1. The document provides examples and concepts related to limits, including definitions, evaluating limits of various functions as the variable approaches a number, and evaluating one-sided and two-sided limits.
2. Worked examples evaluate limits of rational functions, radical functions, and trigonometric functions as the variable approaches numbers or infinity.
3. Key concepts such as left-hand and right-hand limits, and limits at infinity, are demonstrated through multiple examples.

 = 0
u →1 –1. 0.0251314
–0.1 2.775 × 10−6
(2 + h) 2 − 4 4 + 4h + h 2 − 4
17. lim = lim –0.01 2.77775 × 10−10
h→0 h h→0 h
h 2 + 4h –0.001 2.77778 × 10−14
= lim = lim(h + 4) = 4
h →0 h h →0 ( x – sin x) 2
lim =0
x →0 x2
( x + h) 2 − x 2 x 2 + 2 xh + h 2 − x 2
18. lim = lim 2 2
h→0 h h →0 h 22. x (1 − cos x ) / x
h 2 + 2 xh 1. 0.211322
= lim = lim(h + 2 x) = 2 x
h →0 h h →0 0.1 0.00249584
0.01 0.0000249996
19. x sin x 0.001 2.5 × 10−7
2x
1. 0.420735
–1. 0.211322
0.1 0.499167
–0.1 0.00249584
0.01 0.499992 –0.01 0.0000249996
0.001 0.49999992 –0.001 2.5 × 10−7
(1 – cos x) 2
–1. 0.420735 lim =0
x →0 x2
–0.1 0.499167
2
23. t (t − 1) /(sin(t − 1))
–0.01 0.499992
–0.001 0.49999992 2. 3.56519
1.1 2.1035
sin x
lim = 0.5 1.01
x →0 2 x 2.01003
1.001 2.001
1− cos t
20. t 2t
1. 0.229849 0 1.1884
0.1 0.0249792 0.9 1.90317
0.01 0.00249998 0.99 1.99003
0.999 1.999
0.001 0.00024999998
t −12
lim =2
–1. –0.229849 t →1 sin(t − 1)
–0.1 –0.0249792
–0.01 –0.00249998
–0.001 –0.00024999998
64 Section 1.1 Instructor’s Resource Manual
© 2007 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. This material is protected under all copyright laws as they currently exist. No portion of this material may be reproduced, in any form
or by any means, without permission in writing from the publisher.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/51542-0131469657ism1-090702162933-phpapp02/85/solucionario-de-purcell-1-2-320.jpg)

![30. a. lim f ( x) does not exist. b. lim f ( x) does not exist.
x → –3 x →1
b. f(–3) = 1 c. f(1) = 2
c. f(–1) = 1 d. lim f ( x) = 2
x →1+
d. lim f ( x) = 2
x → –1
34.
e. f(1) = 1
f. lim f ( x) does not exist.
x →1
g. lim f ( x) = 1
x →1–
h. lim f ( x) does not exist.
x →1+
i. lim f ( x ) = 2
x →−1+
a. lim g ( x) = 0
31. a. f(–3) = 2 x →1
b. f(3) is undefined. b. g(1) does not exist.
c. lim f ( x) = 2
x → –3− c. lim g ( x ) = 1
x→2
d. lim f ( x) = 4
x → –3+ d. lim g ( x ) = 1
x → 2+
e. lim f ( x) does not exist.
x → –3
35. f ( x) = x – ⎡[ x ]⎤
⎣ ⎦
f. lim f ( x) does not exist.
x →3+
32. a. lim f ( x) = −2
x → –1−
b. lim f ( x) = −2
x → –1+
c. lim f ( x) = −2
x → –1
d. f (–1) = –2
e. lim f ( x) = 0
x →1 a. f(0) = 0
f. f (1) = 0 b. lim f ( x) does not exist.
x →0
33.
c. lim f ( x ) = 1
x →0 –
1
d. lim f ( x) =
x→ 1 2
2
a. lim f ( x) = 0
x →0
66 Section 1.1 Instructor’s Resource Manual
© 2007 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. This material is protected under all copyright laws as they currently exist. No portion of this material may be reproduced, in any form
or by any means, without permission in writing from the publisher.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/51542-0131469657ism1-090702162933-phpapp02/85/solucionario-de-purcell-1-4-320.jpg)





![29. Choose ε > 0. Since lim f ( x) = L, there is a 1.3 Concepts Review
x→ a
δ > 0 such that for 0 < x – a < δ , f ( x) – L < ε . 1. 48
That is, for
2. 4
a − δ < x < a or a < x < a + δ ,
L − ε < f ( x) < L + ε . 3. – 8; – 4 + 5c
Let f(a) = A,
M = max { L − ε , L + ε , A } , c = a – δ, 4. 0
d = a + δ. Then for x in (c, d), f ( x) ≤ M , since
either x = a, in which case
Problem Set 1.3
f ( x) = f (a ) = A ≤ M or 0 < x – a < δ so 1. lim (2 x + 1) 4
x→1
L − ε < f ( x) < L + ε and f ( x) < M .
= lim 2 x + lim 1 3
x→1 x→1
30. Suppose that L > M. Then L – M = α > 0. Now = 2 lim x + lim 1 2,1
α x →1 x→1
take ε < and δ = min{δ1 , δ 2} where = 2(1) + 1 = 3
2
0 < x – a < δ1 ⇒ f ( x) – L < ε and 2. lim (3x 2 – 1) 5
x→ –1
0 < x – a < δ 2 ⇒ g ( x) – M < ε .
= lim 3x 2 – lim 1 3
Thus, for 0 < x – a < δ , x→ –1 x→–1
= 3 lim x 2 – lim 1 8
L – ε < f(x) < L + ε and M – ε < g(x) < M + ε. x→ –1 x→–1
Combine the inequalities and use the fact ⎛ ⎞
2
that f ( x) ≤ g ( x) to get = 3⎜ lim x ⎟ – lim 1 2, 1
⎝ x→ –1 ⎠ x →–1
L – ε < f(x) ≤ g(x) < M + ε which leads to 2
= 3(–1) – 1 = 2
L – ε < M + ε or L – M < 2ε.
However, 3. lim [(2 x +1)( x – 3)] 6
L – M = α > 2ε x→0
which is a contradiction. = lim (2 x +1) ⋅ lim (x – 3) 4, 5
x→ 0 x→ 0
Thus L ≤ M .
