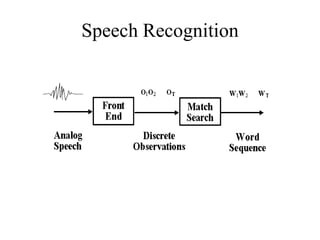
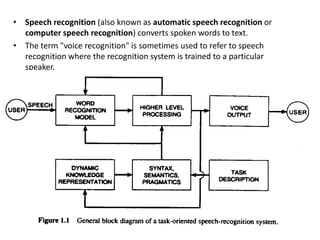
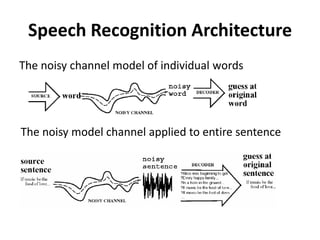
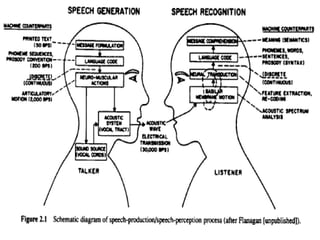
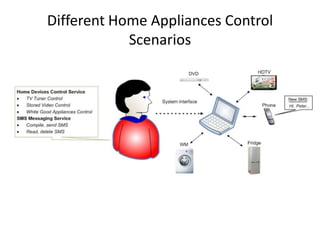
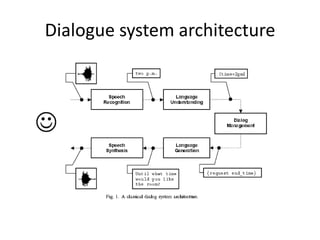
Speech recognition converts spoken words to text through techniques like cepstral analysis and hidden Markov models. It has applications in voice commands, data entry, document preparation, translation, and more. Speech recognition systems work by extracting features from audio then using probabilistic models to find the most likely sequence of words given the input sounds. Dialog systems play a key role in conversational interfaces like home appliance control by understanding speech, maintaining discourse context, and determining appropriate system responses.