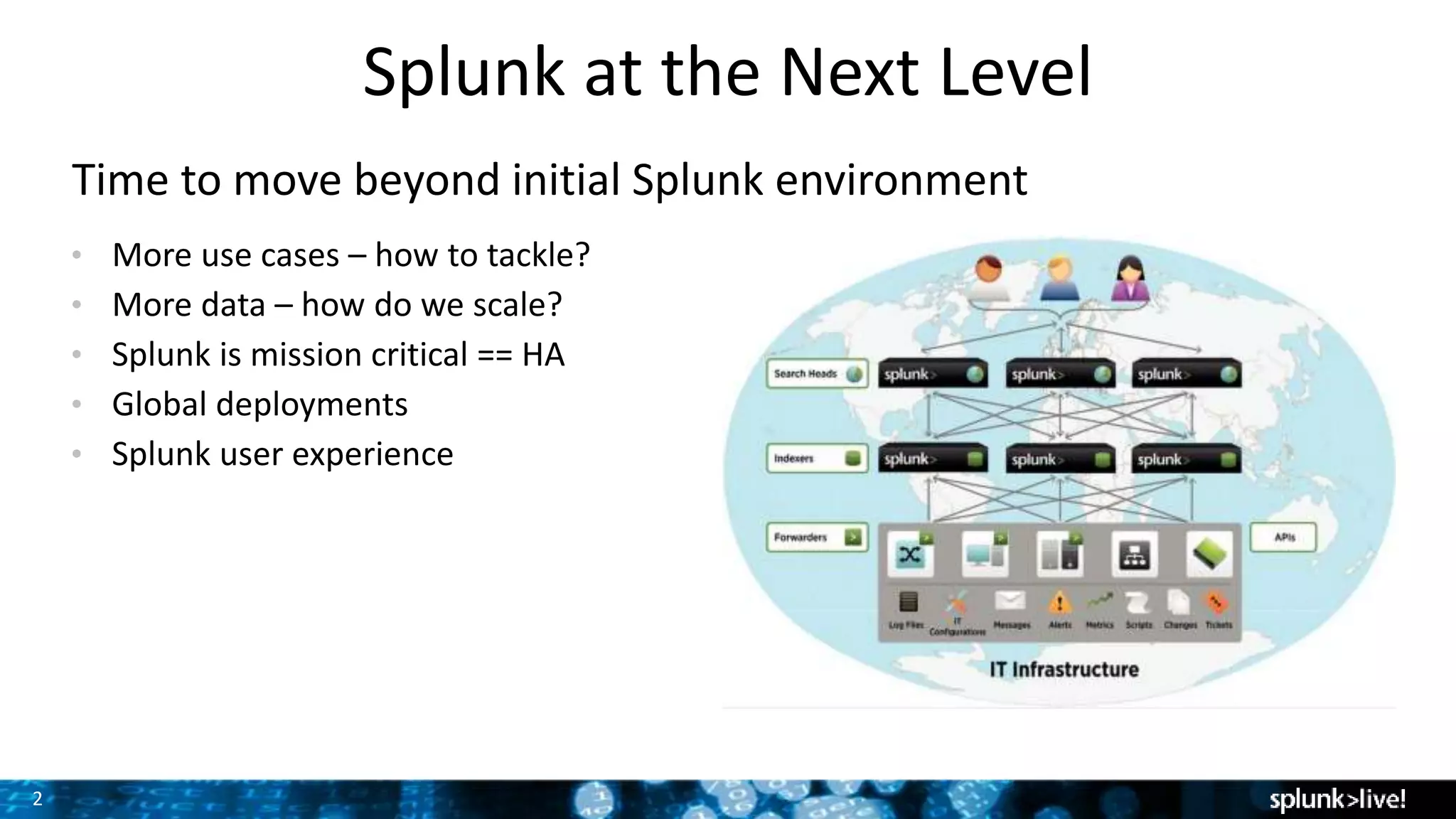
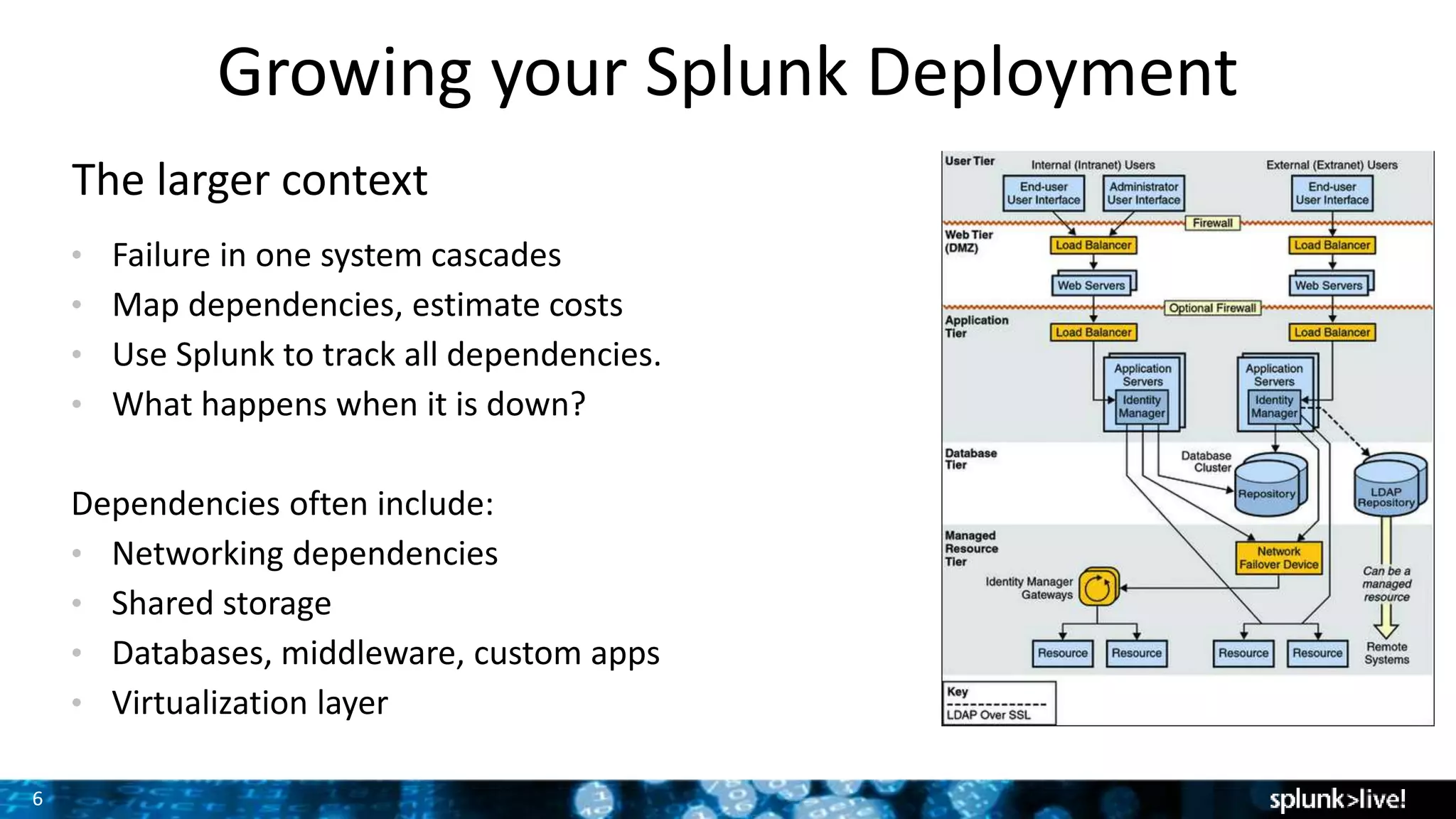
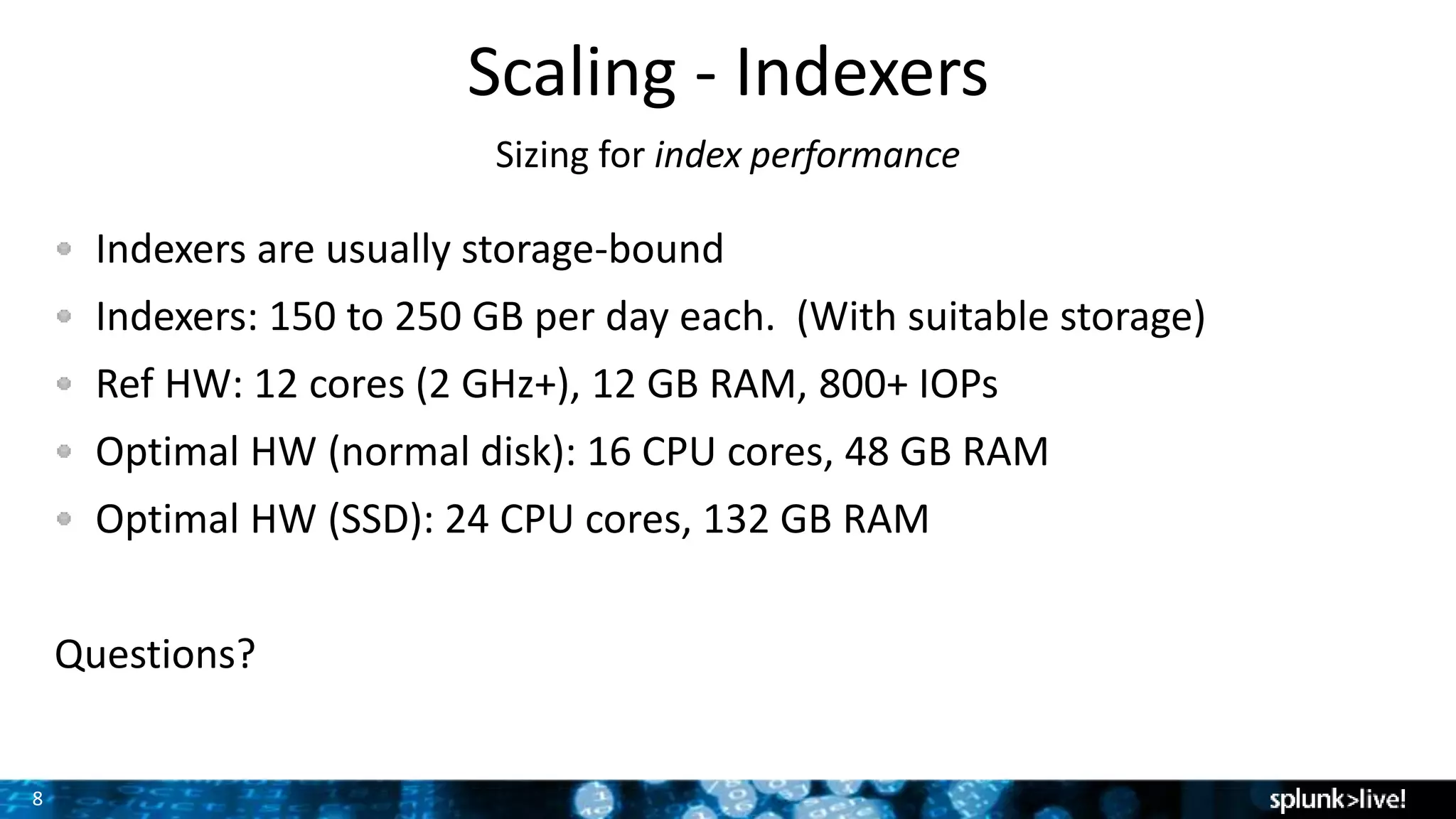
