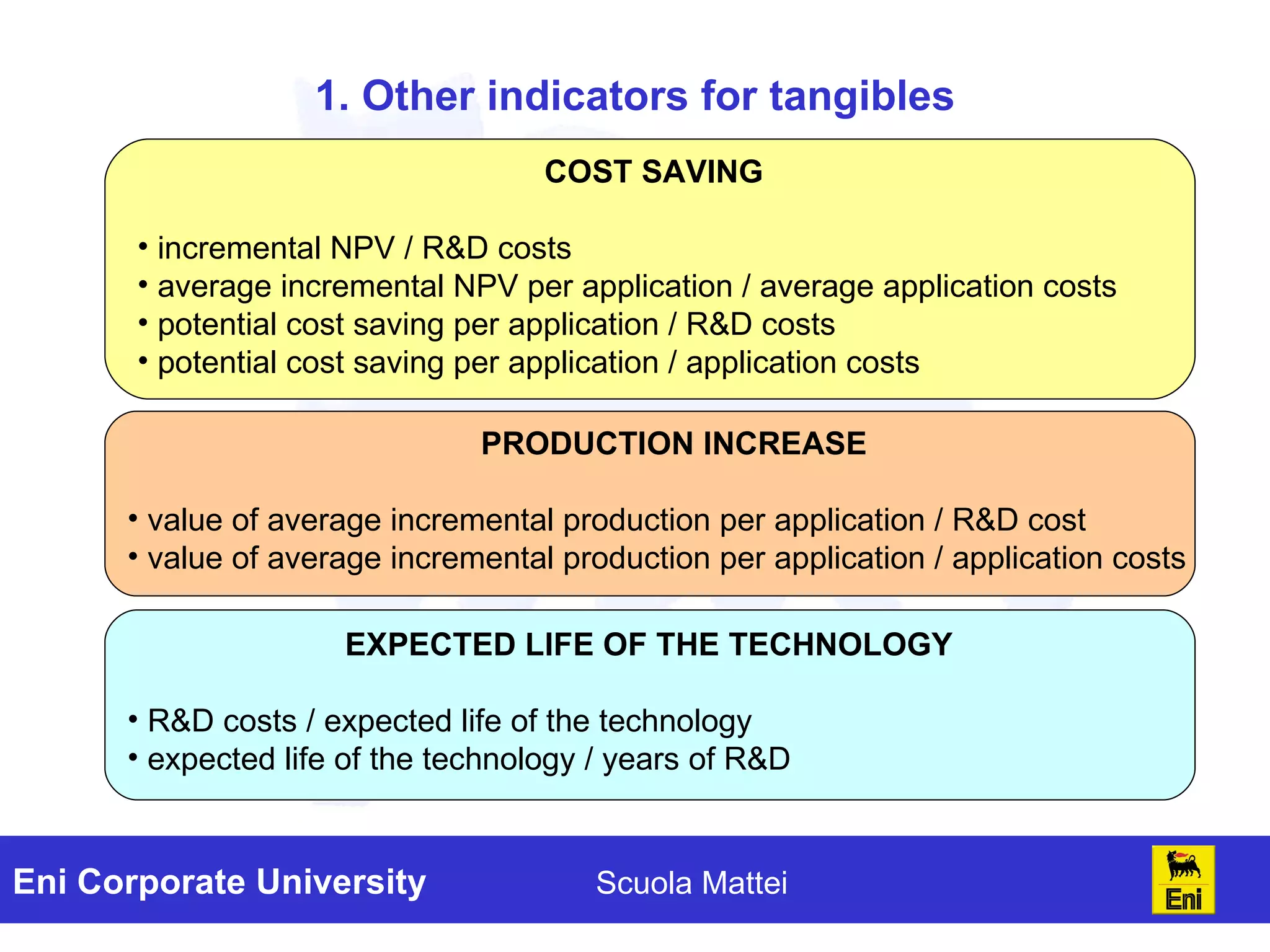
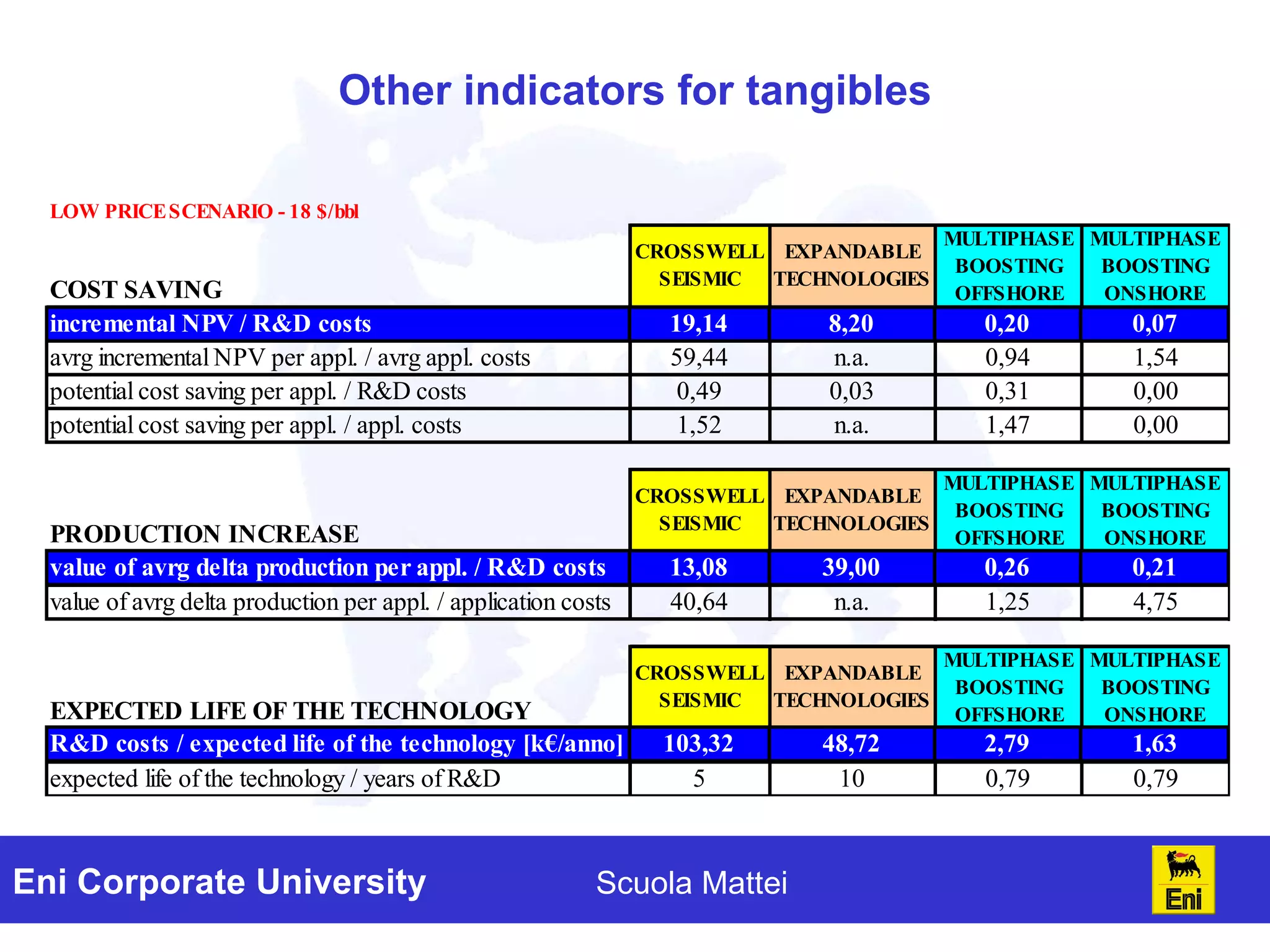
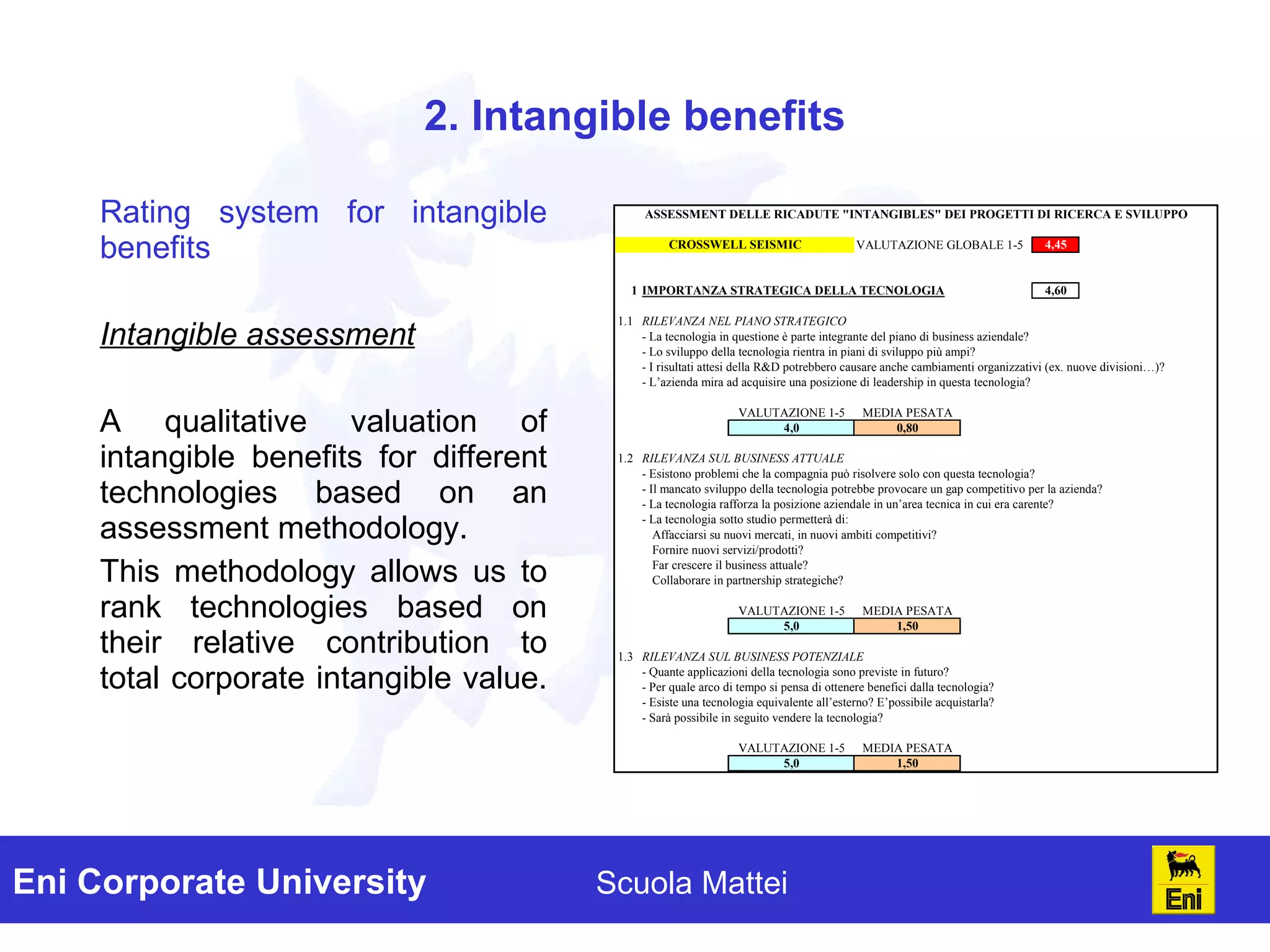