⎛ ⎞ ⎛ ⎞
= ⎜ lim 2 x + lim 1⎟ ⋅ ⎜ lim x – lim 3⎟ 3
31. (b) and (c) are equivalent to the definition of ⎝ x→ 0 x→ 0 ⎠ ⎝ x→0 x→ 0 ⎠
limit. ⎛ ⎞ ⎛ ⎞
= ⎜ 2 lim x + lim 1⎟ ⋅ ⎜ lim x – lim 3⎟ 2, 1
⎝ x →0 x→ 0 ⎠ ⎝ x→0 x→ 0 ⎠
32. For every ε > 0 and δ > 0 there is some x with
= [2(0) +1](0 – 3) = –3
0 < x – c < δ such that f ( x ) – L > ε .
4. lim [(2 x 2 + 1)(7 x 2 + 13)] 6
x 3 – x 2 – 2x – 4 x→ 2
33. a. g(x) =
x 4 – 4x 3 + x 2 + x + 6 = lim (2 x 2 + 1) ⋅ lim (7 x 2 + 13) 4, 3
x→ 2 x→ 2
x+6 ⎛ ⎞ ⎛ ⎞
b. No, because + 1 has = ⎜ 2 lim x 2 + lim 1⎟ ⋅ ⎜ 7 lim x 2 + lim 13 ⎟ 8,1
x – 4x + x 2 + x + 6
4 3
⎝ x→ 2 x→ 2 ⎠ ⎝ x→ 2 x→ 2 ⎠
an asymptote at x ≈ 3.49.
⎡ ⎛ ⎞
2 ⎤⎡ ⎛ ⎞
2 ⎤
= ⎢2⎜ lim x ⎟ + 1⎥ ⎢7⎜ lim x ⎟ + 13⎥ 2
1 ⎢ ⎝ x→ 2 ⎠ ⎥⎢ ⎝ x→ 2 ⎠ ⎥
c. If δ ≤ , then 2.75 < x < 3 ⎣ ⎦⎣ ⎦
4
or 3 < x < 3.25 and by graphing = [2( 2 ) 2 + 1][7( 2 ) 2 + 13] = 135
x3 − x 2 − 2 x − 4
y = g ( x) =
x 4 − 4 x3 + x 2 + x + 6
on the interval [2.75, 3.25], we see that
x3 – x 2 – 2 x – 4
0< <3
x 4 – 4 x3 + x 2 + x + 6
so m must be at least three.
72 Section 1.3 Instructor’s Resource Manual
© 2007 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. This material is protected under all copyright laws as they currently exist. No portion of this material may be reproduced, in any form
or by any means, without permission in writing from the publisher.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/51542-0131469657ism1-090702162933-phpapp02/85/solucionario-de-purcell-1-10-320.jpg)
![2x + 1 9. lim (2t 3 +15)13 8
5. lim 7 t→ –2
x→2 5 – 3x 13
⎡ ⎤
lim (2 x + 1) = ⎢ lim (2t3 + 15) ⎥ 4, 3
= x→2 4, 5 ⎣t→–2 ⎦
lim (5 – 3 x) 13
⎡ ⎤
x→2
= ⎢2 lim t 3 + lim 15⎥ 8
lim 2 x + lim 1 ⎣ t→ –2 t→ –2 ⎦
x→2 x→2
= 3, 1 13
lim 5 – lim 3 x ⎡ 3 ⎤
x→2 x→2 = ⎢ 2 ⎛ lim t ⎞ + lim 15⎥
⎜ ⎟ 2, 1
2 lim x + 1 ⎢ ⎝ t → –2 ⎠ t → –2 ⎥
⎣ ⎦
x→2
= 2 = [2(–2) 3 + 15]13 = –1
5 – 3 lim x
x→2
2(2) + 1 lim –3w3 + 7 w2 9
= = –5 10.
w→ –2
5 – 3(2 )
= lim (–3w3 + 7 w2 ) 4, 3
3 w→ –2
4x +1
6. lim 7
x → –3 7 – 2 x 2 = –3 lim w3 + 7 lim w2 8
3 w→ –2 w→ –2
lim (4 x + 1)
= x → –3
4, 5 3 2
lim (7 – 2 x ) 2 = –3 ⎛ lim w ⎞ + 7 ⎛ lim w ⎞
⎜ ⎟ ⎜ ⎟ 2
x → –3 ⎝ w→ –2 ⎠ ⎝ w→ –2 ⎠
lim 4 x 3 + lim 1 = –3(–2)3 + 7(–2) 2 = 2 13
x → –3 x → –3
= 3, 1
lim 7 – lim 2 x 2
x → –3 x → –3 1/ 3
⎛ 4 y3 + 8 y ⎞
4 lim x 3 + 1 11. lim ⎜ ⎟ 9
= x → –3
8 y →2 ⎜ y + 4 ⎟
⎝ ⎠
7 – 2 lim x 2
x → –3 1/ 3 7
⎛ 4 y3 + 8 y ⎞
3 = ⎜ lim ⎟
4⎛ lim x ⎞ + 1
⎜ ⎟ ⎜ y →2 y + 4 ⎟
⎝ ⎠
= ⎝
x → –3 ⎠
2
2 13
7 – 2⎛ lim x ⎞ ⎡ lim (4 y 3 + 8 y ) ⎤
⎜ ⎟ ⎢ y →2 ⎥
⎝ x → –3 ⎠ =⎢ 4, 3
⎥
=
4(–3)3 + 1 107
= ⎢ y →2( y + 4) ⎥
lim
⎣ ⎦
7 – 2(–3) 2 11
13
⎛ 4 lim y 3 + 8 lim y ⎞
7. lim 3 x – 5 9 ⎜ y →2 y →2 ⎟
x →3
=⎜ ⎟ 8, 1
⎜ y →2 y + y → 2 4 ⎟
lim lim
= lim (3 x – 5) 5, 3 ⎝ ⎠
x →3
1/ 3
= 3 lim x – lim 5 2, 1 ⎡ ⎛ ⎞
3 ⎤
x →3 x →3 ⎢ 4 ⎜ lim y ⎟ + 8 lim y ⎥
⎢ y →2 ⎠ y →2 ⎥
= 3(3) – 5 = 2 =⎢ ⎝ ⎥ 2
lim y + 4
⎢ y →2 ⎥
⎢ ⎥
8. lim 5x2 + 2 x 9 ⎣ ⎦
x → –3 1/ 3
⎡ 4(2)3 + 8(2) ⎤
= 2
lim (5 x + 2 x ) 4, 3 =⎢ ⎥ =2
x → –3 ⎢
⎣ 2+4 ⎥
⎦
= 5 lim x 2 + 2 lim x 8
x → –3 x → –3
2
= 5 ⎛ lim x ⎞ + 2 lim x
⎜ ⎟ 2
⎝ x→ –3 ⎠ x → –3
= 5(–3)2 + 2(–3) = 39
Instructor’s Resource Manual Section 1.3 73
© 2007 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. This material is protected under all copyright laws as they currently exist. No portion of this material may be reproduced, in any form