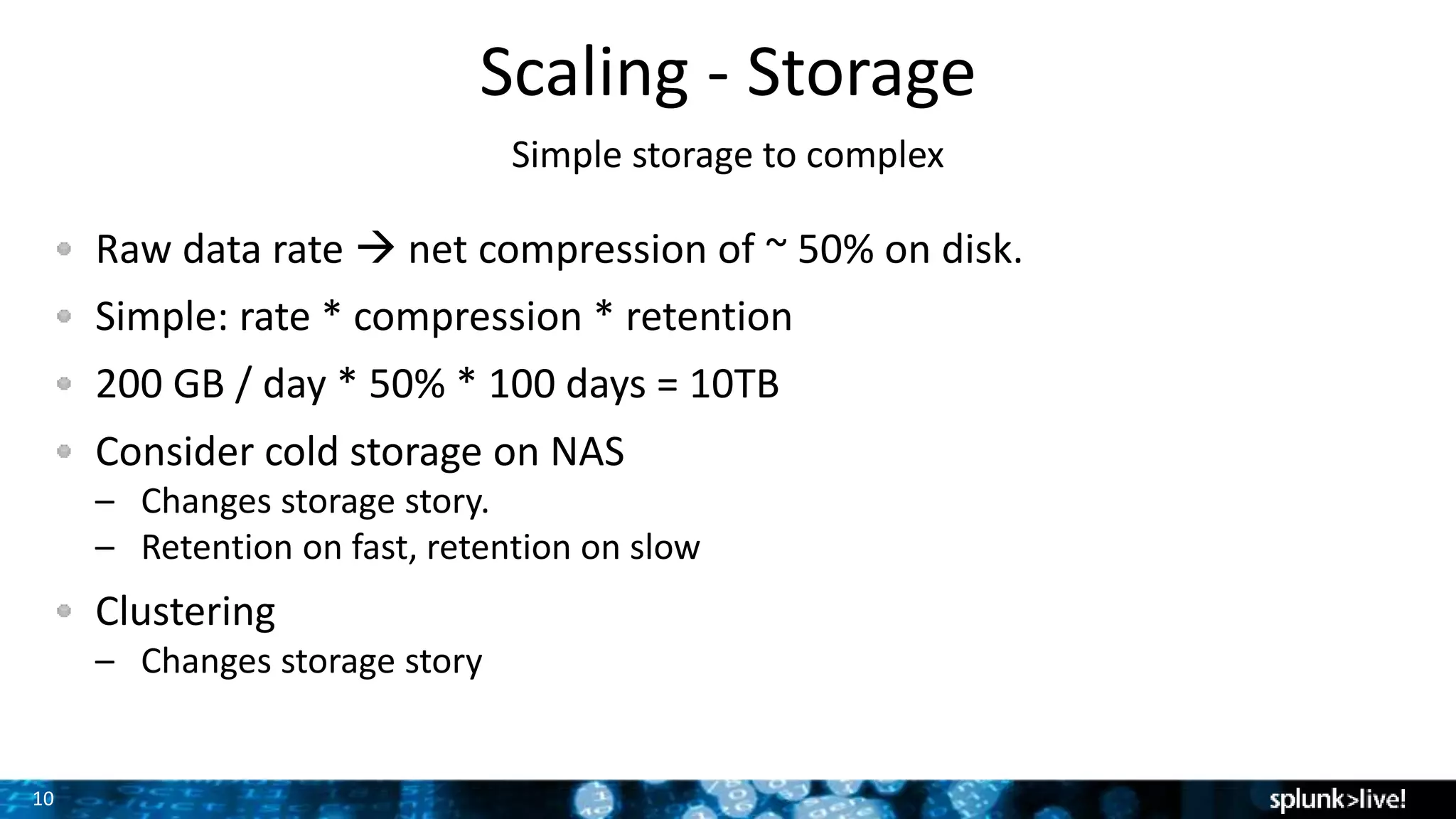
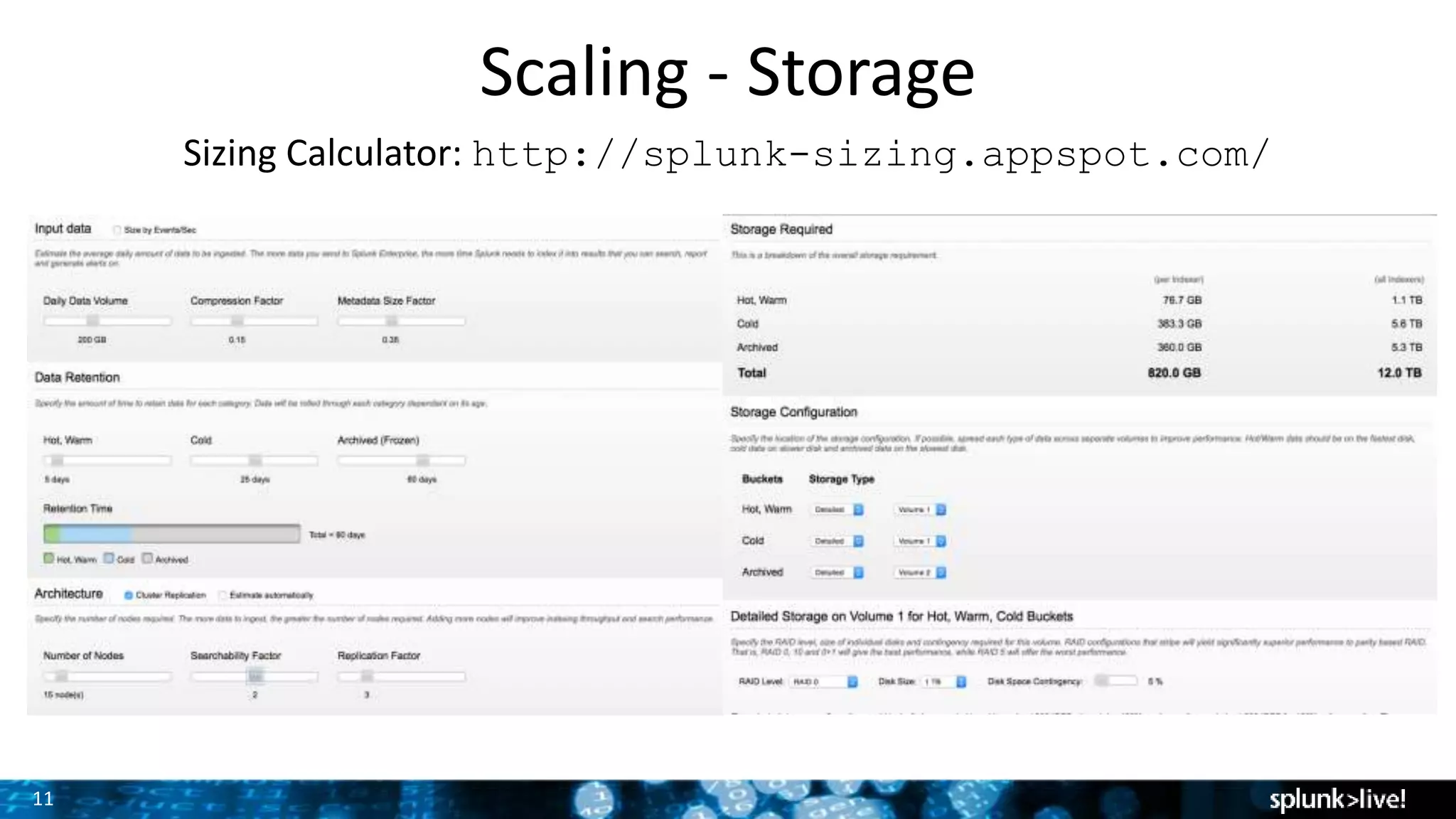