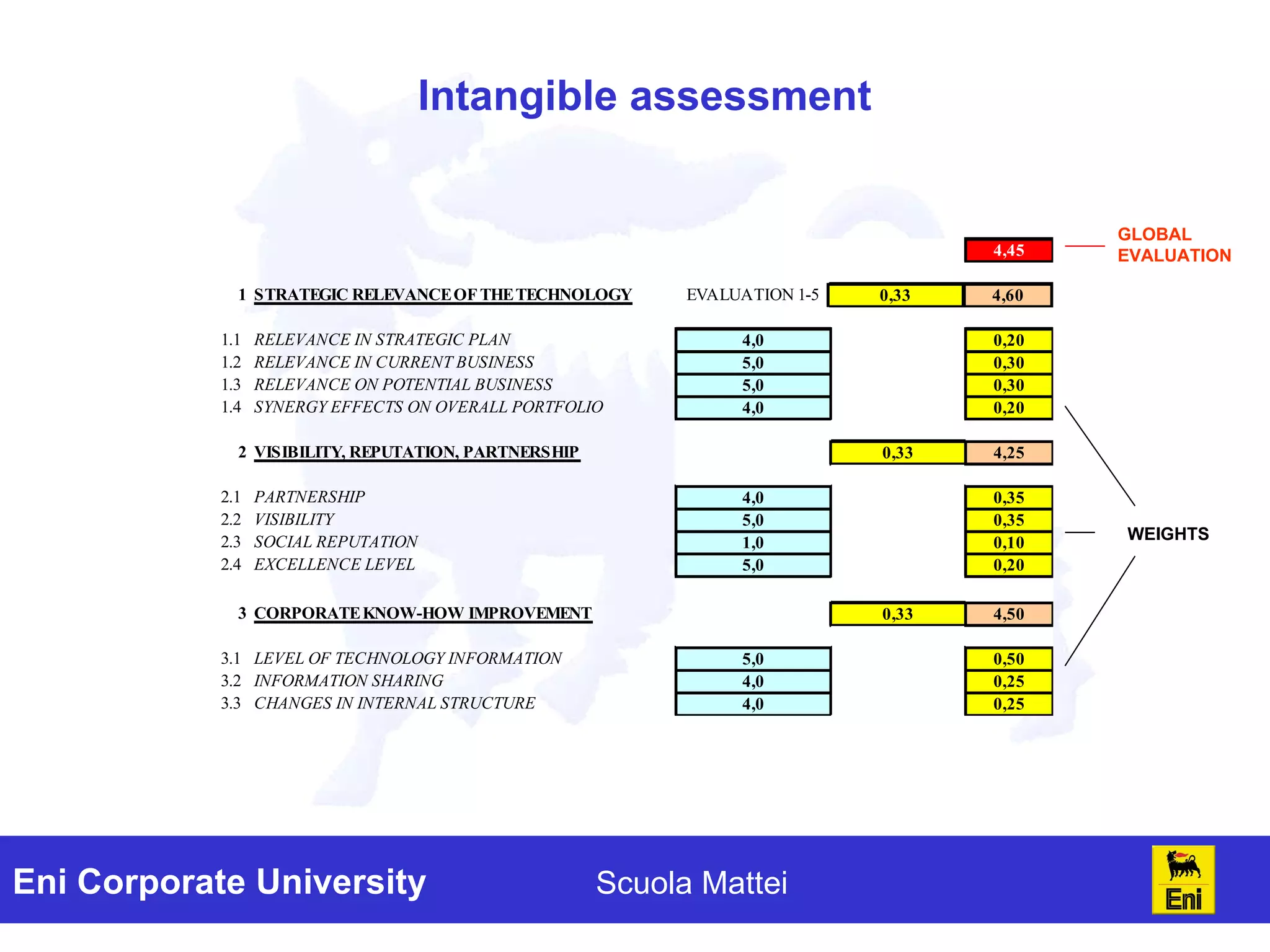
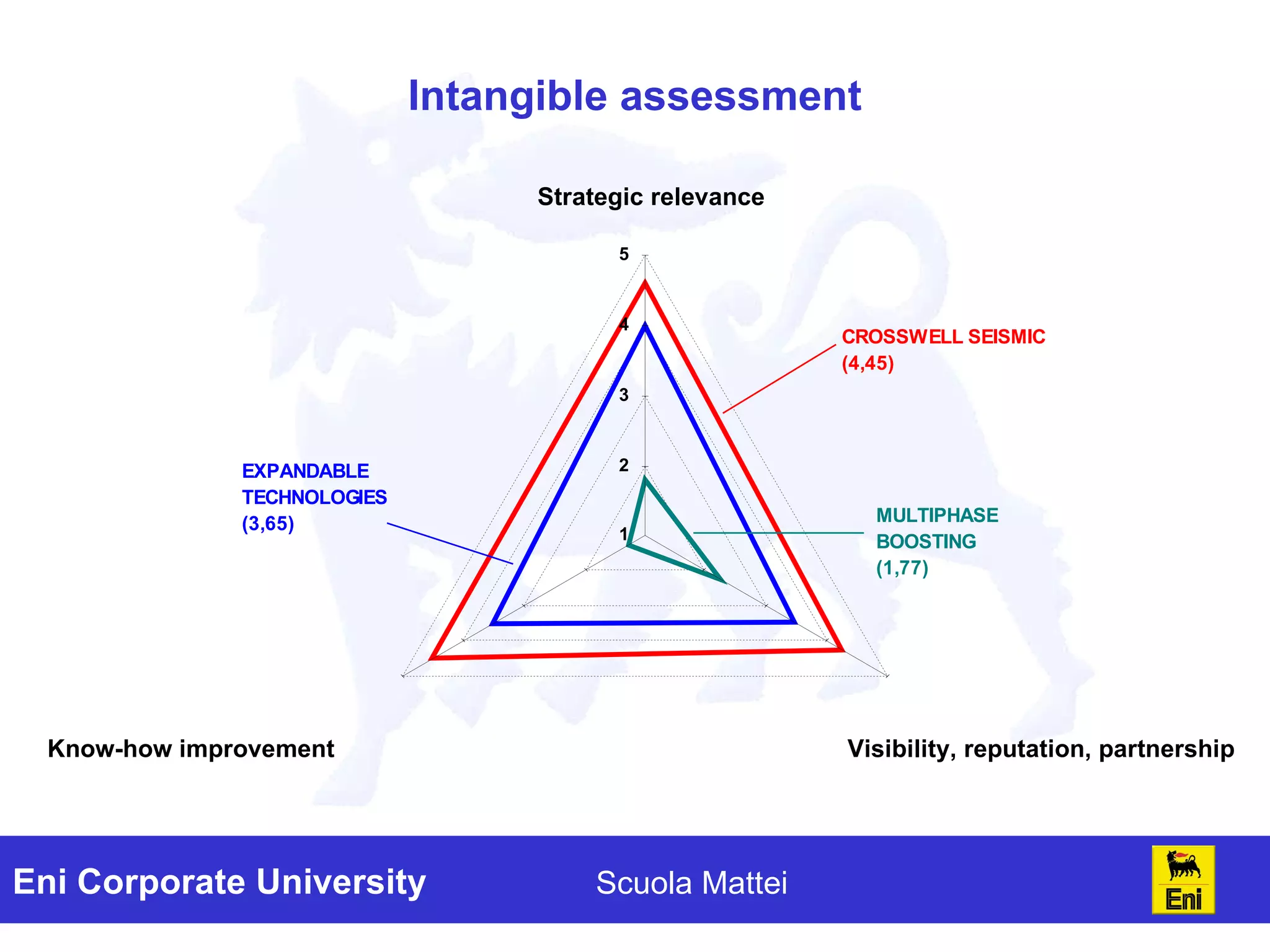
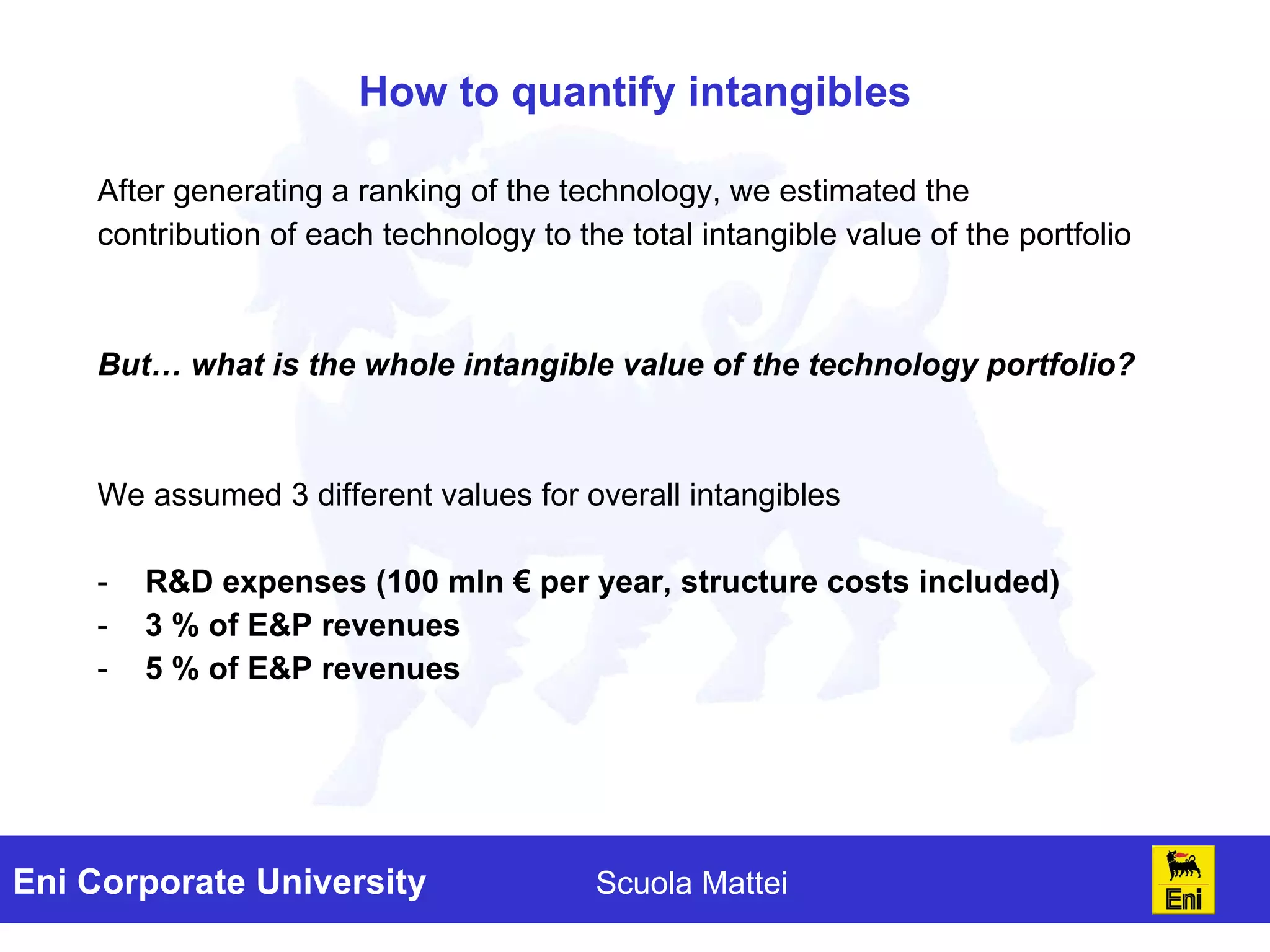
