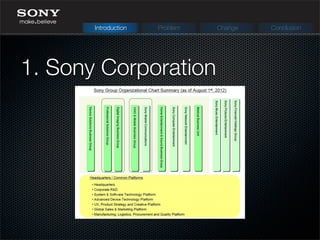
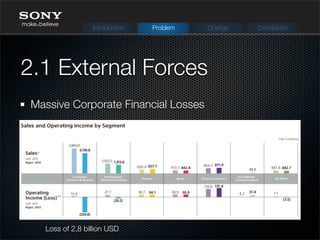
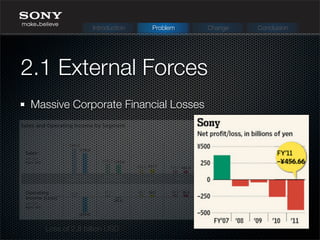
The document discusses Sony Corporation's history and challenges with change management. It describes Sony's evolution over time from 1946 to present day, expanding into new product areas. Problems arose from massive losses, strong competition, and a siloed culture. New CEOs implemented changes like restructuring, job cuts, and focusing on core businesses. The current CEO Kazuo Hirai's vision is to restructure the organization around mobile, entertainment and digital while building new partnerships. Recommendations include improving communication, outsourcing R&D temporarily, and focusing on a limited number of core products.