or by any means, without permission in writing from the publisher.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/51542-0131469657ism1-090702162933-phpapp02/85/solucionario-de-purcell-1-11-320.jpg)
![12. lim (2 w 4 – 9 w 3 +19)–1 /2 x 2 + 7 x + 10 ( x + 2)( x + 5)
w→ 5 18. lim = lim
1
x→2 x+2 x→2 x+2
= lim 7 = lim( x + 5) = 7
w→ 5 2w − 9 w3 + 19
4 x→2
lim 1
= w→5
1, 9 x2 + x − 2 ( x + 2)( x − 1)
4 3 19. lim = lim
lim 2w – 9 w + 19 x →1 x −12 x →1 ( x + 1)( x − 1)
w→ 5
1 x + 2 1+ 2 3
= lim = =
= 4,5 x →1 x + 1 1+1 2
lim (2w – 9 w3 + 19)
4
w→ 5
x 2 – 14 x – 51 ( x + 3)( x – 17)
1 20. lim = lim
= 1,3 2
x→ –3 x – 4 x – 21 x→ –3 ( x + 3)( x – 7)
lim 2 w4 − lim 9 w3 + lim 19 x – 17 –3 – 17
w→5 w→5 w→5 = lim = =2
x→ –3 x – 7 –3 – 7
1
= 8
2 lim w − 9 lim w3 + 19
4 u2 – ux + 2u – 2 x ( u + 2 )( u – x )
w→5 w→5 21. lim 2 = lim
u →–2 u –u– 6 u→ –2 ( u + 2)(u – 3)
1 u– x x+2
= 2 = lim =
4 3
u → –2 u – 3 5
2 ⎛ lim w ⎞ − 9 ⎛ lim w ⎞ + 19
⎜ ⎟ ⎜ ⎟
⎝ w→ 5 ⎠ ⎝ w→5 ⎠
x 2 + ux – x – u ( x – 1)( x + u)
1 22. lim = lim
= x→1 x 2 + 2x – 3 x →1 ( x – 1)( x + 3)
2(5)4 − 9(5)3 + 19 x + u 1+ u u + 1
= lim = =
1 1 x→1 x + 3 1+ 3 4
= =
144 12
2 x2 – 6 xπ + 4 π2 2( x – π)( x – 2 π)
23. lim = lim
x2 − 4 (
lim x − 4
x→2
2
) 4−4 x→ π x –π 2 2
x→ π ( x – π)( x + π)
2( x – 2π) 2(π – 2 π)
13. lim = = =0
lim ( x + 4) 4 + 4 = lim = = –1
2
x→2 x +4 2
x→ π x + π π+π
x→2
(w + 2)(w 2 – w – 6)
x2 − 5x + 6 ( x − 3)( x − 2 ) 24. lim
14. lim = lim w 2 + 4w + 4
x→2 x−2 x→2 ( x − 2) w→ –2
( w + 2) 2 ( w – 3)
= lim ( x − 3) = −1 = lim = lim ( w – 3)
x→2 w→ –2 ( w + 2 )2 w→ –2
= –2 – 3 = –5
x2 − 2 x − 3 ( x − 3)( x + 1)
15. lim = lim
x →−1 x +1 x →−1 ( x + 1) 25. lim f 2 ( x) + g 2 ( x)
x→a
= lim ( x − 3) = −4
x →−1 = lim f 2 ( x) + lim g 2 ( x)
x→a x→a
x2 + x (
lim x + x
x →−1
2
) 0 2
= ⎛ lim f ( x) ⎞ + ⎛ lim g ( x) ⎞
⎜ ⎟ ⎜ ⎟
2
16. lim = = =0
x →−1 x2 + 1 lim ( x 2
+ 1) 2 ⎝ x →a ⎠ ⎝ x→a ⎠
x →−1
= (3) 2 + (–1)2 = 10
( x − 1)( x − 2)( x − 3) x−3
17. lim = lim
x →−1 ( x − 1)( x − 2)( x + 7) x →−1 x + 7 2 f ( x) – 3g ( x ) x → a[2 f ( x) – 3 g ( x)]
lim
26. lim =
−1 − 3 2 x → a f ( x) + g ( x) lim [ f ( x) + g ( x)]
= =− x→a
−1 + 7 3 2 lim f ( x) – 3 lim g ( x)
x→a x→a 2(3) – 3(–1) 9
= = =
lim f ( x) + lim g ( x) 3 + (–1) 2
x→a x→a
74 Section 1.3 Instructor’s Resource Manual
© 2007 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. This material is protected under all copyright laws as they currently exist. No portion of this material may be reproduced, in any form
or by any means, without permission in writing from the publisher.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/51542-0131469657ism1-090702162933-phpapp02/85/solucionario-de-purcell-1-12-320.jpg)
![27. lim 3 g ( x) [ f ( x) + 3] = lim 3 g ( x) ⋅ lim [ f ( x) + 3] 35. Suppose lim f (x) = L and lim g(x) = M.
x→a x→a x→a x→c x→c
f ( x) g ( x) – LM ≤ g ( x) f ( x) – L + L g ( x ) – M
= 3 lim g ( x) ⋅ ⎡ lim f ( x) + lim 3⎤ = 3 – 1 ⋅ (3 + 3)
x→a ⎢x→a
⎣ x→a ⎥⎦ as shown in the text. Choose ε 1 = 1. Since
= –6 lim g ( x) = M , there is some δ1 > 0 such that if
x →c
4 0 < x – c < δ1 , g ( x) – M < ε1 = 1 or
28. lim [ f ( x) – 3]4 = ⎡ lim ( f ( x) – 3) ⎤
⎢ x→a ⎥
x→a ⎣ ⎦ M – 1 < g(x) < M + 1
4
= ⎡ lim f ( x) – lim 3⎤ = (3 – 3) 4 = 0
⎢ x→a
M – 1 ≤ M + 1 and M + 1 ≤ M + 1 so for
⎣ x →a ⎥
⎦
0 < x – c < δ1 , g ( x) < M + 1. Choose ε > 0.
