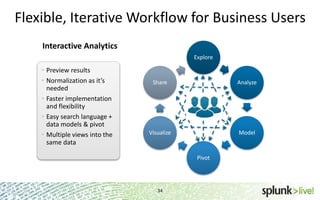
- It provides an interactive interface for business users to explore and query data in Hadoop in an easy and flexible way, with the ability to preview results while MapReduce jobs are running.
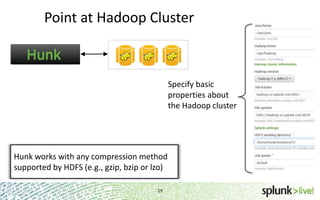
- Integration with Hadoop is done through Hadoop client libraries, requiring only read access to data stored in HDFS. Hunk supports various Hadoop distributions and operating