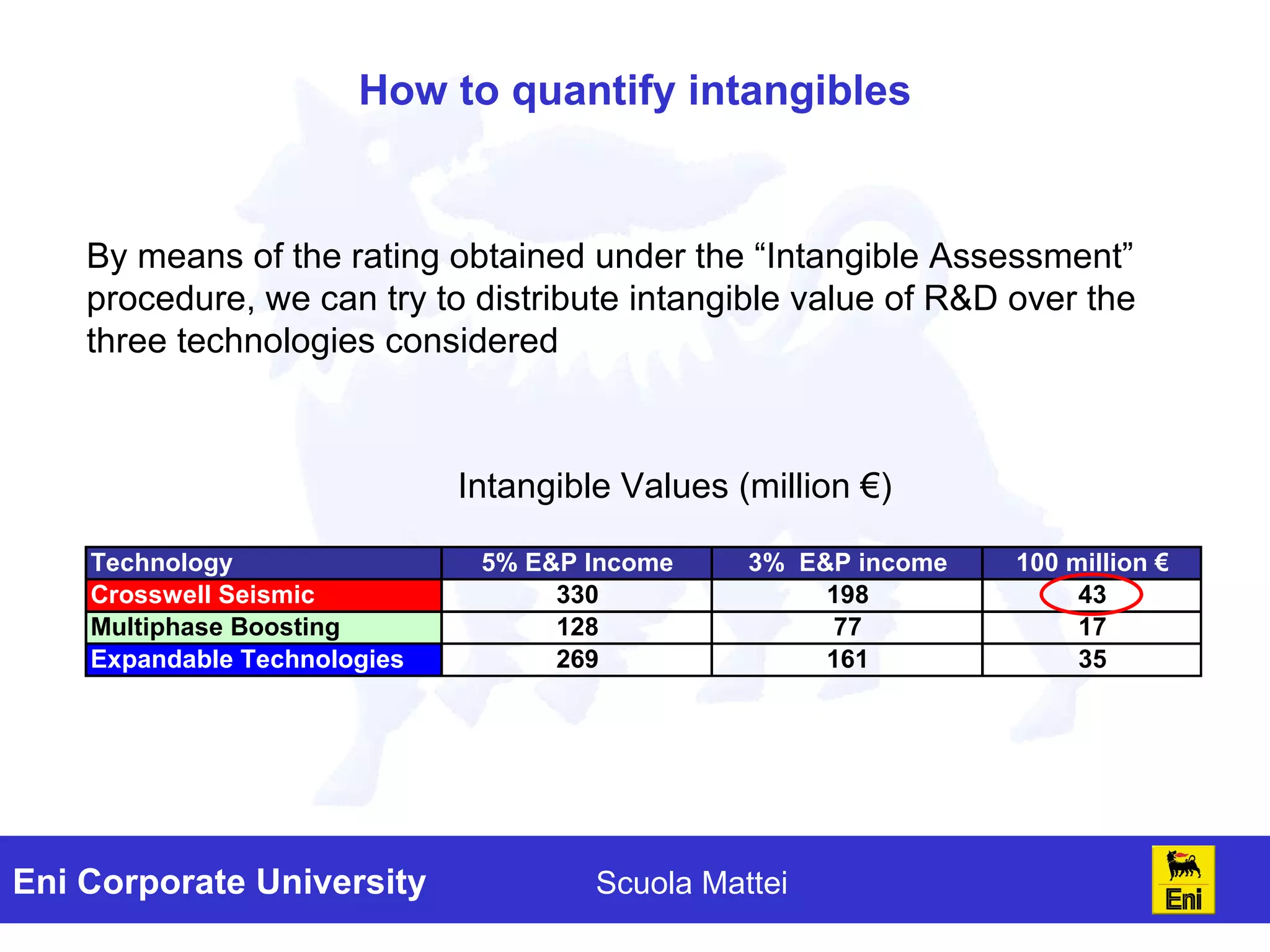
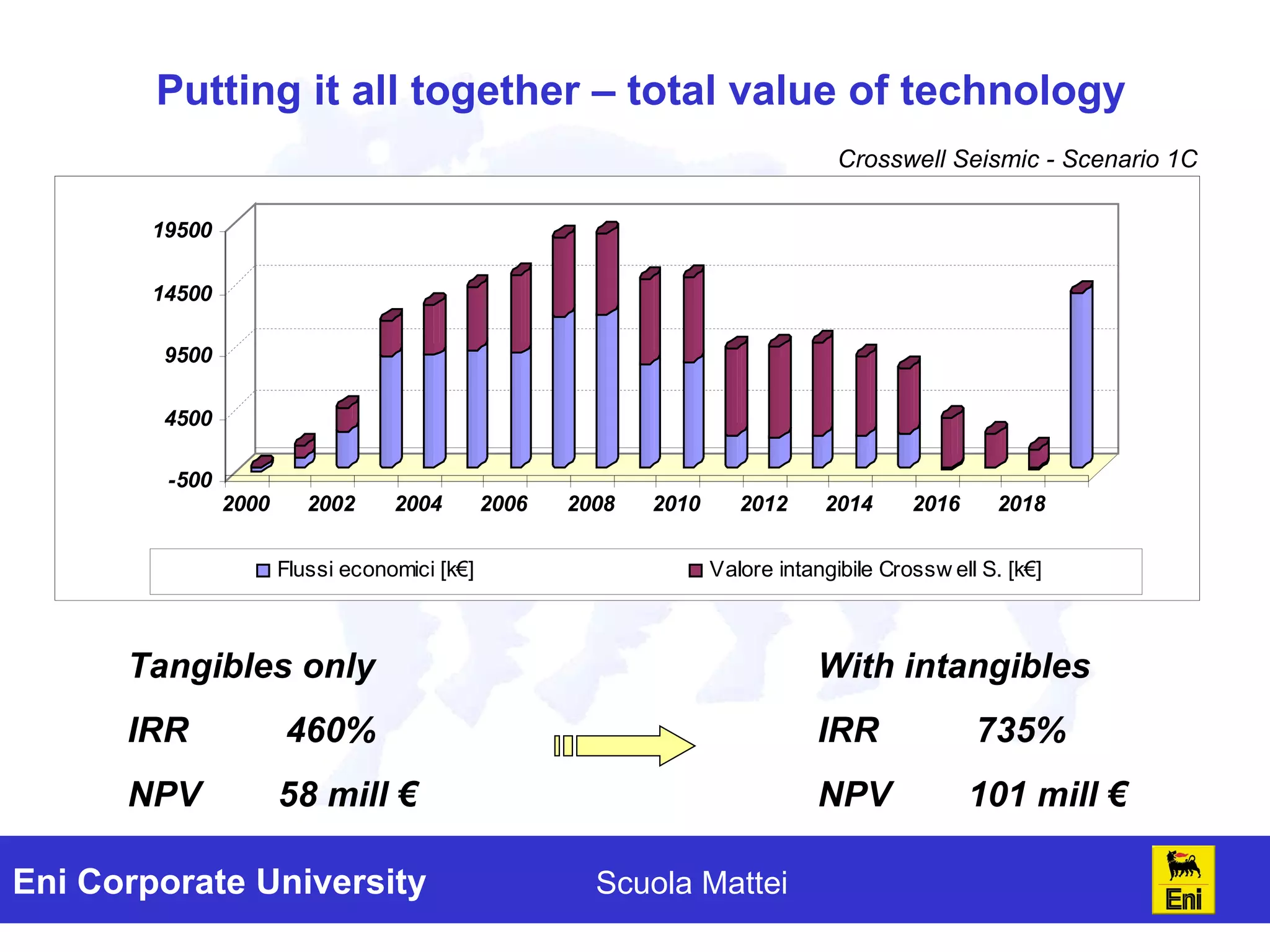
