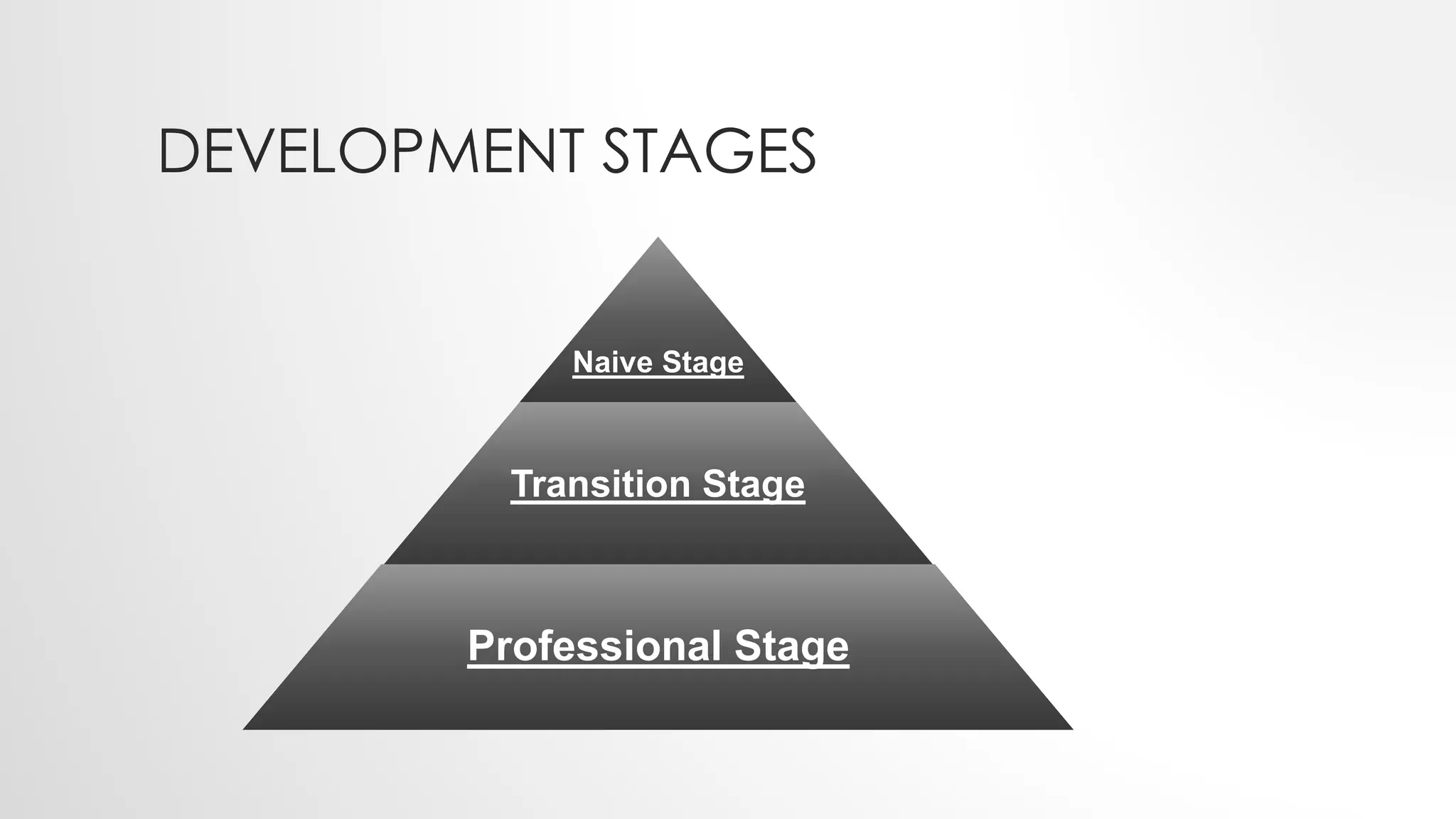
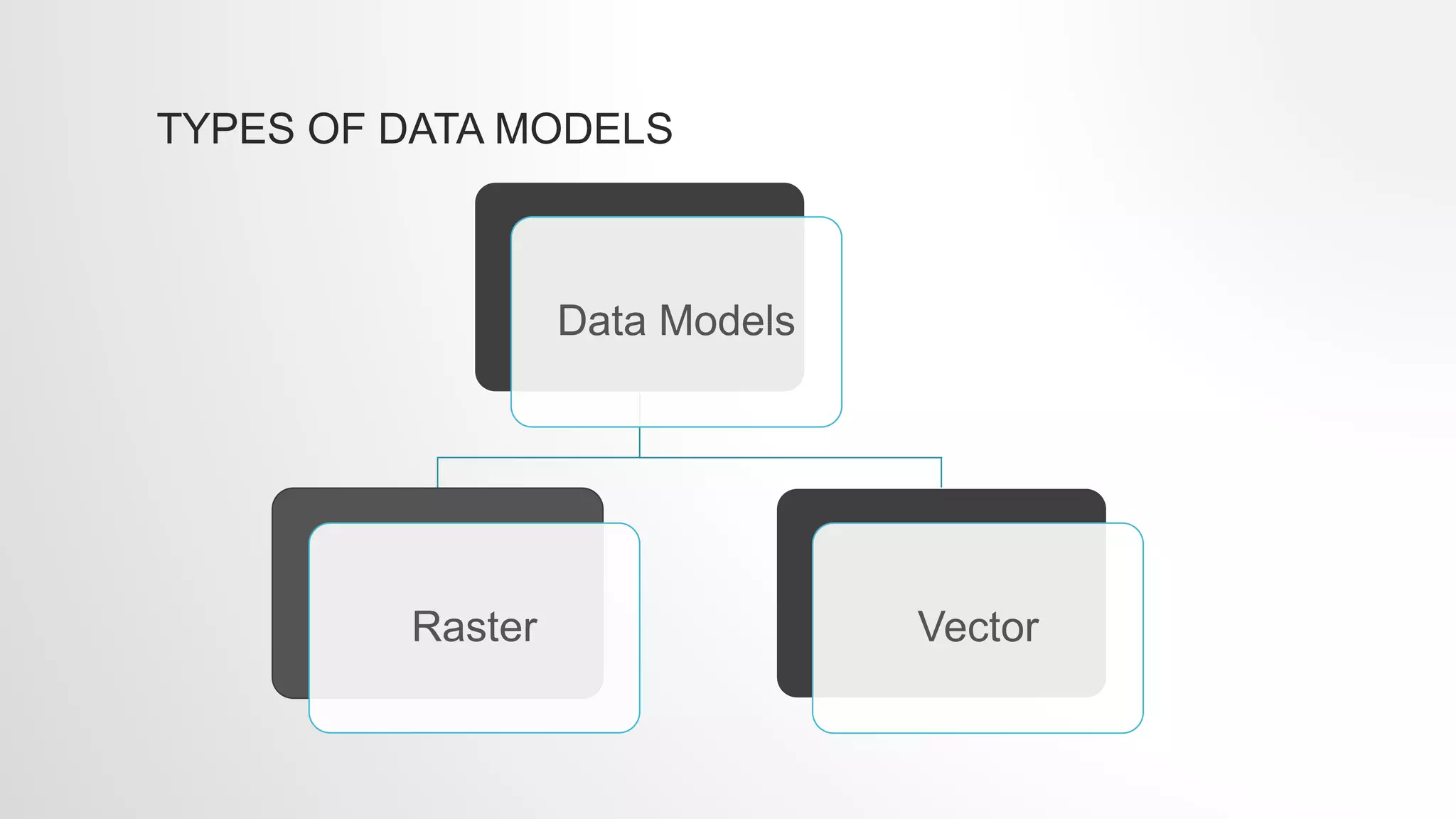
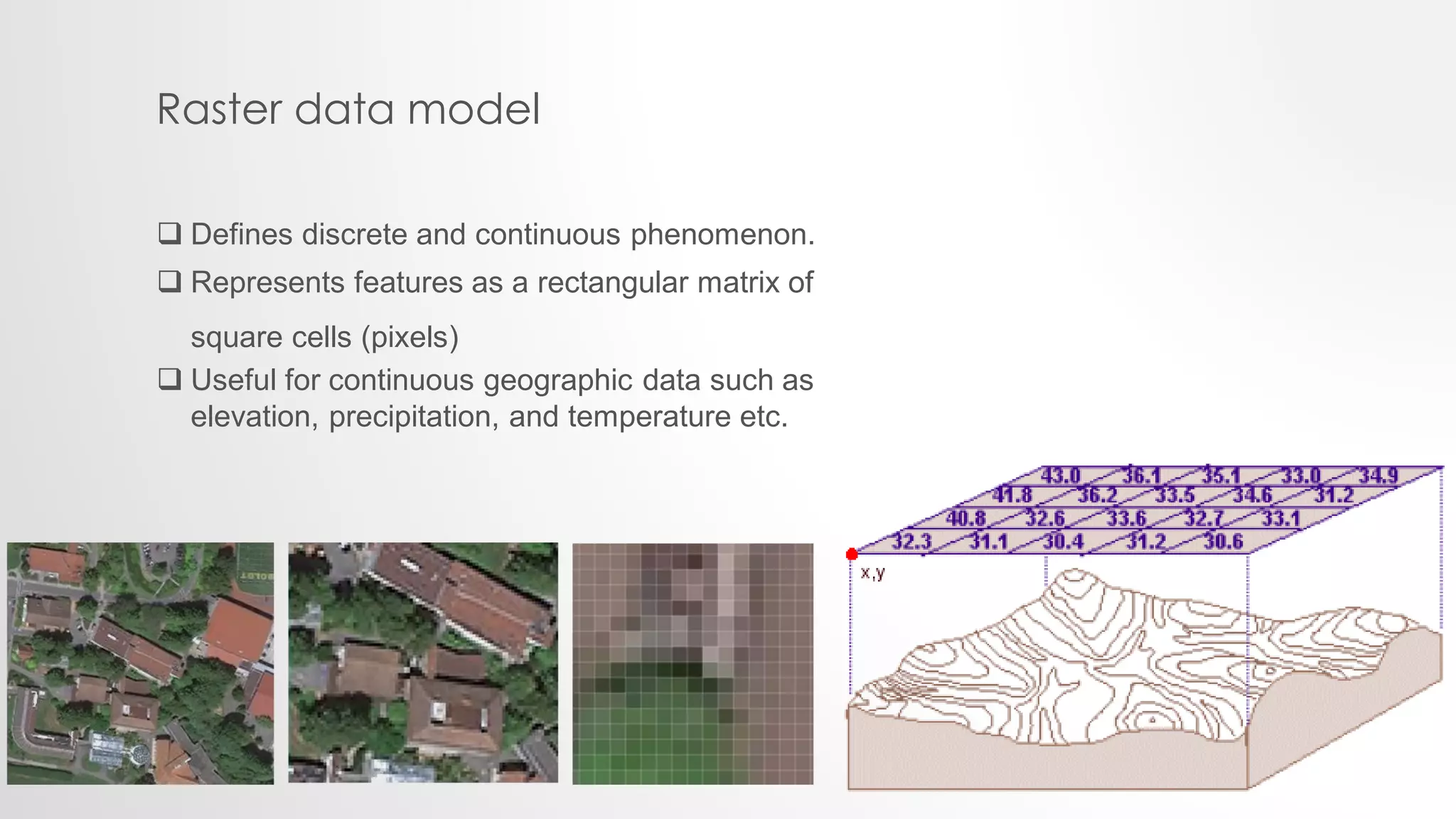
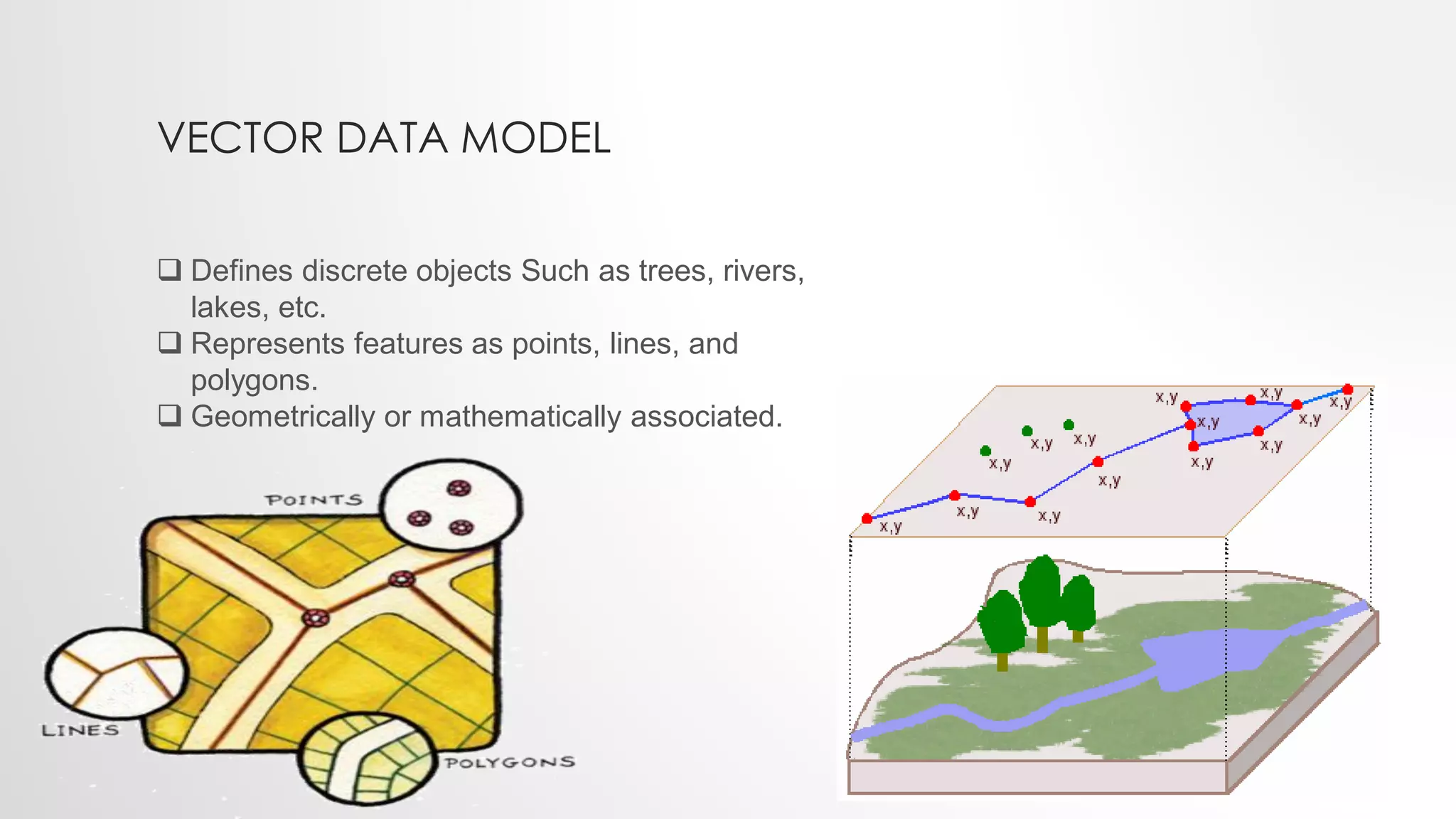
The lecture by Sadia Sheikh discusses spatial data modeling, covering types of spatial phenomena (discrete and continuous), their development stages (naive, transition, and professional), and types of data models (raster and vector). Discrete data includes distinct objects like roads, while continuous data encompasses phenomena like elevation. The lecture emphasizes the importance of data models in representing spatial information accurately.