29. lim ⎡ f (t ) + 3g (t ) ⎤ = lim f (t ) + 3 lim g (t ) Since lim f (x) = L and lim g(x) = M, there
t →a
⎣ ⎦ t →a t →a x→c x→c
exist δ 2 and δ 3 such that 0 < x – c < δ 2 ⇒
= lim f (t ) + 3 lim g (t )
t →a t →a ε
f ( x) – L < and 0 < x – c < δ 3 ⇒
= 3 + 3 –1 = 6 L + M +1
ε
⎛ ⎞
3 g ( x) – M < . Let
3
30. lim [ f (u) + 3g(u)] = ⎜ lim [ f (u) + 3g(u)]⎟ L + M +1
u →a ⎝ u →a ⎠
3 δ = min{δ1 , δ 2 , δ 3 }, then 0 < x – c < δ ⇒
⎡ ⎤
= ⎢ lim f (u ) + 3 lim g(u) ⎥ = [3 + 3( –1)]3 = 0 f ( x) g ( x) – LM ≤ g ( x) f ( x) – L + L g ( x ) – M
⎣u→ a u →a ⎦
ε ε
< ( M + 1) +L =ε
3x 2
– 12 3( x – 2 )(x + 2) L + M +1 L + M +1
31. lim = lim
x→2 x–2 x→2 x –2 Hence,
= 3 lim (x + 2) = 3(2 + 2) = 12
x→2 lim f ( x) g ( x) = LM = ⎛ lim f ( x) ⎞ ⎛ lim g ( x) ⎞
⎜ ⎟⎜ ⎟
x →c ⎝ x →c ⎠ ⎝ x →c ⎠
(3x 2 + 2 x + 1) – 17 3x 2 + 2 x – 16
32. lim
x→2 x–2
= lim
x →2 x–2 36. Say lim g ( x ) = M , M ≠ 0 , and choose
x →c
(3 x + 8)( x – 2) 1
= lim = lim (3 x + 8) ε1 = M
x→2 x–2 x →2 2 .
= 3 lim x + 8 = 3(2) + 8 = 14 There is some δ1 > 0 such that
x→2
1
0 < x − c < δ1 ⇒ g ( x) − M < ε1 = M or
1
– 1 2– x
– x–2 2
2 2x 2x
33. lim x
= lim = lim 1 1
x→2 x – 2 x→2 x – 2 x →2 x – 2 M− M < g ( x) < M + M .
2 2
1 –1 –1 1
= lim – = = =– 1 1 1 1
x→2 2 x 2 lim x 2(2) 4 M − M ≥ M and M + M ≥ M
x →2 2 2 2 2
1 1 2
3 3 3( 4 – x 2 ) –3( x + 2 )( x – 2 ) so g ( x) > M and <
– 4 2 g ( x) M
x2 4x2 4x2
34. lim = lim = lim
x→2 x–2 x–2 x→2
x→2 x–2 Choose ε > 0.
Since lim g(x) = M there is δ 2 > 0 such that
–3 ⎛ lim x + 2 ⎞
⎜ ⎟ –3(2 + 2) x→c
–3( x + 2)
= lim = ⎝ x →2 ⎠= 1 2
x→2 4x 2 2
4(2)2 0 < x − c < δ 2 ⇒ g ( x) − M < M .
4 ⎛ lim x ⎞
⎜ ⎟ 2
⎝ x→2 ⎠ Let δ = min{δ1 , δ 2}, then
3
=– 1 1 M – g ( x)
4 0< x–c <δ ⇒ – =
g ( x) M g ( x) M
1 2 2 1 2
= g ( x) − M < g ( x) − M = ⋅ M ε
2
M g ( x) M M2 2
=ε
Instructor’s Resource Manual Section 1.3 75
© 2007 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. This material is protected under all copyright laws as they currently exist. No portion of this material may be reproduced, in any form
or by any means, without permission in writing from the publisher.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/51542-0131469657ism1-090702162933-phpapp02/85/solucionario-de-purcell-1-13-320.jpg)
![1 1 1
Thus, lim = = . x–3 ( x – 3) x 2 – 9
x→c g(x) M lim g (x) 43. lim = lim
x→c x →3+ x2 – 9 x →3+ x2 – 9
Using statement 6 and the above result,
f ( x) 1 ( x – 3) x 2 – 9 x2 – 9
lim = lim f ( x) ⋅ lim = lim = lim
x →c g ( x ) x →c x →c g ( x ) x →3+ ( x – 3)( x + 3) x →3+ x+3
lim f ( x ) 32 – 9
1
= lim f ( x) ⋅ = x →c . = =0
x →c lim g ( x ) lim g ( x) 3+3
x →c x →c
1+ x 1+1 2
37. lim f (x) = L ⇔ lim f ( x) = lim L 44. lim = =
x→c x→ c x→ c x →1– 4 + 4 x 4 + 4(1) 8
⇔ lim f (x) – lim L = 0
x→c x →c
⇔ lim [ f (x) – L] = 0 ( x 2 + 1) x (22 + 1) 2 5⋅ 2 2
x→c 45. lim = = =
2 2 2
x → 2+ (3 x − 1) (3 ⋅ 2 − 1) 5 5
2
⎡ ⎤
38. lim f (x) = 0 ⇔ ⎢ lim f (x) ⎥ = 0
x→c ⎣ x→c ⎦ 46. lim ( x − x ) = lim x − lim x = 3− 2 =1
2 x →3− x →3− x →3−
⇔ lim f ( x) = 0
x→c
x
⇔ lim f 2 ( x) = 0 47. lim = –1
x →c x →0 – x
⇔ lim f 2 ( x) = 0
x →c 48. lim x 2 + 2 x = 32 + 2 ⋅ 3 = 15
⇔ lim f ( x) = 0 x →3+
x→c
1
2 49. f ( x) g ( x) = 1; g ( x) =
39. lim x = ⎛ lim x ⎞ = f ( x)
2
⎜ ⎟ lim x = lim x 2
x →c ⎝ x →c ⎠ x →c x →c 1
2
lim g ( x) = 0 ⇔ lim =0
x →a x →a f ( x)
= ⎛ lim x ⎞ = c 2 = c
⎜ ⎟
⎝ x →c ⎠ 1
⇔ =0
lim f ( x)
x +1 x–5 x→a
40. a. If f ( x) = , g ( x) = and c = 2, then No value satisfies this equation, so lim f ( x)
x–2 x–2 x→ a
lim [ f (x) + g (x)] exists, but neither must not exist.
x→c
lim f (x) nor lim g(x) exists. ⎛ x 1⎞
x→c x→c 50. R has the vertices ⎜ ± , ± ⎟
⎝ 2 2⎠
2 Each side of Q has length x 2 + 1 so the
b. If f ( x) = , g ( x) = x, and c = 0, then
x
lim [ f (x) ⋅ g( x)] exists, but lim f (x) does perimeter of Q is 4 x 2 + 1. R has two sides of
x 2 so the
x→c x→c
length 1 and two sides of length
not exist.
perimeter of R is 2 + 2 x 2 .
