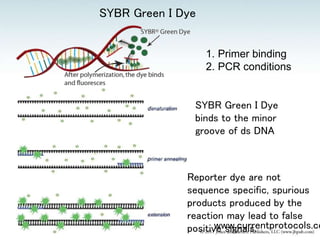
The document provides an overview of real-time PCR (polymerase chain reaction). It discusses extracting RNA from tissue, converting the RNA to cDNA using reverse transcriptase, performing real-time PCR, and analyzing the results. Several key steps are described, including the importance of RNA quality, using appropriate reverse transcriptase primers and PCR primers, including necessary controls, and selecting appropriate reference standards for normalization.