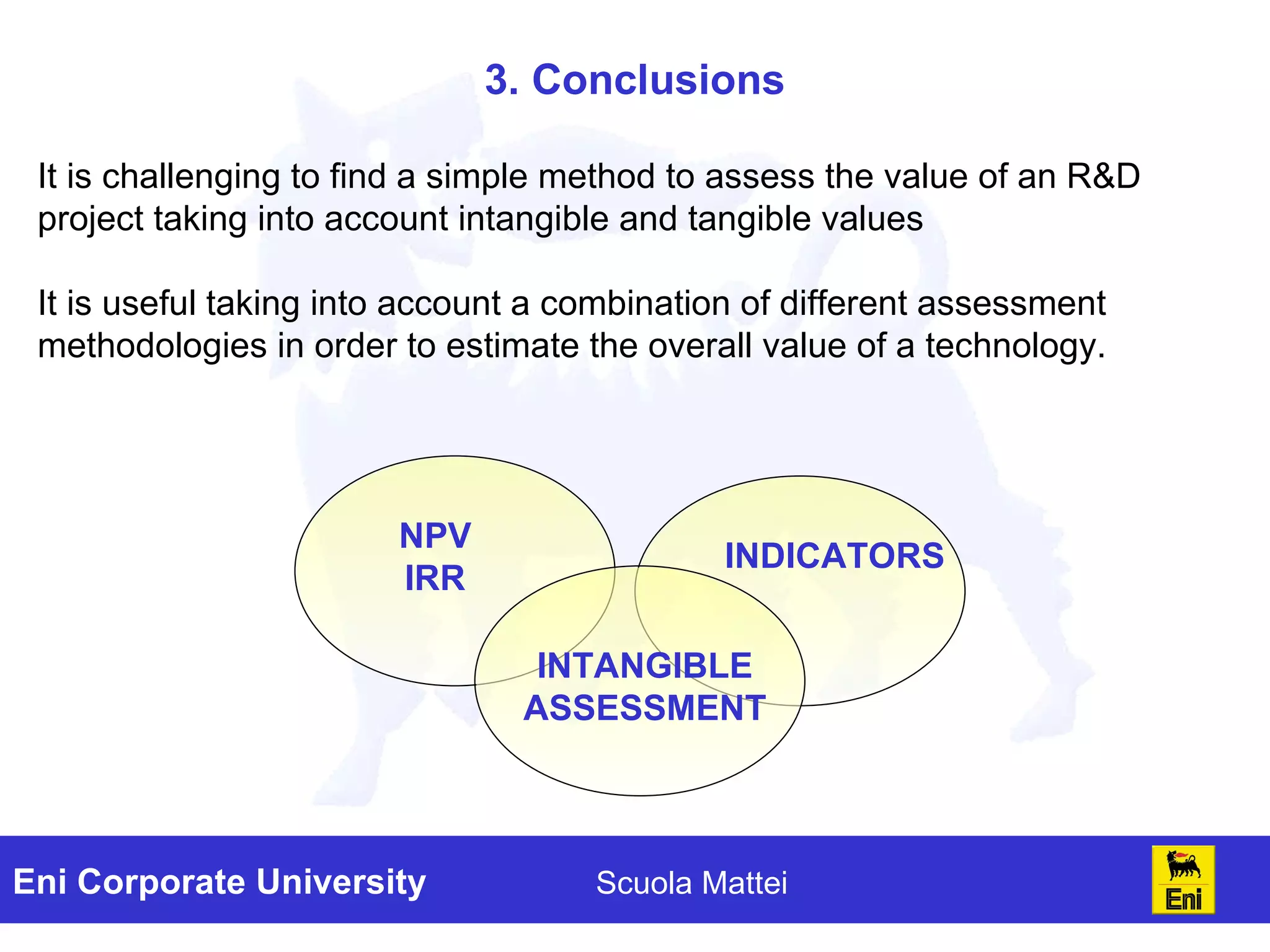
The document discusses the evaluation of technology investments beyond traditional metrics like NPV and IRR, emphasizing the importance of intangible benefits and alternative indicators. It introduces various methods for assessing intangibles, such as market capitalization and brand valuation, and proposes a qualitative ranking system for technologies based on their contribution to corporate value. The conclusion highlights the complexity of accurately valuing R&D projects, suggesting a mix of methodologies for a comprehensive assessment.