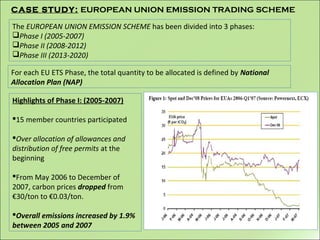
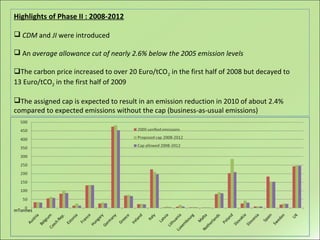
This document discusses carbon trading as a mechanism under the Kyoto Protocol to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. It defines carbon trading as a cap-and-trade program where countries are given an emissions cap and can trade excess allowances. The document outlines the Kyoto Protocol commitments, describes the EU Emissions Trading Scheme in its phases, and discusses benefits like alternative energy incentives but also disadvantages like a lack of centralized oversight.