3+ x 3–3
41. lim = =0 perimeter of R 2 x2 + 2
x → –3+ x –3 lim = lim
x →0 + perimeter of Q x →0+ 4 x 2 + 1
π3 + x3 π3 + (– π)3 2 02 + 2 2 1
42. lim = =0 = = =
x → – π+ x –π 4 0 +12 4 2
76 Section 1.3 Instructor’s Resource Manual
© 2007 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. This material is protected under all copyright laws as they currently exist. No portion of this material may be reproduced, in any form
or by any means, without permission in writing from the publisher.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/51542-0131469657ism1-090702162933-phpapp02/85/solucionario-de-purcell-1-14-320.jpg)

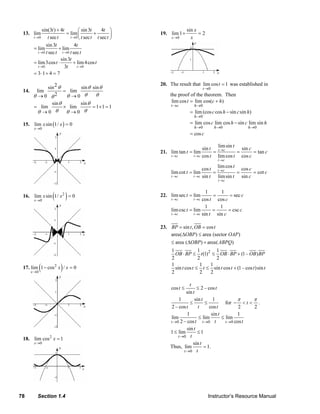


![3 3 1
46. lim = 0, lim = 0; 49. f ( x ) = 2 x + 3 – 3
, thus
x →∞ 9 – x 2 x→ – ∞ 9 – x 2 x –1
Horizontal asymptote y = 0 ⎡ 1 ⎤
lim [ f ( x) – (2 x + 3)] = lim ⎢ – ⎥=0
3 3 x →∞ 3
x →∞ ⎣ x –1 ⎦
lim = – ∞, lim = ∞,
x →3 + 9 – x2 x →3 – 9 – x2 The oblique asymptote is y = 2x + 3.
3 3
lim = ∞, lim = – ∞; 4x + 3
x → –3+ 9 – x
2
x → –3– 9 – x
2 50. f ( x) = 3x + 4 – , thus
x2 + 1
Vertical asymptotes x = –3, x = 3
⎡ 4x + 3⎤
lim [ f ( x) – (3 x + 4)] = lim ⎢ – ⎥
x →∞ x →∞ ⎣ x 2 + 1 ⎦
⎡ 4+ 3 ⎤
x x2 ⎥
= lim ⎢ – =0.
x →∞ ⎢ 1+ 1 ⎥
⎢
⎣ 2 ⎥
x ⎦
The oblique asymptote is y = 3x + 4.
51. a. We say that lim f ( x) = – ∞ if to each
x →c +
negative number M there corresponds a δ > 0
such that 0 < x – c < δ ⇒ f(x) < M.
14 14
47. lim = 0, lim = 0;
x →∞ 2 x+7 2 x→ – ∞ 2 x2 + 7 b. We say that lim f ( x) = ∞ if to each
Horizontal asymptote y = 0 x →c –
2
Since 2x + 7 > 0 for all x, g(x) has no vertical positive number M there corresponds a δ > 0
asymptotes. such that 0 < c – x < δ ⇒ f(x) > M.
52. a. We say that lim f ( x) = ∞ if to each
x →∞
positive number M there corresponds an
N > 0 such that N < x ⇒ f(x) > M.
b. We say that lim f ( x ) = ∞ if to each
x → –∞
positive number M there corresponds an
N < 0 such that x < N ⇒ f(x) > M.
53. Let ε > 0 be given. Since lim f ( x ) = A, there is
x →∞
2x 2 2 a corresponding number M1 such that
48. lim = lim = = 2, ε
x →∞ 2
x +5 x →∞ 1+ 5 1 x > M1 ⇒ f ( x) – A < . Similarly, there is a
x2 2
2x 2 2 ε
lim = lim = = –2 number M2 such that x > M 2 ⇒ g ( x) – B < .
x→ – ∞ x→ – ∞ – 1 2
x2 + 5 – 1+ 5
x2 Let M = max{M1 , M 2 } , then
Since x 2 + 5 > 0 for all x, g(x) has no vertical x > M ⇒ f ( x) + g ( x) – ( A + B)
asymptotes. = f ( x) – A + g ( x) – B ≤ f ( x) – A + g ( x) – B
ε ε
< =ε
+
2 2
Thus, lim [ f ( x) + g ( x)] = A + B
x →∞
54. Written response
82 Section 1.5 Instructor’s Resource Manual
© 2007 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. This material is protected under all copyright laws as they currently exist. No portion of this material may be reproduced, in any form
or by any means, without permission in writing from the publisher.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/51542-0131469657ism1-090702162933-phpapp02/85/solucionario-de-purcell-1-20-320.jpg)

![13. lim f (t ) = lim (3 – t ) = 0
1.6 Concepts Review t →3+ t →3+
lim f (t ) = lim (t – 3) = 0
1. lim f ( x) t →3 – t →3–
x →c
lim f (t ) = f (3); continuous
t →3
2. every integer
14. lim f (t ) = lim (3 – t )2 = 0
3. lim f ( x) = f (a); lim f ( x) = f (b)
t →3+ t →3+
x→a+ x →b –
lim f (t ) = lim (t 2 – 9) = 0
4. a; b; f(c) = W t →3– t →3 –
lim f (t ) = f (3); continuous
t →3
Problem Set 1.6 15. lim f ( x) = −2 = f (3); continuous
t →3
1. lim[( x – 3)( x – 4)] = 0 = f (3); continuous
x →3 16. g is discontinuous at x = –3, 4, 6, 8; g is left
continuous at x = 4, 8; g is right continuous at
2. lim ( x 2 – 9) = 0 = g (3); continuous x = –3, 6
x →3
17. h is continuous on the intervals
3 (−∞, −5), [ −5, 4] , (4, 6), [ 6,8] , (8, ∞)
3. lim and h(3) do not exist, so h(x) is not
x →3 x – 3
continuous at 3. x 2 – 49 ( x – 7)( x + 7)
18. lim = lim = lim ( x + 7)
x →7 x – 7 x →7 x–7 x →7
4. lim t – 4 and g(3) do not exist, so g(t) is not = 7 + 7 = 14
t →3
Define f(7) = 14.
continuous at 3.
t –3 2 x 2 –18 2( x + 3)( x – 3)
5. lim and h(3) do not exist, so h(t) is not 19. lim = lim
x →3 3 – x x →3 3– x
t →3t –3
continuous at 3. = lim[–2( x + 3)] = –2(3 + 3) = –12
x →3
Define f(3) = –12.