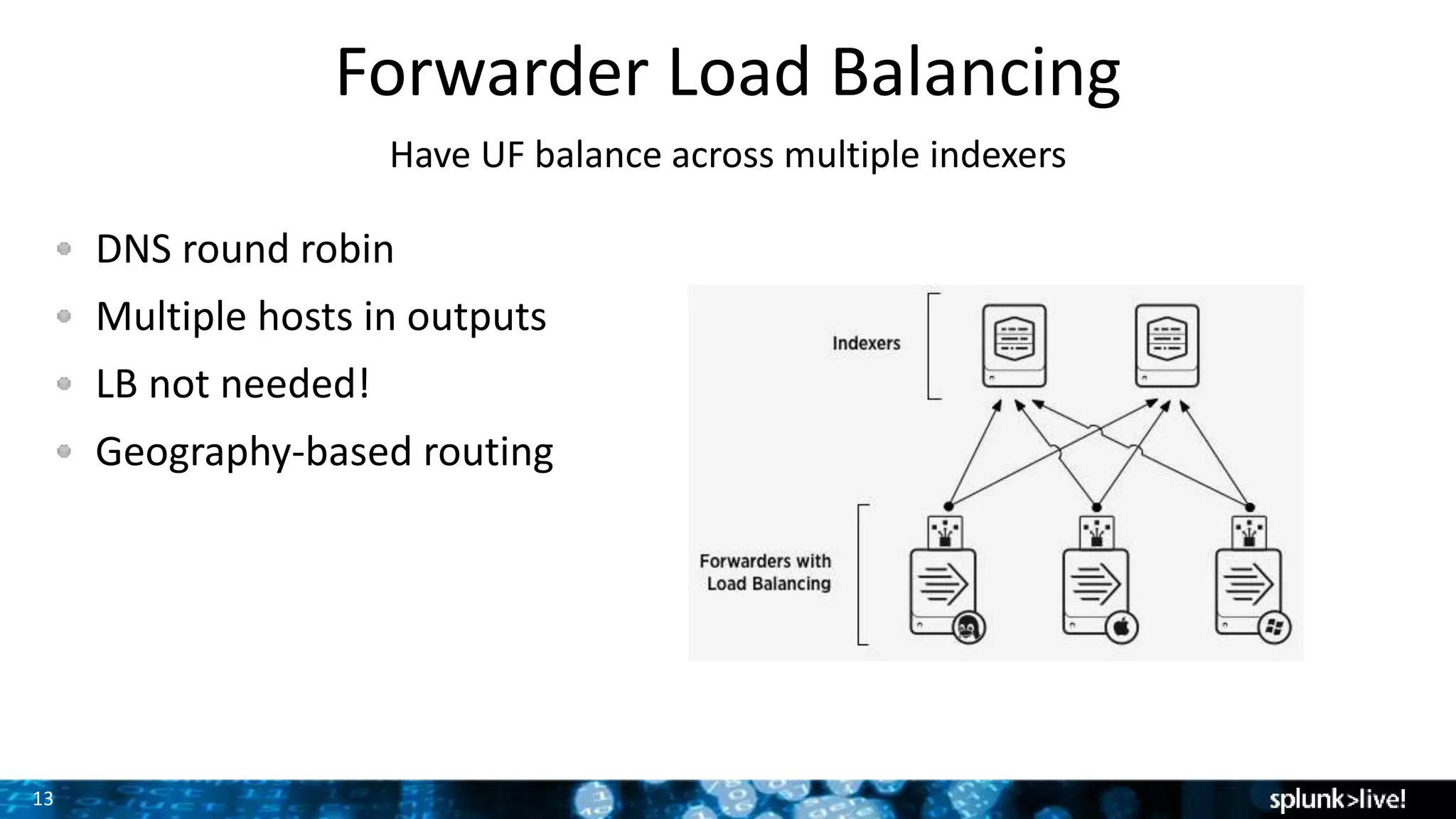
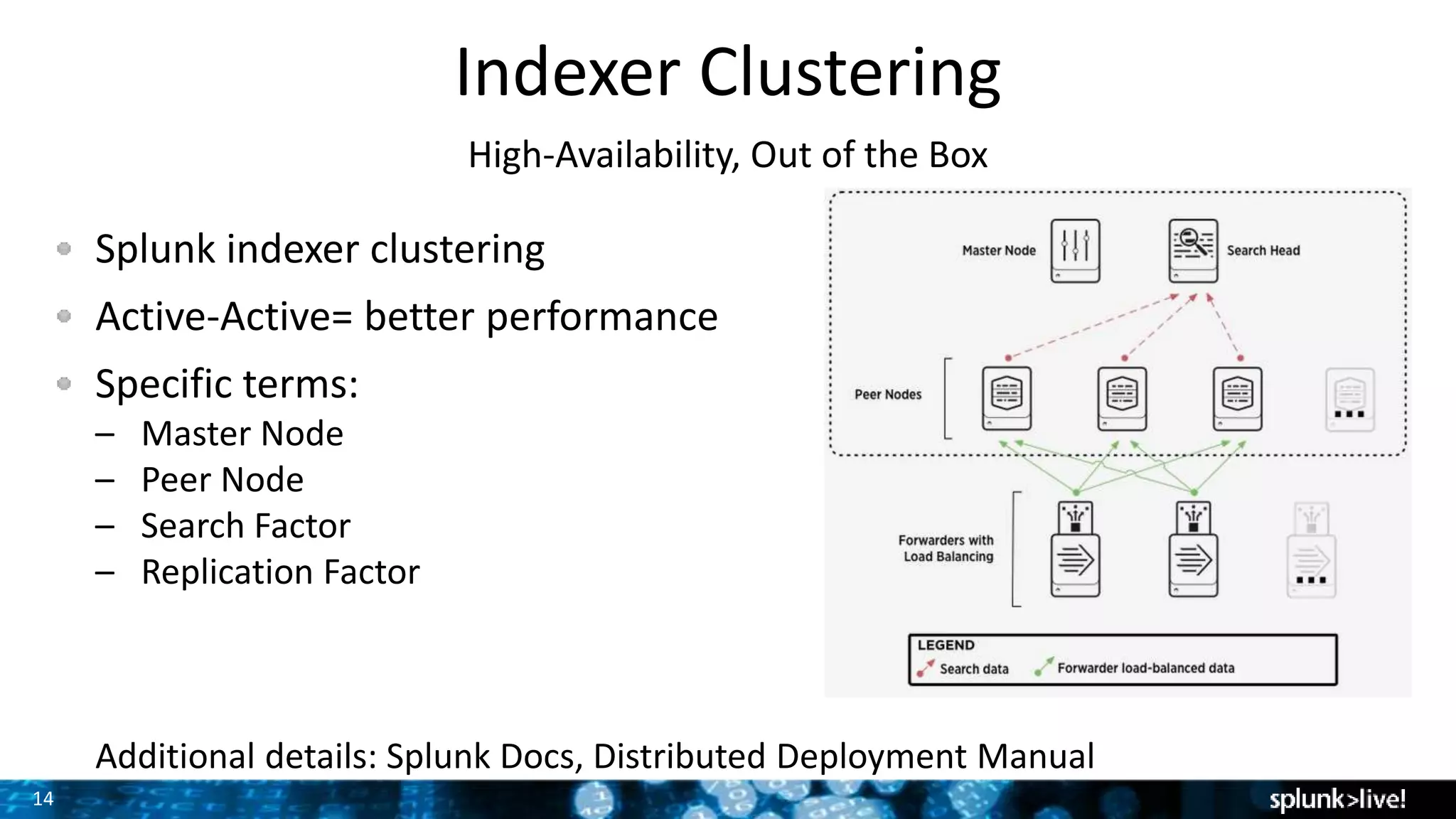
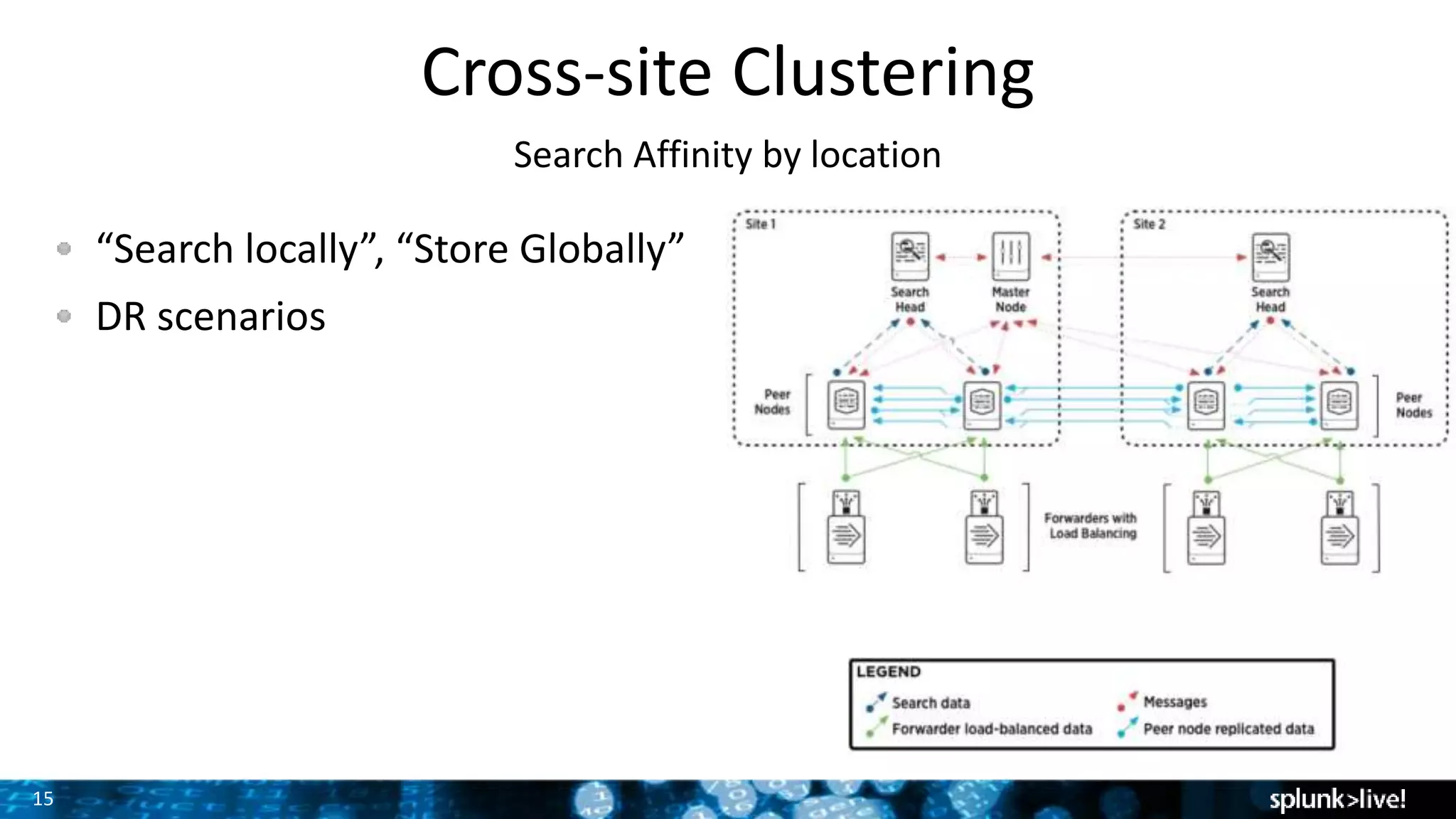
