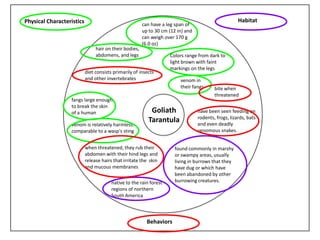
The Goliath tarantula is the largest species of tarantula. They can have a leg span of up to 30 cm and weigh over 170 grams. Their fangs are large enough to break human skin, but their venom is relatively harmless, similar to a wasp's sting. For defense, they rub their abdomens with their legs to release irritating hairs. Goliath tarantulas live in the rainforests of northern South America and prefer marshy areas, making burrows in the ground. They have dark brown or light brown coloring with faint markings and feed primarily on insects but are also known to eat small vertebrates.