6. h(3) does not exist, so h(t) is not continuous at 3.
sin(θ )
7. lim t = 3 = f (3); continuous 20. lim =1
t →3 θ →0 θ
Define g(0) = 1
8. lim t – 2 = 1 = g (3); continuous
t →3
t –1 ( t –1)( t + 1)
21. lim = lim
9. h(3) does not exist, so h(t) is not continuous at 3. t →1 t –1 t →1 (t –1)( t + 1)
t –1 1 1
10. f(3) does not exist, so f(x) is not continuous at 3. = lim = lim =
–1)( t + 1)
t →1 (t t →1 t +1 2
t 3 – 27 (t – 3)(t 2 + 3t + 9) 1
11. lim = lim Define H(1) = .
t →3 t – 3 t →3 t –3 2
= lim(t 2 + 3t + 9) = (3)2 + 3(3) + 9 = 27 = r (3) x4 + 2 x2 – 3 ( x 2 –1)( x 2 + 3)
t →3 22. lim = lim
continuous x → –1 x +1 x → –1 x +1
( x + 1)( x – 1)( x 2 + 3)
12. From Problem 11, lim r (t ) = 27, so r(t) is not = lim
t →3 x → –1 x +1
continuous at 3 because lim r (t ) ≠ r (3). = lim [( x – 1)( x 2 + 3)]
t →3 x → –1
= (–1 – 1)[(–1)2 + 3] = –8
Define φ(–1) = –8.
84 Section 1.6 Instructor’s Resource Manual
© 2007 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. This material is protected under all copyright laws as they currently exist. No portion of this material may be reproduced, in any form
or by any means, without permission in writing from the publisher.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/51542-0131469657ism1-090702162933-phpapp02/85/solucionario-de-purcell-1-22-320.jpg)
![⎛ x2 – 1 ⎞ ⎛ ( x – 1)( x + 1) ⎞
37.
23. lim sin ⎜ ⎟ = lim sin ⎜ ⎟
x → –1 ⎜ x + 1 ⎟ x→ –1 ⎝ x +1 ⎠
⎝ ⎠
= lim sin( x –1) = sin(–1 – 1) = sin(−2) = – sin 2
x → –1
Define F(–1) = –sin 2.
24. Discontinuous at x = π ,30
33 – x 2
25. f ( x) = 38.
(π – x)( x – 3)
Discontinuous at x = 3, π
26. Continuous at all points
27. Discontinuous at all θ = nπ + π where n is any
2
integer.
28. Discontinuous at all u ≤ −5
39.
29. Discontinuous at u = –1
30. Continuous at all points
1
31. G ( x) =
(2 – x)(2 + x)
Discontinuous on (−∞, −2] ∪ [2, ∞)
32. Continuous at all points since 40.
lim f ( x) = 0 = f (0) and lim f ( x) = 1 = f (1).
x →0 x →1
33. lim g ( x ) = 0 = g (0)
x →0
lim g ( x) = 1, lim g ( x) = –1
x →1+ x →1–
lim g(x ) does not exist, so g(x) is discontinuous
x→1
at x = 1.
34. Discontinuous at every integer
Discontinuous at all points except x = 0, because
1 lim f ( x ) ≠ f (c) for c ≠ 0 . lim f ( x ) exists only
35. Discontinuous at t = n + where n is any integer x →c x →c
2 at c = 0 and lim f ( x) = 0 = f (0) .
x →0
36.
41. Continuous.
42. Discontinuous: removable, define f (10) = 20
43. Discontinuous: removable, define f (0) = 1
44. Discontinuous: nonremovable.
45. Discontinuous, removable, redefine g (0) = 1
46. Discontinuous: removable, define F (0) = 0
Instructor’s Resource Manual Section 1.6 85
© 2007 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. This material is protected under all copyright laws as they currently exist. No portion of this material may be reproduced, in any form
or by any means, without permission in writing from the publisher.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/51542-0131469657ism1-090702162933-phpapp02/85/solucionario-de-purcell-1-23-320.jpg)
![47. Discontinuous: nonremovable. 52. Let f ( x) = x3 + 3 x − 2. f is continuous on [0, 1].
48. Discontinuous: removable, define f (4) = 4 f(0) = –2 < 0 and f(1) = 2 > 0. Thus, there is at
least one number c between 0 and 1 such that
49. The function is continuous on the intervals x 3 + 3x − 2 = 0.
( 0,1] , (1, 2], (2,3], … 53. Because the function is continuous on [ 0,2π ] and
Cost $ (cos 0)03 + 6sin 5 0 – 3 = –3 < 0,
0.72
(cos 2π)(2π)3 + 6sin 5 (2π) – 3 = 8π3 – 3 > 0, there
0.60 is at least one number c between 0 and 2π such
0.48 that (cos t )t 3 + 6sin 5 t – 3 = 0.
54. Let f ( x ) = x − 7 x + 14 x − 8 . f(x) is
0.36 3 2
0.24
continuous at all values of x.
0.12 f(0) = –8, f(5) = 12
Because 0 is between –8 and 12, there is at least
1 2 3 4 5
one number c between 0 and 5 such that
6
Length of call in minutes f ( x ) = x 3 − 7 x 2 + 14 x − 8 = 0 .