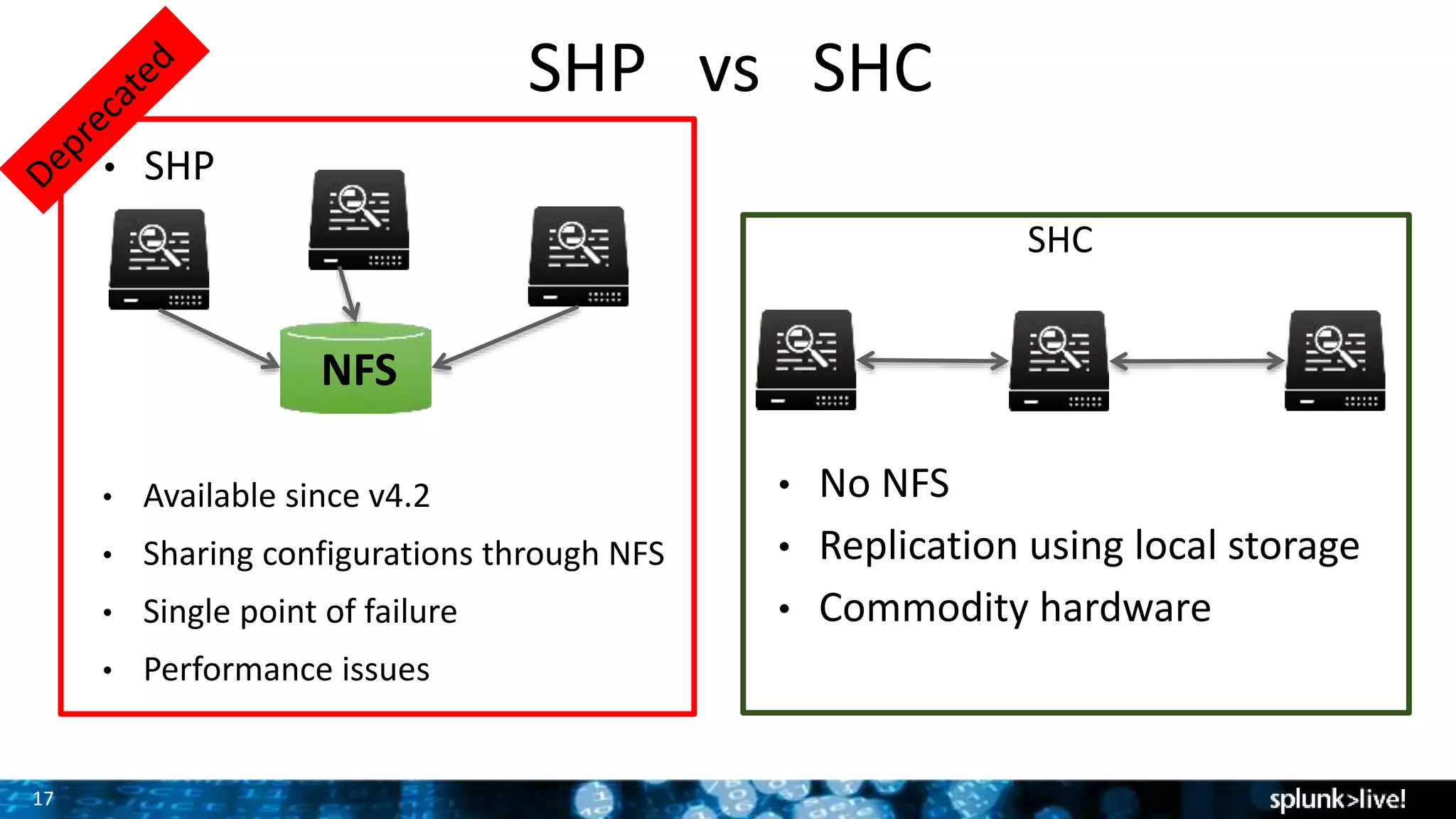
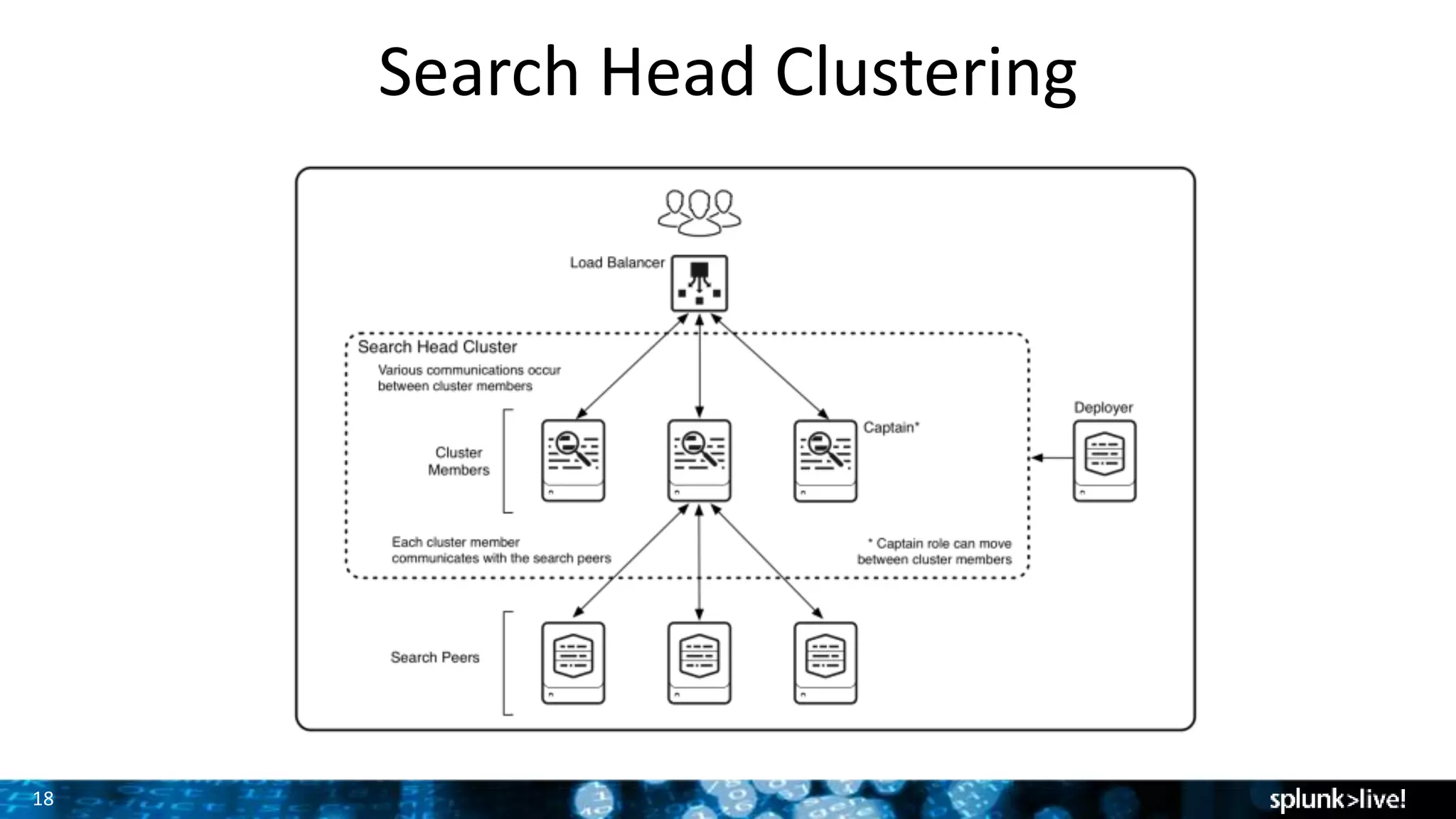
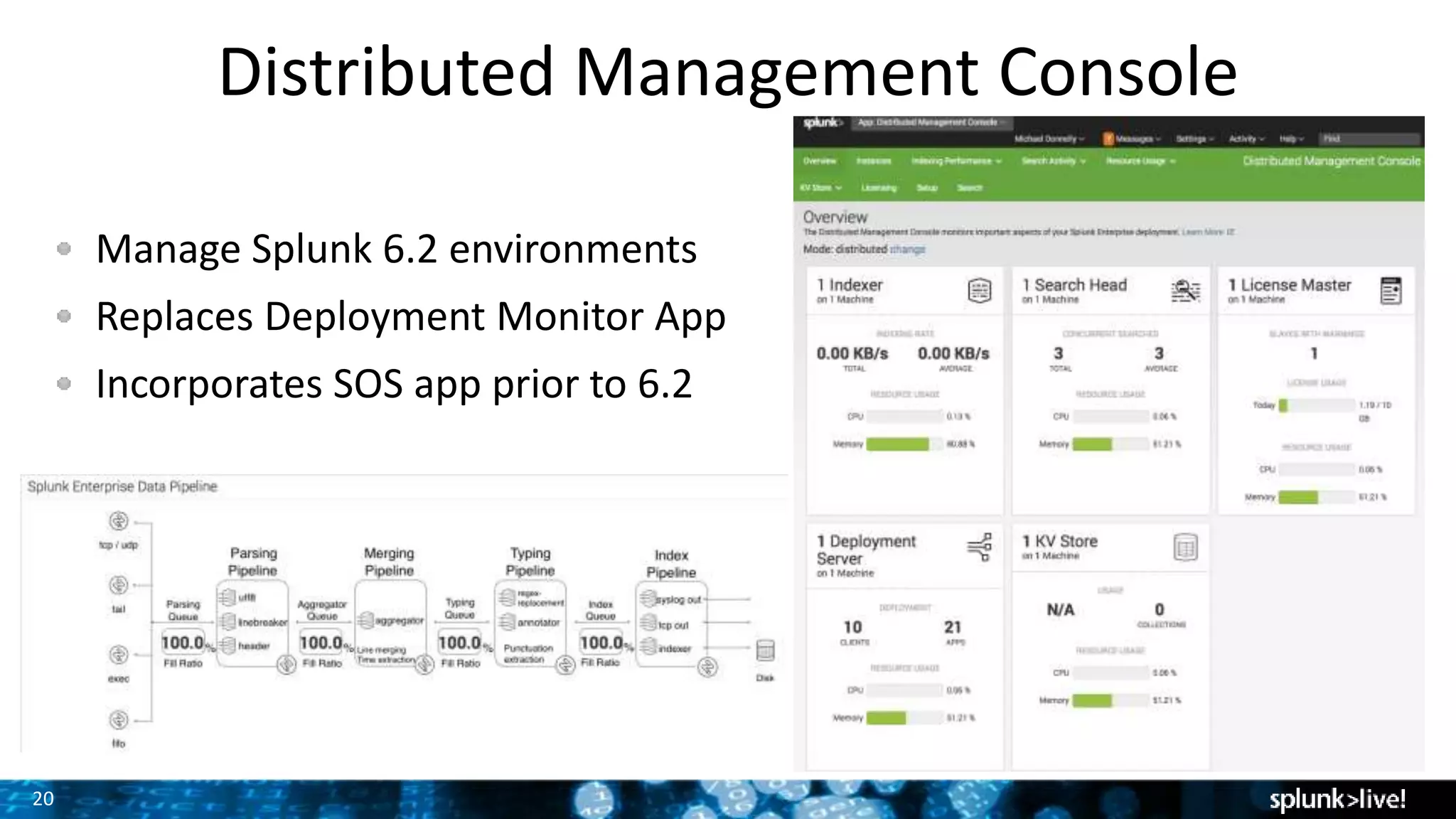
The document discusses strategies for enhancing and scaling Splunk deployments, highlighting the importance of monitoring dependencies and supporting business-critical services. It covers topics such as indexer and search head clustering, load balancing, and centralized management practices. Recommendations for optimal hardware configurations and storage solutions are provided to ensure effective performance and availability.