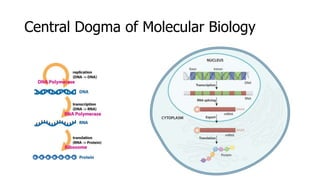
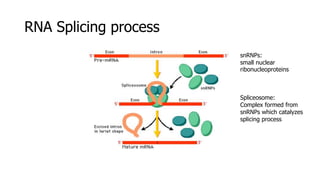
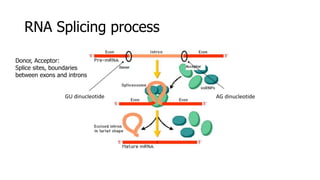
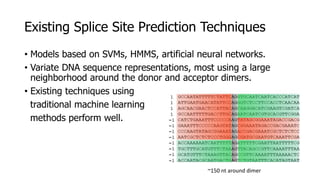
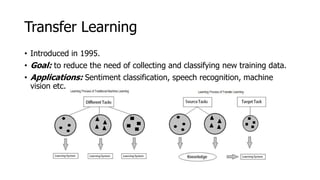
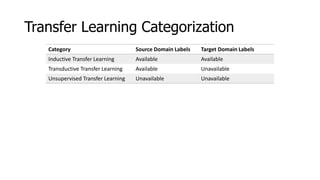
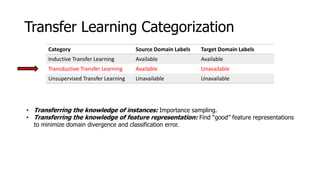
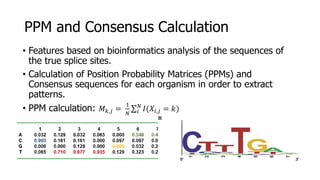
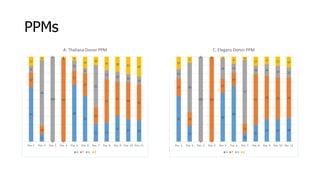
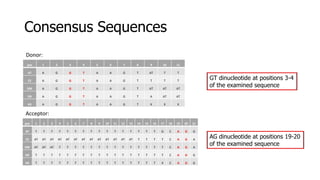
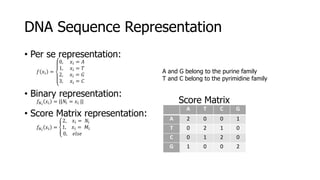
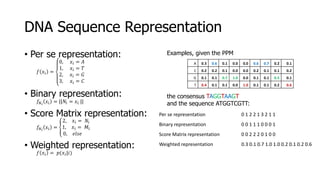
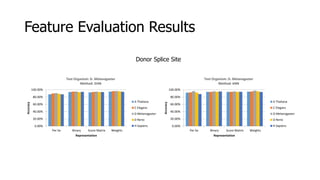
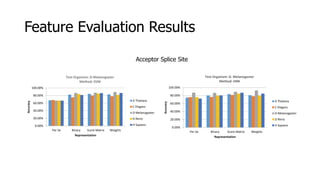
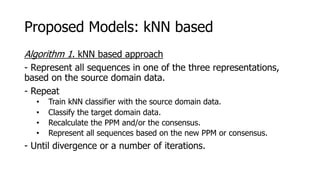
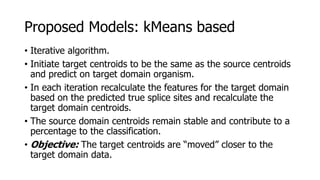
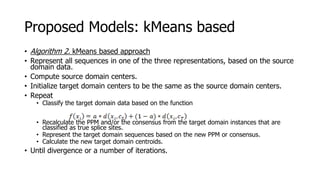
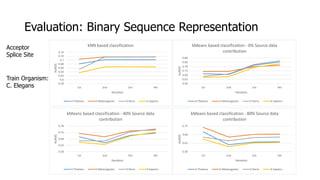
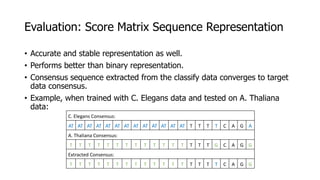
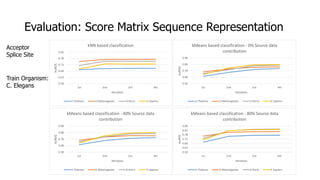
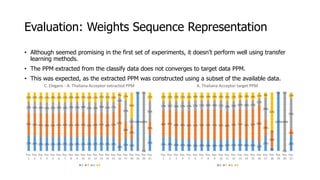
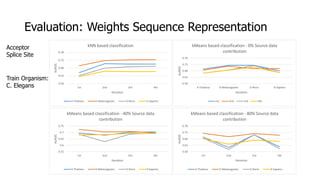
The document discusses a master's thesis on splice site recognition across various organisms using transfer learning to improve splice site prediction accuracy. It evaluates existing methods and proposes a bioinformatics analysis approach combined with traditional machine learning techniques. The findings suggest that transfer learning can enhance accuracy in predicting splice sites, particularly when substantial differences exist between source and target domain sequences.