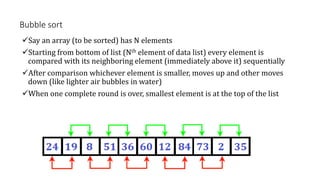
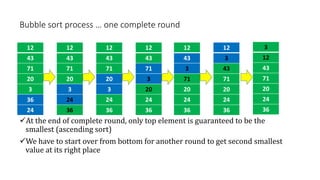
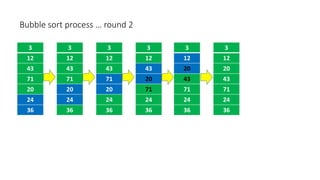
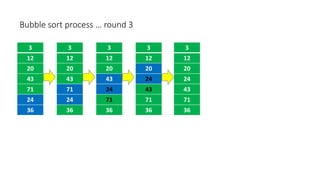
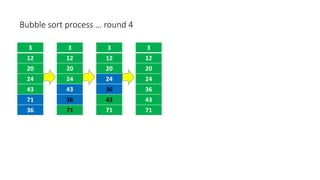
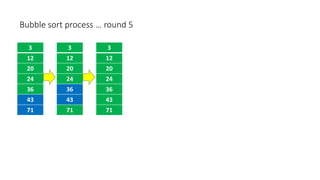
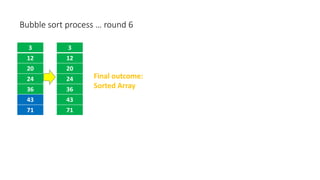
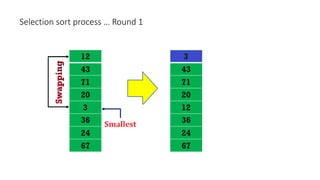
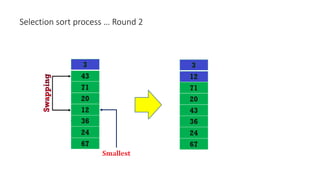
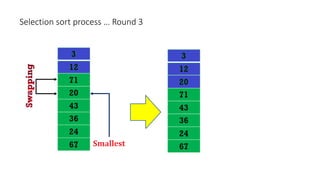
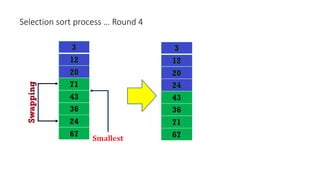
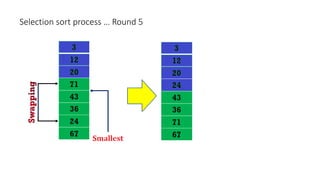
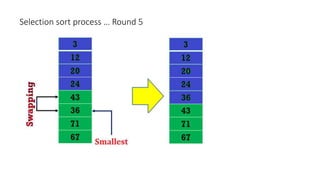
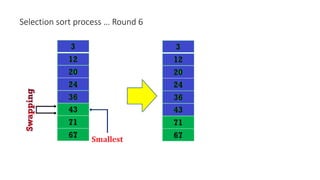
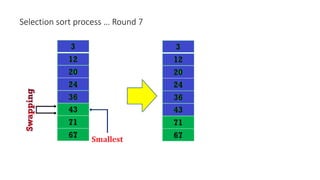
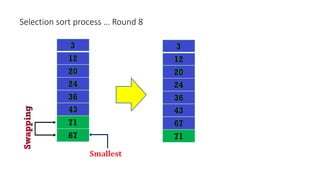
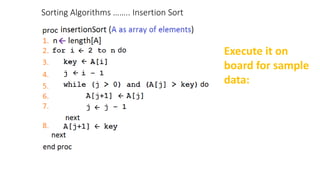
The document discusses three sorting algorithms - insertion sort, selection sort, and bubble sort. It provides descriptions of the sorting processes for each algorithm along with code examples and characteristics. Videos are also included to demonstrate how each algorithm works through animations of the sorting process.





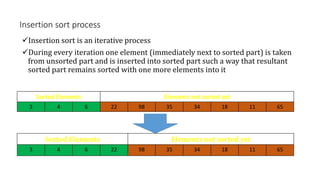
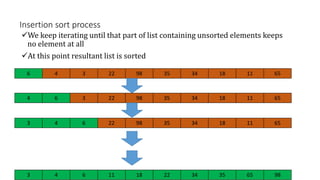

![Insertion Sort … C++ Code
int data[MAX]={10, 25, 90, 5, 61, 44, 82, 72, 38,
59};
int n = MAX-1, key, j, i;
for(i=1; i<MAX; i++){
key = data[i];
j = i-1;
while(j>=0 && data[j] > key){
data[j+1]=data[j]; j--;
}
data[j+1]=key;
}
for(i=0; i<MAX;i++){
std::cout<<data[i]<<",";
}
Execute it on board for
given data:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsweek7-221201171150-39db8385/85/Data-structure-pptx-11-320.jpg)