This equation has three solutions (x = 1,2,4)
50. The function is continuous on the intervals
[0, 200], (200,300], (300, 400], …
Cost $
80
60
40
20 55. Let f ( x ) = x − cos x. . f(x) is continuous at all
values of x ≥ 0. f(0) = –1, f(π/2) = π / 2
100 200 300 400 500 Because 0 is between –1 and π / 2 , there is at
Miles Driven
least one number c between 0 and π/2 such that
51. The function is continuous on the intervals f ( x ) = x − cos x = 0.
(0, 0.25], (0.25, 0.375], (0.375, 0.5], … The interval [0.6,0.7] contains the solution.
Cost $
4
3
2
1
56. Let f ( x) = x5 + 4 x3 – 7 x + 14
f(x) is continuous at all values of x.
0.25 0.5 0.75 1
f(–2) = –36, f(0) = 14
Miles Driven
Because 0 is between –36 and 14, there is at least
one number c between –2 and 0 such that
f ( x) = x5 + 4 x3 – 7 x + 14 = 0.
86 Section 1.6 Instructor’s Resource Manual
© 2007 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. This material is protected under all copyright laws as they currently exist. No portion of this material may be reproduced, in any form
or by any means, without permission in writing from the publisher.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/51542-0131469657ism1-090702162933-phpapp02/85/solucionario-de-purcell-1-24-320.jpg)
![57. Suppose that f is continuous at c, so 63. Let f(x) be the difference in times on the hiker’s
lim f ( x) = f (c). Let x = c + t, so t = x – c, then watch where x is a point on the path, and suppose
x →c x = 0 at the bottom and x = 1 at the top of the
as x → c , t → 0 and the statement mountain.
lim f ( x) = f (c) becomes lim f (t + c ) = f (c). So f(x) = (time on watch on the way up) – (time
x →c t →0
on watch on the way down).
Suppose that lim f (t + c) = f (c) and let x = t + f(0) = 4 – 11 = –7, f(1) = 12 – 5 = 7. Since time is
t→ 0
c, so t = x – c. Since c is fixed, t → 0 means that continuous, f(x) is continuous, hence there is
x → c and the statement lim f (t + c) = f (c) some c between 0 and 1 where f(c) = 0. This c is
t →0 the point where the hiker’s watch showed the
becomes lim f ( x) = f (c) , so f is continuous at same time on both days.
x →c
c. ⎡ π⎤
64. Let f be the function on ⎢0, 2 ⎥ such that f(θ) is
⎣ ⎦
58. Since f(x) is continuous at c,
the length of the side of the rectangle which
lim f ( x) = f (c) > 0. Choose ε = f ( c ) , then
x →c makes angle θ with the x-axis minus the length of
there exists a δ > 0 such that the sides perpendicular to it. f is continuous on
0 < x − c < δ ⇒ f ( x) − f (c) < ε . ⎡ π⎤
⎢0, 2 ⎥ . If f(0) = 0 then the region is
⎣ ⎦
Thus, f ( x ) − f ( c ) > −ε = − f ( c ) , or f ( x ) > 0 . circumscribed by a square. If f(0) ≠ 0, then
Since also f ( c ) > 0 , f ( x ) > 0 for all x in ⎛π ⎞
observe that f (0) = − f ⎜ ⎟ . Thus, by the
(c − δ , c + δ ). ⎝2⎠
Intermediate Value Theorem, there is an angle
59. Let g(x) = x – f(x). Then, π
g(0) = 0 – f(0) = –f(0) ≤ 0 and g(1) = 1 – f(1) ≥ 0 θ 0 between 0 and such that f (θ 0 ) = 0.
2
since 0 ≤ f(x) ≤ 1 on [0, 1] . If g(0) = 0, then Hence, D can be circumscribed by a square.
f(0) = 0 and c = 0 is a fixed point of f. If g(1) = 0,
then f(1) = 1 and c = 1 is a fixed point of f. If 65. Yes, g is continuous at R .
neither g(0) = 0 nor g(1) = 0, then g(0) < 0 and
lim g ( r ) = = lim g ( r )
GMm
g(1) > 0 so there is some c in [0, 1] such that
r →R− R2 r →R+
g(c) = 0. If g(c) = 0 then c – f(c) = 0 or
f(c) = c and c is a fixed point of f. 66. No. By the Intermediate Value Theorem, if f
were to change signs on [a,b], then f must be
60. For f(x) to be continuous everywhere,
0 at some c in [a,b]. Therefore, f cannot
f(1) = a(1) + b = 2 and f(2) = 6 = a(2) + b
a+b=2 change sign.
2a + b = 6 67. a. f(x) = f(x + 0) = f(x) + f(0), so f(0) = 0. We
– a = –4 want to prove that lim f (x) = f (c), or,
x→c
a = 4, b = –2 equivalently, lim [ f (x) – f (c)] = 0. But
x→c
61. For x in [0, 1], let f(x) indicate where the string f(x) – f(c) = f(x – c), so
originally at x ends up. Thus f(0) = a, f(1) = b. lim[ f ( x) – f (c)] = lim f ( x – c). Let
f(x) is continuous since the string is unbroken. x →c x →c
Since 0 ≤ a, b ≤ 1 , f(x) satisfies the conditions of h = x – c then as x → c, h → 0 and
Problem 59, so there is some c in [0, 1] with lim f ( x – c) = lim f (h) = f (0) = 0. Hence
x →c h →0
f(c) = c, i.e., the point of string originally at c
lim f (x) = f (c) and f is continuous at c.
ends up at c. x→c
Thus, f is continuous everywhere, since c
62. The Intermediate Value Theorem does not imply was arbitrary.
the existence of a number c between –2 and 2
such that f (c ) = 0. The reason is that the b. By Problem 43 of Section 0.5, f(t) = mt for
all t in Q. Since g(t) = mt is a polynomial
function f ( x ) is not continuous on [ −2, 2] . function, it is continuous for all real
numbers. f(t) = g(t) for all t in Q, thus
f(t) = g(t) for all t in R, i.e. f (t ) = mt.
Instructor’s Resource Manual Section 1.6 87
© 2007 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. This material is protected under all copyright laws as they currently exist. No portion of this material may be reproduced, in any form
or by any means, without permission in writing from the publisher.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/51542-0131469657ism1-090702162933-phpapp02/85/solucionario-de-purcell-1-25-320.jpg)

![11. True: Since both sin x and cos x are 25. True: Choose ε = 0. 001 f (2) then since
continuous for all real numbers, by lim f ( x ) = f (2), there is some δ
Theorem C we can conclude that x→2
such that 0 < x − 2 < δ ⇒
f ( x) = 2 sin 2 x − cos x is also
f ( x ) − f (2) < 0. 001 f (2), or
continuous for all real numbers.
