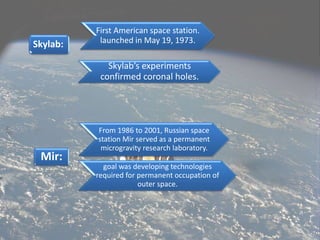
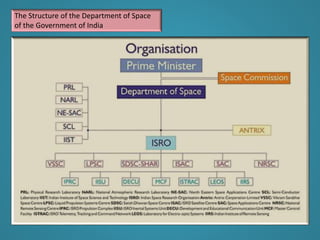
Space research involves scientific studies carried out in outer space using scientific equipment. It includes various disciplines like Earth science, materials science, biology, medicine, and physics. Space research emerged after World War II based on advancing rocket technology and includes fields like earth observations, geodesy, space physics, planetology, astronomy, materials sciences, life sciences, and physics. Some notable space research missions and satellites include the Upper Atmosphere Research Satellite, International Gamma-Ray Astrophysics Laboratory, Hubble Space Telescope, Salyut 1, Skylab, and Mir space stations. India has also made significant contributions to space research through organizations like ISRO.