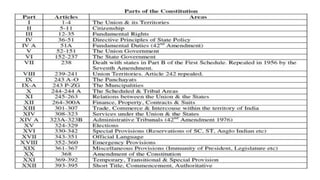
The document provides a comprehensive overview of the evolution of Indian polity and constitution, detailing the legislative framework, historical background, and landmark laws from British rule to independence. It highlights key acts and amendments that shaped India's governance including the Government of India Act, 1935, and the Indian Independence Act, 1947, leading to the formation of the Constitution on January 26, 1950. Additionally, it discusses the structure of fundamental rights, directive principles of state policy, and fundamental duties as enshrined in the Constitution.