−0. 001 f (2 ) < f ( x ) − f (2 )
12. True. By definition, lim f ( x ) = f ( c ) . < 0.001f(2)
x →c Thus, 0.999f(2) < f(x) < 1.001f(2) and
f(x) < 1.001f(2) for 0 < x − 2 < δ .
13. True. 2 ∈ [1,3] Since f(2) < 1.001f(2), as f(2) > 0,
f(x) < 1.001f(2) on (2 − δ , 2 + δ ).
14. False: lim may not exist
x →0 − 26. False: That lim [ f ( x ) + g ( x )] exists does
x→c
15. False: Consider f ( x) = sin x. not imply that lim f ( x ) and
x→c
x–3
16. True. By the definition of continuity on an lim g( x ) exist; e.g., f ( x) = and
interval. x→c x+2
x+7
g ( x) = for c = −2 .
17. False: Since −1 ≤ sin x ≤ 1 for all x and x+2
1 sin x
lim = 0 , we get lim =0. 27. True: Squeeze Theorem
x →∞ x x →∞ x
28. True: A function has only one limit at a
18. False. It could be the case where
point, so if lim f ( x ) = L and
lim f ( x ) = 2 x→ a
x →−∞
lim f ( x ) = M , L = M
x→ a
19. False: The graph has many vertical
asymptotes; e.g., x = ± π/2, ± 3π/2, 29. False: That f(x) ≠ g(x) for all x does not
± 5π/2, … imply that lim f ( x) ≠ lim g ( x). For
x →c x →c
20. True: x = 2 ; x = –2 2
x +x–6
example, if f ( x) = and
x–2
21. True: As x → 1+ both the numerator and
5
denominator are positive. Since the g ( x) =x, then f(x) ≠ g(x) for all x,
numerator approaches a constant and 2
the denominator approaches zero, the but lim f ( x ) = lim g ( x ) = 5.
x→2 x→ 2
limit goes to + ∞ .
30. False: If f(x) < 10, lim f ( x ) could equal 10
22. False: lim f ( x) must equal f(c) for f to be x→2
x →c if there is a discontinuity point (2, 10).
continuous at x = c. For example,
– x3 + 6 x 2 − 2 x − 12
23. True: lim f ( x) = f ⎛ lim x ⎞ = f (c), so f is
⎜ ⎟
f ( x) =
x–2
< 10 for
x →c ⎝ x →c ⎠
continuous at x = c. all x, but lim f ( x) = 10.
x →2
x
24. True: lim = 1 = f ( 2.3) 31. True: lim f ( x) = lim f 2 ( x)
x →2.3 2 x →a x →a
2
= ⎡ lim f ( x) ⎤ = (b)2 = b
⎢ x→a ⎥
⎣ ⎦
32. True: If f is continuous and positive on
[a, b], the reciprocal is also
continuous, so it will assume all
1 1
values between and .
f ( a) f (b )
Instructor’s Resource Manual Section 1.7 89
© 2007 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. This material is protected under all copyright laws as they currently exist. No portion of this material may be reproduced, in any form
or by any means, without permission in writing from the publisher.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/51542-0131469657ism1-090702162933-phpapp02/85/solucionario-de-purcell-1-27-320.jpg)

![24. a. f(1) = 0 28.
b. lim f ( x) = lim (1 – x) = 0
x →1+ x →1+
c. lim f ( x) = lim x = 1
x →1– x →1–
d. lim f ( x) = –1 because
x → –1
lim f ( x) = lim x3 = –1 and
x → –1– x → –1–
lim f ( x) = lim x = –1
x → –1+ x → –1+
29. a(0) + b = –1 and a(1) + b = 1
25. a. f is discontinuous at x = 1 because f(1) = 0, b = –1; a + b = 1
but lim f (x ) does not exist. f is a–1=1
x→1
a=2
discontinuous at x = –1 because f(–1) does
not exist.
30. Let f ( x) = x5 – 4 x3 – 3 x + 1
b. Define f(–1) = –1 f(2) = –5, f(3) = 127
Because f(x) is continuous on [2, 3] and
26. a. 0 < u – a < δ ⇒ g (u ) – M < ε f(2) < 0 < f(3), there exists some number c
between 2 and 3 such that f(c) = 0.
b. 0 < a – x < δ ⇒ f ( x) – L < ε
31. Vertical: None, denominator is never 0.
27. a. lim[2 f ( x) – 4 g ( x)] x x
x →3 Horizontal: lim = lim = 0 , so
= 2 lim f ( x) – 4 lim g ( x ) x →∞ x 2
+1 x →−∞ x 2 +1
x →3 x →3 y = 0 is a horizontal asymptote.
= 2(3) – 4(–2) = 14
32. Vertical: None, denominator is never 0.
x2 – 9
b. lim g ( x) = lim g ( x )( x + 3)
x →3 x – 3 x →3 x2 x2
Horizontal: lim = lim = 1 , so
= lim g ( x ) ⋅ lim ( x + 3) = –2 ⋅ (3 + 3) = –12 x →∞ x 2
+ 1 x →−∞ x 2 + 1
x →3 x →3
y = 1 is a horizontal asymptote.
c. g(3) = –2
x2
33. Vertical: x = 1, x = −1 because lim =∞
d. lim g ( f ( x)) = g ⎛ lim f ( x) ⎞ = g (3) = –2
⎜ ⎟ x →1+ x2 − 1
x →3 ⎝ x →3 ⎠
x2
and lim =∞
2 x →−1− x2 − 1
e. lim f ( x) – 8 g ( x)
x →3
2 x2 x2
= lim = 1 , so
= ⎡ lim f ( x) ⎤ – 8 lim g ( x)
Horizontal: lim
⎢ x →3 ⎥ x →∞ x 2
− 1 x→−∞ x 2 − 1
⎣ ⎦ x →3
y = 1 is a horizontal asymptote.
= (3) 2 – 8(–2) = 5
g ( x) – g (3) –2 – g (3) −2 − (−2)
f. lim = =
x →3 f ( x) 3 3
=0
Instructor’s Resource Manual Section 1.7 91
© 2007 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. This material is protected under all copyright laws as they currently exist. No portion of this material may be reproduced, in any form
or by any means, without permission in writing from the publisher.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/51542-0131469657ism1-090702162933-phpapp02/85/solucionario-de-purcell-1-29-320.jpg)

