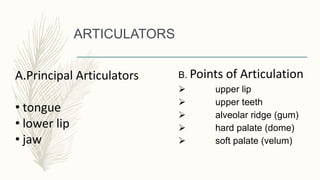
Respiration provides the energy for speech through breathing. There are two phases of respiration: inhalation where the diaphragm draws air into the lungs and exhalation where air is forced back out. Phonation occurs when the larynx catches the exhaled breath and the vocal folds transform it into sound, influencing pitch, loudness, and quality. Resonance is the modification and amplification of sound through organs like the pharynx, nose, and mouth. There are two types of resonance: sympathetic and conductive. Articulation is the process where vocal sounds become speech sounds through articulators like the tongue, lips, and jaw acting on various points of articulation including the alveolar ridge and soft palate